Overview
The article examines the significant challenges encountered by aging doctors and outlines strategies to effectively address these issues within the healthcare system.
With a considerable number of physicians approaching retirement, the healthcare sector is grappling with potential shortages and heightened burnout among medical professionals.
This situation necessitates proactive measures, including:
- The implementation of mentorship programs
- The provision of mental health support
to ensure the delivery of high-quality patient care.
Introduction
The medical profession is undergoing a significant transformation in its demographic landscape, marked by a growing number of physicians approaching retirement age. This trend not only raises urgent concerns about the impending shortage of healthcare providers but also underscores the unique challenges faced by older doctors, including burnout and cognitive decline.
As the healthcare system navigates these pressing issues, organizations must consider how to effectively support aging physicians while ensuring the delivery of high-quality patient care.
By exploring the intersection of these challenges and potential strategies, we can uncover critical insights necessary for sustaining a robust medical workforce amidst demographic change.
Examine the Demographics of Aging Physicians
The demographic landscape of medical professionals is undergoing a significant transformation, with a notable increase in the age of doctors. Recent data reveals that:
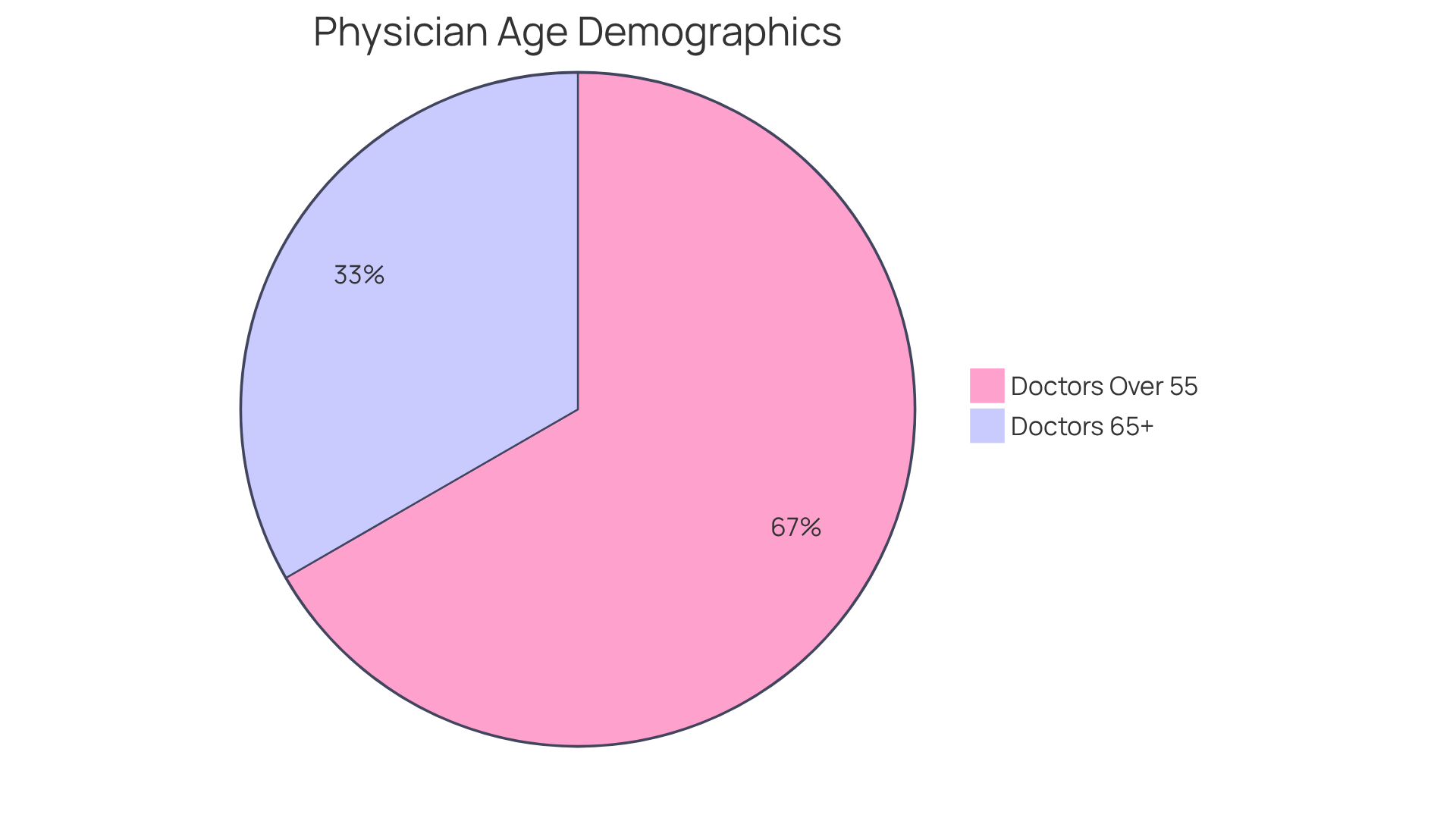
- Approximately 20% of clinical doctors fall within the age of doctors who are 65 or older.
- Nearly 40% of active medical professionals are over 55.
This trend is particularly pronounced in primary health, where the age of doctors is expected to exacerbate existing shortages. Understanding these demographics is essential for stakeholders in the healthcare industry, as it informs workforce planning and patient management strategies. As senior doctors retire, there will be an urgent need to recruit and train younger professionals to address service provision shortages, particularly in underserved regions.
Identify Challenges Faced by Older Physicians
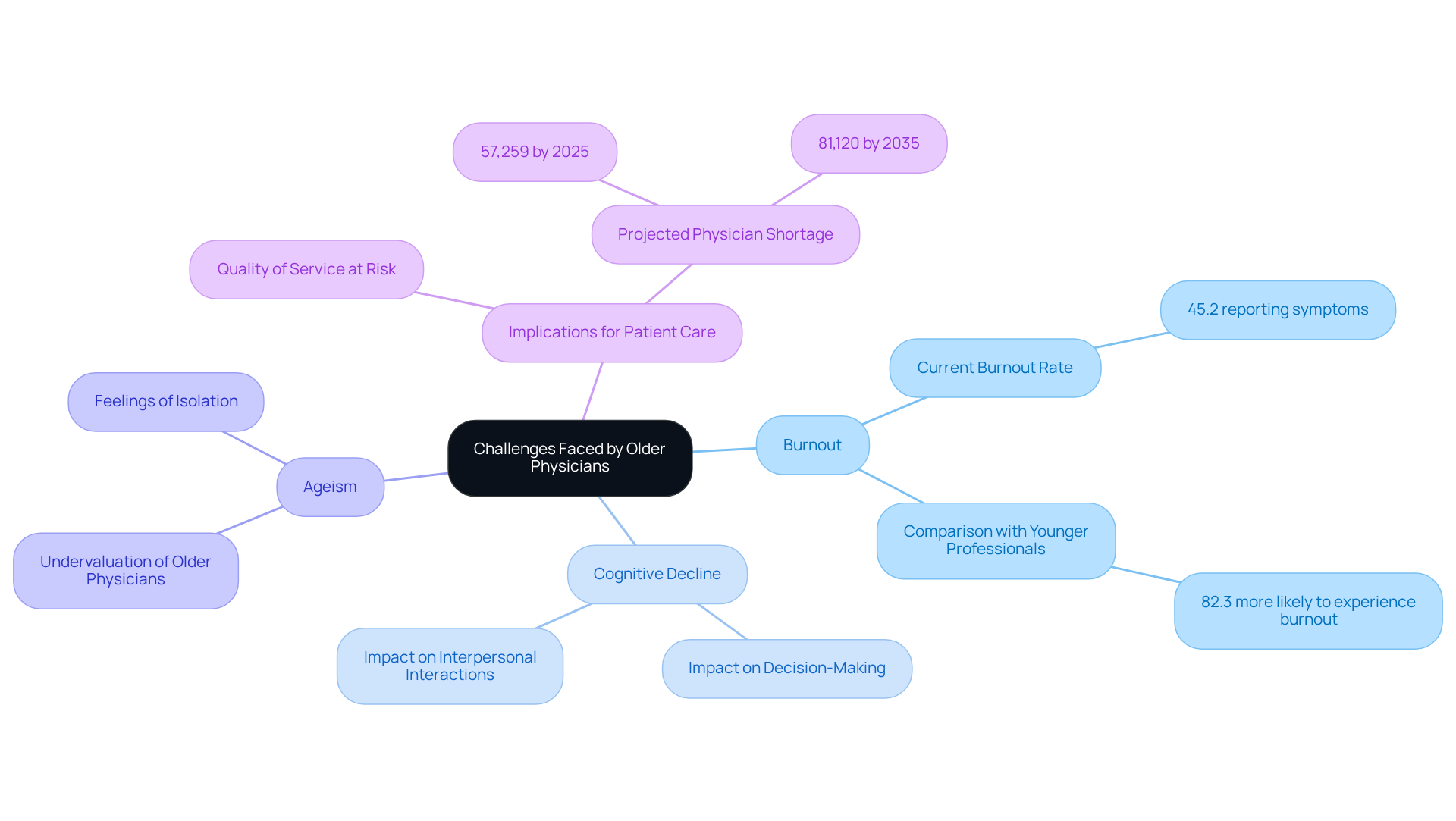
Senior doctors encounter a myriad of challenges that profoundly impact their ability to deliver high-quality care. Burnout remains a critical issue, with approximately 45.2% of medical professionals reporting at least one symptom in 2023, a decrease from a peak of 62.8% in 2021. This statistic highlights the persistent mental health crisis within the profession. Notably, younger medical professionals are 82.3% more likely to experience burnout than their peers in other fields, underscoring the widespread nature of this concern across various age groups. Additionally, cognitive decline poses a significant threat, as it can adversely affect decision-making and interpersonal interactions, complicating the provision of care.
Furthermore, ageism within the healthcare system often leads to older medical professionals being undervalued or overlooked due to the age of doctors, exacerbating feelings of isolation and frustration. These challenges not only impact the well-being of the doctors themselves but also have far-reaching implications for patient care. As senior physicians may find it increasingly difficult to adapt to evolving medical practices and technologies, the quality of service they provide could be at risk. The United States is projected to face a shortage of 57,259 doctors by 2025 and 81,120 by 2035, emphasizing the urgent need to address burnout among senior medical professionals. Addressing these issues is vital for sustaining a robust medical workforce and ensuring that individuals receive the highest quality of care.
Analyze the Impact on Healthcare Systems and Patient Care
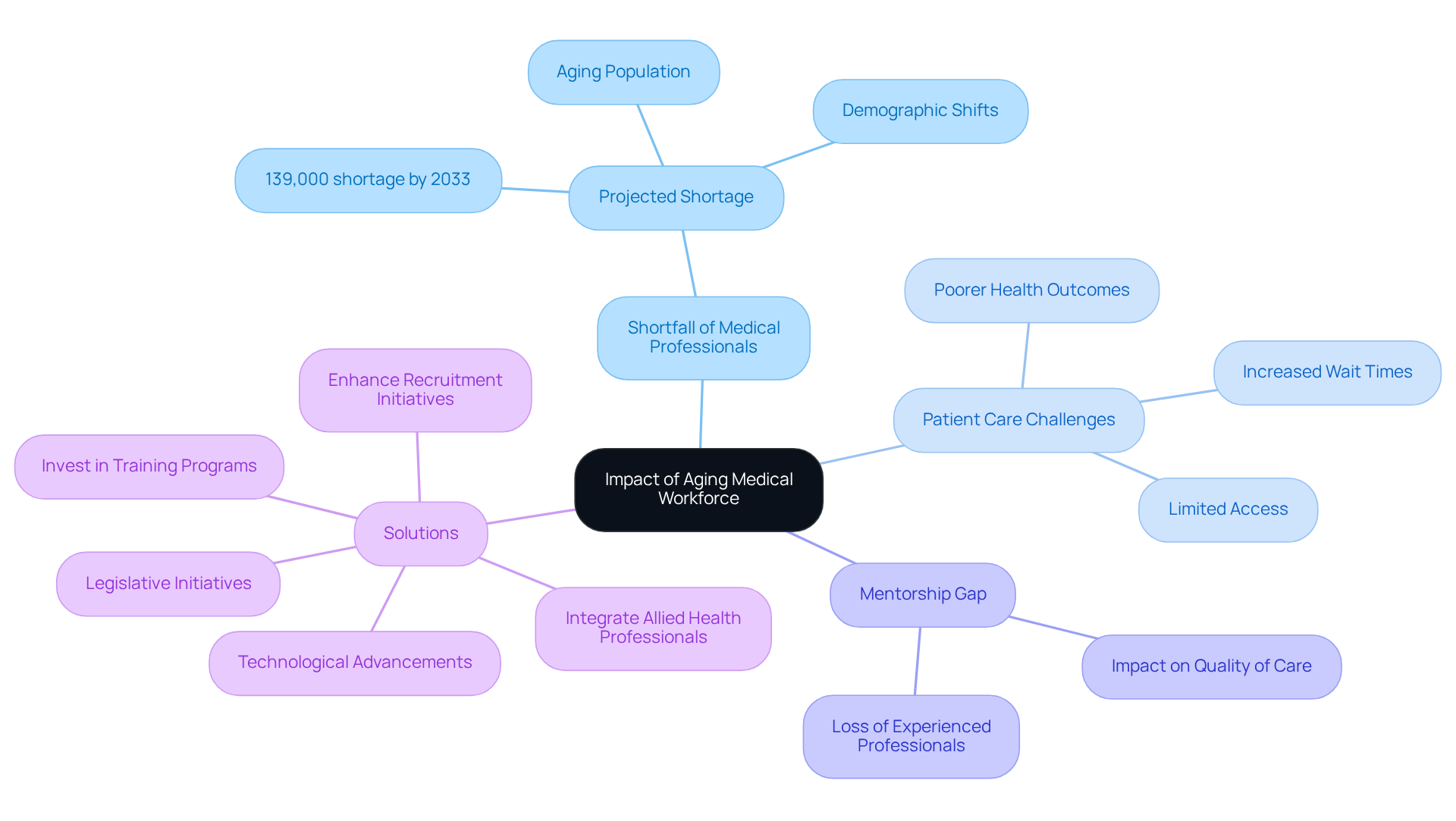
The challenges posed by the aging medical professional workforce are largely influenced by the age of doctors, which presents significant issues for healthcare systems and treatment. As seasoned doctors retire, the U.S. is projected to face a shortfall of up to 139,000 medical professionals by 2033, largely due to the age of doctors, demographic shifts, and an increasing elderly population. This impending scarcity is expected to exacerbate wait times for patients, limit access to care, and potentially lead to poorer health outcomes, especially among at-risk populations. Furthermore, the departure of experienced medical professionals creates a mentorship gap for younger doctors, which can adversely affect the quality of care provided.
To counter these trends, healthcare organizations must take proactive steps to enhance recruitment initiatives and invest in comprehensive training programs for new doctors. This approach is essential to ensure a robust pipeline of healthcare professionals who are equipped to address the evolving demands of patient care. Additionally, integrating allied health professionals into the workforce can help alleviate some of the pressures resulting from physician shortages.
Legislative initiatives and technological advancements are also vital in addressing these workforce challenges, as they can streamline processes and improve service delivery. Moreover, it is essential to consider geographic disparities in medical resources, as certain regions may experience more acute shortages than others, thereby affecting overall access to care.
Explore Strategies for Addressing Aging Physician Challenges
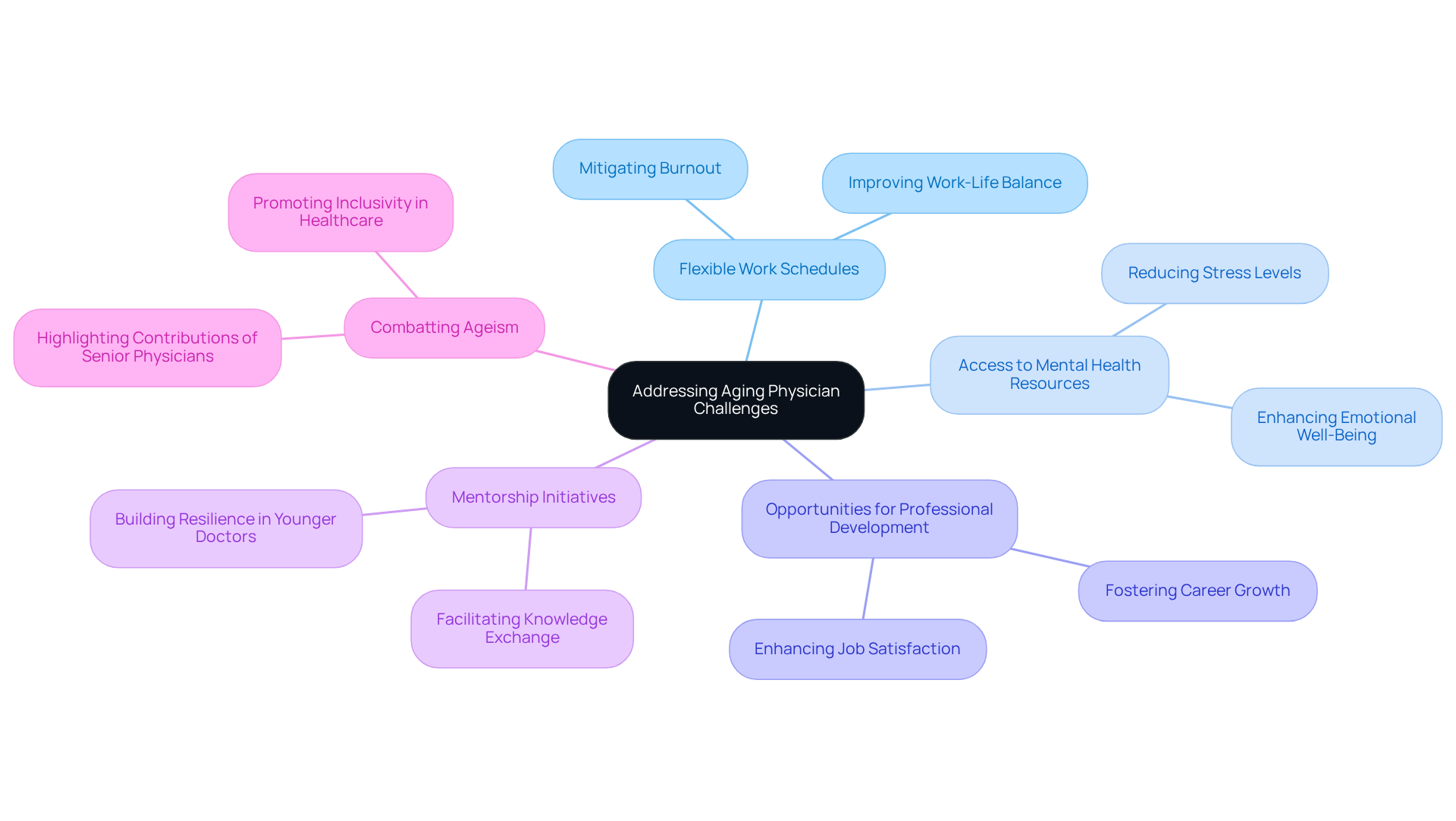
To effectively address the challenges faced by senior doctors, medical organizations must implement strategic initiatives that create a supportive work environment. Prioritizing mental health and well-being is crucial in mitigating burnout, which has become increasingly prevalent among healthcare providers. This goal can be achieved through:
- Flexible work schedules
- Access to mental health resources
- Opportunities for professional development
Additionally, establishing mentorship initiatives that connect younger medical practitioners with experienced mentors is essential. Such programs facilitate vital knowledge exchange and enhance the abilities of the upcoming generation of doctors. Evidence shows that these initiatives improve job satisfaction and retention rates among younger doctors, fostering a more resilient workforce.
Furthermore, organizations should promote policies that combat ageism and highlight the invaluable contributions of seasoned medical professionals, especially in relation to the age of doctors. By taking these comprehensive steps, healthcare systems can better support aging physicians, ultimately ensuring the delivery of high-quality care to patients.
Conclusion
The increasing age of physicians presents a critical challenge for the healthcare system, necessitating urgent attention and strategic action. As a significant portion of the medical workforce approaches retirement, understanding the implications of this demographic shift is essential for maintaining quality patient care and ensuring adequate healthcare provision. Acknowledging the challenges faced by older doctors, such as burnout, cognitive decline, and ageism, is vital for fostering a supportive environment that allows them to continue contributing effectively to patient care.
Key insights from the article highlight the urgent need for proactive measures to address the impending physician shortage. With projections indicating a potential shortfall of over 139,000 doctors by 2033, it is imperative that healthcare organizations enhance recruitment efforts, invest in training programs, and create mentorship initiatives that bridge the gap between experienced and younger physicians. By prioritizing mental health resources and promoting flexible work arrangements, healthcare institutions can better support aging doctors and mitigate the risks associated with burnout.
Ultimately, the challenges posed by an aging physician workforce extend beyond individual practitioners; they impact the entire healthcare system and patient outcomes. It is crucial for stakeholders to recognize the significance of these issues and take decisive action to implement strategies that support aging physicians. Emphasizing collaboration, legislative support, and technological advancements will not only address current challenges but also lay the groundwork for a resilient healthcare workforce capable of meeting the evolving needs of patients in the future.


