Overview
This article delves into the projected costs associated with Medicare in 2025, encompassing premiums, deductibles, and income-related adjustments that significantly impact market access for beneficiaries. Notably, the anticipated rise in costs, such as the standard Part B premium increasing to $185.00 and the Part D deductible reaching $590, highlights potential financial barriers for patients. These developments necessitate strategic adjustments by healthcare stakeholders to ensure continued access to essential services and medications.
Introduction
As the landscape of Medicare continues to evolve, understanding the intricacies of its cost structure has never been more critical for beneficiaries and stakeholders alike. With rising premiums, deductibles, and income-related adjustments, the financial implications of Medicare are significant. These factors influence patient access to essential healthcare services and medications.
This article delves into the key components of Medicare costs for 2025, including:
- The projected increases in premiums and deductibles for Parts A, B, and D.
- The impact of income-related adjustments on higher-income beneficiaries.
- The importance of strategic approaches for pharmaceutical companies to enhance market access and improve patient outcomes amidst these changes.
By leveraging comprehensive data insights, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of Medicare, ensuring that patients receive the care they need in an increasingly challenging environment.
Clarify Medicare Cost Structure and Components
Healthcare costs encompass several key elements: premiums, deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments.
- Premiums represent the monthly payments required for health insurance coverage. The 2025 Medicare costs indicate that the standard monthly premium for the health insurance program B is projected to be $185.00, reflecting an increase from the previous year.
- Deductibles denote the out-of-pocket expenses that recipients must cover before Medicare begins to pay for services. The 2025 Medicare costs include a Part B deductible established at $257.
- Following the deductible, recipients are responsible for a portion of their expenses, typically 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most services, known as coinsurance.
- Lastly, copayments are fixed amounts that beneficiaries pay for specific services or medications.
Understanding these elements is essential for stakeholders aiming to anticipate costs and devise effective strategies. CareSet’s monthly updates on government healthcare programs deliver valuable insights into drug utilization and treatment pathways, thereby enhancing provider engagement and empowering stakeholders to navigate the complexities of patient care adeptly.
Recent updates indicate that higher-income recipients may face increased premiums, with individuals earning $500,000 or more in 2023 incurring significantly higher costs for Medicare D. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services underscores that “The D risk adjustment model is not intended to predict expenses for specific drugs,” highlighting the focus on overall risk rather than individual drug costs. Furthermore, the revised section D risk adjustment model now accounts for higher risk scores for low-income recipients, ensuring that plans receive appropriate reimbursement for their expected expenses. For example, the case study titled ‘D Risk Adjustment for Low-Income Subsidy Individuals’ illustrates how these adjustments impact low-income recipients, providing a practical context for comprehending the model’s implications.
As healthcare stakeholders adapt to these changes, recognizing local market implications—such as variations in service utilization and patient demographics—will be vital to mitigate potential revenue losses. By connecting these cost elements to broader market access strategies, stakeholders can leverage CareSet’s extensive insights to prepare more effectively for the evolving landscape of healthcare expenses, particularly the 2025 Medicare costs.
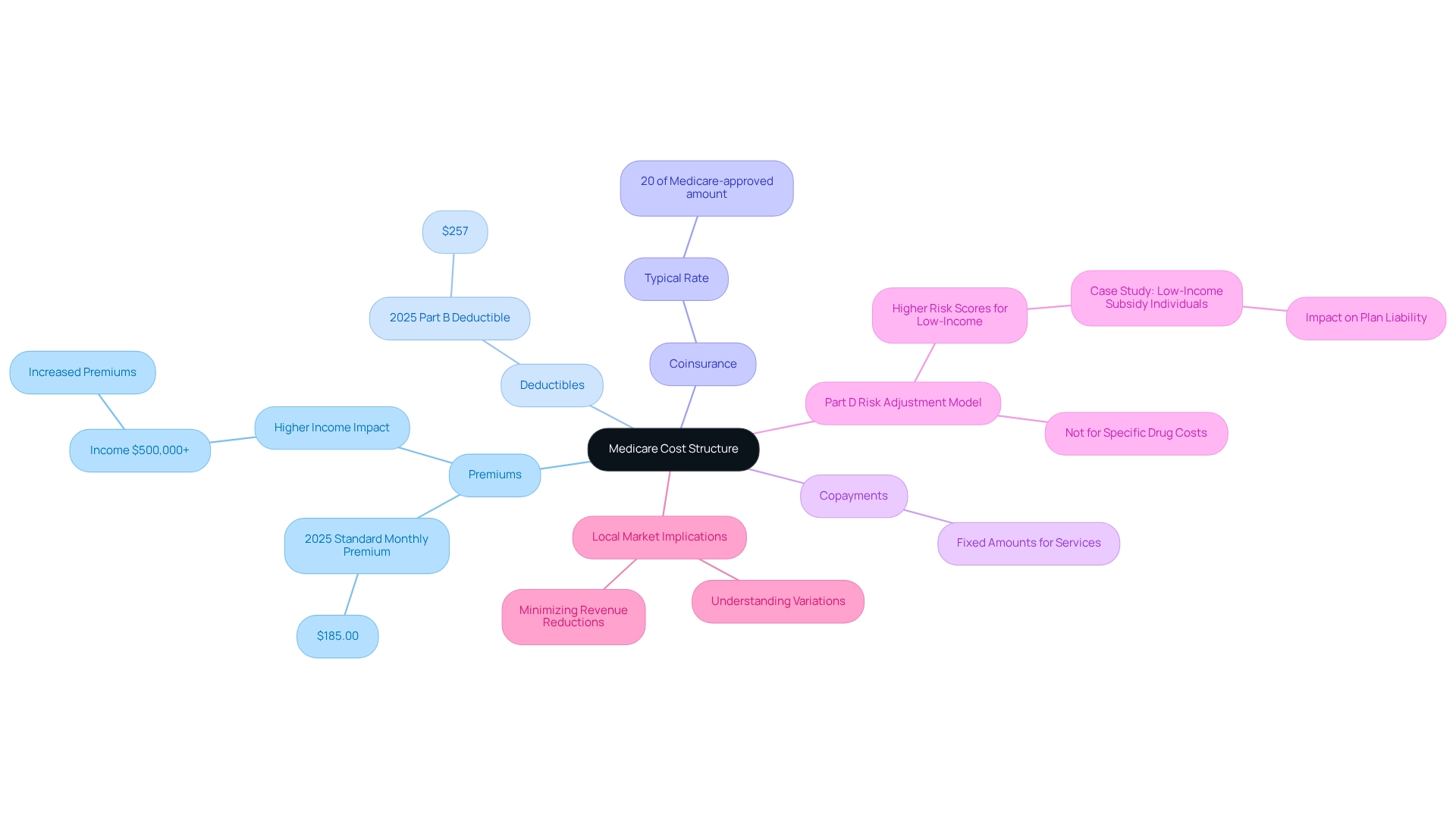
Analyze 2025 Premiums and Deductibles for Medicare Parts A, B, and D
In 2025, the premiums and deductibles for Medicare Parts A, B, and D reflect a notable trend of increasing costs that could significantly impact patient access to healthcare services and medications:
-
Part A: Most beneficiaries are exempt from paying a premium for Part A, provided they or their spouse have contributed Medicare taxes for a minimum of 10 years. However, the deductible for inpatient hospital stays has risen to $1,676, which may pose a financial burden for some patients navigating their treatment pathways.
-
Section B: The standard monthly fee for Section B is established at $185.00, along with a deductible of $257. The 2025 Medicare costs represent a critical consideration for beneficiaries when evaluating their healthcare options, especially as they move through various lines of therapy defined by ICD and HCPCS codes.
-
Section D: The highest deductible for Section D plans has risen to $590, up from $545 in 2024. Additionally, the national base premium for Part D is now $36.78. This upward trend in costs, especially the 2025 Medicare costs, may deter some patients from accessing necessary medications, particularly those with limited financial resources, impacting their journey from diagnosis to treatment.
These rising figures highlight the significance of comprehending the changing landscape of healthcare, particularly the 2025 Medicare costs, as they directly affect patient choices concerning access to services and the affordability of medications. Moreover, the examination of transportation benefits in Advantage plans shows a troubling reduction in availability, from 36% in 2024 to 30% in 2025, which could further obstruct access to care for at-risk groups. As healthcare economist Anthony Damico observes, “Most individual and SNP Advantage plans still do not provide these benefits, although a greater number of SNP plans typically offer these advantages, especially food and produce.” This emphasizes the difficulties individuals encounter in obtaining essential services. Furthermore, individuals can subscribe for updates on health news and policy changes from the Rights group, promoting proactive involvement with the changing healthcare landscape. The increasing expenses of healthcare require a strategic approach to ensure that recipients can still access essential services and medications, especially as they navigate the complexities of provider interventions and treatment approvals.
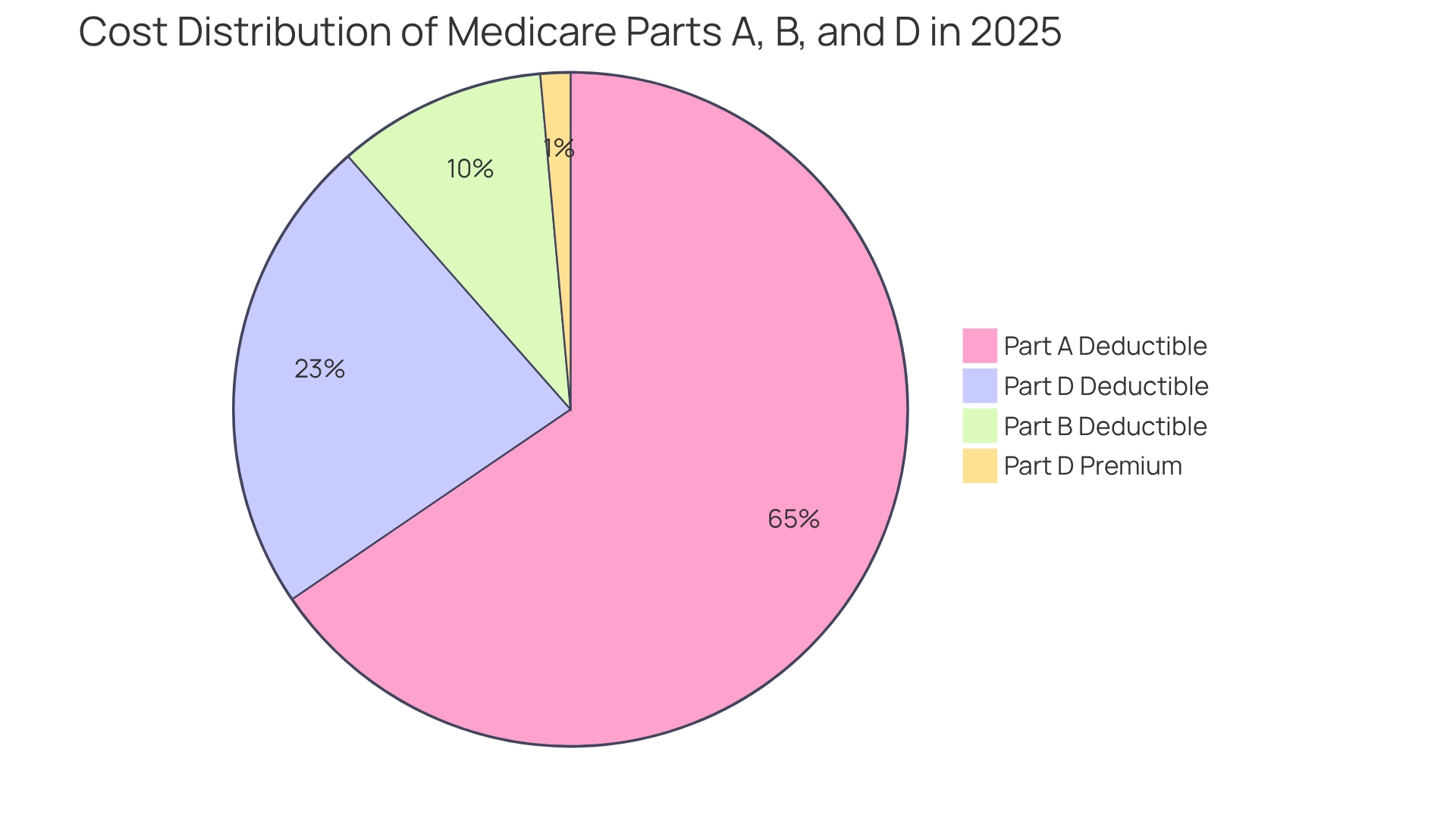
Examine Income-Related Adjustments and Financial Factors Impacting Medicare Costs
Income-related adjustments, known as the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA), have a significant impact on beneficiaries with higher incomes. For 2025, individuals with a modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeding $106,000 and couples surpassing $212,000 will incur increased premiums for Medicare Parts B and D.
- Part B IRMAA: Premiums will range from $259.00 to $628.90, depending on income levels, creating a substantial financial burden for many.
- Part D IRMAA: Similar adjustments will apply, further affecting the overall cost of prescription drug coverage.
These financial adjustments can create barriers to access for higher-income recipients, influencing their healthcare choices and the strategies that pharmaceutical companies must implement. CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data insights empower pharmaceutical stakeholders to navigate these complexities effectively, providing critical information on how IRMAA impacts market access strategies.
Recent analyses indicate an increase in the percentage of participants paying IRMAA, prompting questions about the fairness and effectiveness of the system. An examination of the Trustees Report on healthcare illustrates this trend, leading to discussions on how these adjustments affect beneficiaries’ healthcare choices.
Historically, the IRMAA brackets were frozen from 2011 to 2019 due to the Affordable Care Act, which has implications for understanding the current adjustments. Additionally, the release schedule for CPI-U data is crucial for anticipating future health insurance premium adjustments and IRMAA calculations.
Expert insights suggest that if an individual’s income exceeds $106,000 on their 2023 taxes, they should anticipate paying IRMAA in addition to their standard Part B premium. David Fei, CFP®, ChFEBC℠, AIF®, emphasizes this point, stating, “If your income exceeded $106,000 (MAGI) on your 2023 taxes, then you can expect to pay IRMAA on top of your original full Part B premium.” This underscores the importance of understanding the financial elements that affect healthcare expenses, especially the 2025 Medicare costs, for individuals in higher income brackets. As the landscape evolves, staying informed about these adjustments will be crucial for stakeholders in the pharmaceutical sector, ensuring they can effectively navigate the complexities of market access.
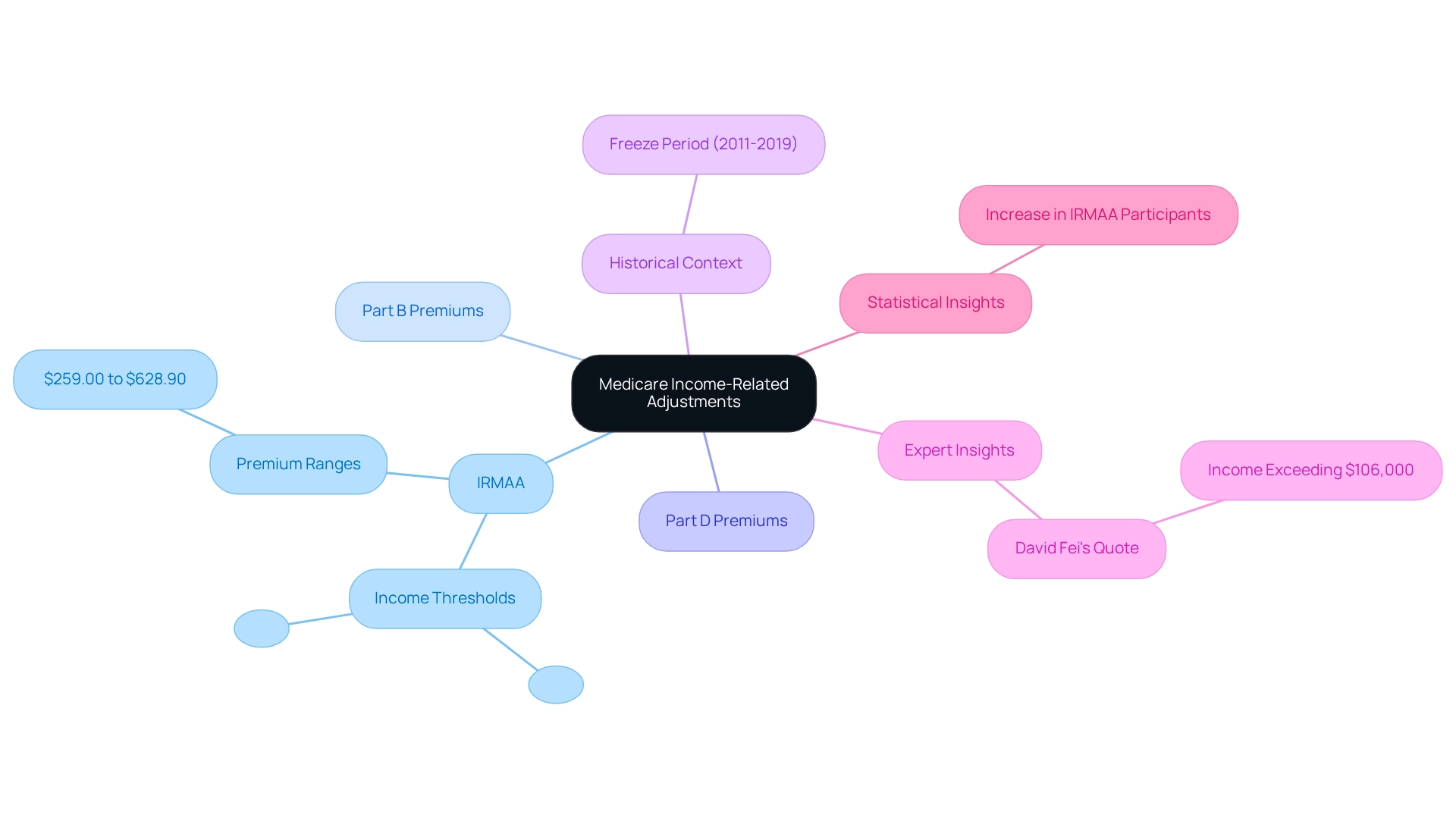
Apply Insights to Pharmaceutical Market Access Strategies
Navigating the complexities of the 2025 healthcare landscape necessitates that pharmaceutical companies adopt strategic approaches aimed at enhancing market access and improving patient outcomes while considering the impact of 2025 Medicare costs. Key strategies include:
- Targeted patient engagement
- Pricing strategies
- Collaboration with payers
- Data-driven insights
Targeted patient engagement is critical, particularly in recognizing the financial burdens faced by patients. Tailoring engagement strategies to address these specific needs can significantly enhance patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans. CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data insights can help identify patient demographics and financial challenges, facilitating more effective engagement. Notably, dual special needs plan enrollment has tripled over the past ten years, underscoring the importance of understanding the demographics of beneficiaries. Aligning drug pricing with the anticipated out-of-pocket costs, particularly the 2025 Medicare costs, is essential for improving accessibility. Utilizing CareSet’s data insights can inform pricing strategies that not only support patient adherence but also foster trust in pharmaceutical offerings.
Collaboration with payers is another crucial strategy. Engaging proactively with Advantage plans and Part D sponsors can lead to improved coverage options. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasizes the significance of fair, clear plan offerings and enhancing access to care, which highlights the necessity for pharmaceutical companies to align their strategies with the evolving healthcare landscape. Working with CareSet can provide valuable insights into payer dynamics, ensuring that patients have improved access to essential medications, particularly as the Advantage landscape becomes increasingly complex. Utilizing claims data enables companies to recognize trends in prescribing habits and patient demographics. CareSet’s insights are invaluable for informing targeted marketing and sales strategies, ultimately leading to more effective outreach and engagement. The growth of special needs plans in Medicare Advantage, with a 14% increase in enrollment from 2023 to 2024, exemplifies how the Medicare landscape is adapting to meet the needs of vulnerable populations.
By implementing these strategies, informed by CareSet’s comprehensive data insights, pharmaceutical companies can enhance their market access initiatives. This ensures they meet the evolving needs of Medicare beneficiaries while driving improved health outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding the evolving cost structure of Medicare for 2025 is essential for beneficiaries and stakeholders alike. The key components—premiums, deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments—are projected to increase, impacting patient access to necessary healthcare services and medications. This anticipated rise in costs for Medicare Parts A, B, and D underscores the financial challenges beneficiaries may face, particularly with higher deductibles and premiums. Such shifts highlight the critical need for careful planning and strategizing among all involved stakeholders.
Furthermore, the impact of income-related adjustments on beneficiaries with higher incomes introduces another layer of complexity. The increased premiums under the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA) can impose additional financial burdens, influencing healthcare decisions and access to services. Pharmaceutical companies must remain vigilant in understanding these adjustments and adapt their market access strategies to better support patients navigating these financial challenges.
To effectively address these changes, strategic approaches are essential. By focusing on targeted patient engagement and aligning drug pricing with anticipated out-of-pocket costs, pharmaceutical companies can enhance patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans. Collaboration with payers and leveraging data-driven insights will further ensure that patients have improved access to necessary medications.
As the Medicare landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive will be crucial for all stakeholders. By embracing these strategies and understanding the nuances of Medicare costs, stakeholders can help ensure that beneficiaries receive the care they need in an increasingly challenging environment.

