Overview
The 2025 IRMAA brackets have a profound impact on Medicare costs, imposing additional premiums on higher-income beneficiaries based on their modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from two years prior. Understanding the specific income thresholds and corresponding surcharges is crucial for effective financial planning. These adjustments can significantly increase healthcare expenses for those affected, making it essential to grasp their implications. By recognizing these changes, beneficiaries can better prepare for the financial responsibilities that lie ahead.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Medicare presents a formidable challenge, particularly for higher-income beneficiaries who must contend with the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA). This additional charge, designed to ensure that affluent individuals contribute fairly to their Medicare coverage, can have a profound impact on financial planning during retirement.
As the Medicare landscape continues to evolve, grasping the intricacies of IRMAA—including its calculation, the income brackets for 2025, and strategies to mitigate costs—becomes imperative for millions of retirees. With projections indicating that over 5.2 million individuals will be affected, the stakes are undeniably high. Therefore, it is crucial for beneficiaries to devise informed strategies that enable them to manage their healthcare expenses effectively.
Define IRMAA and Its Purpose in Medicare
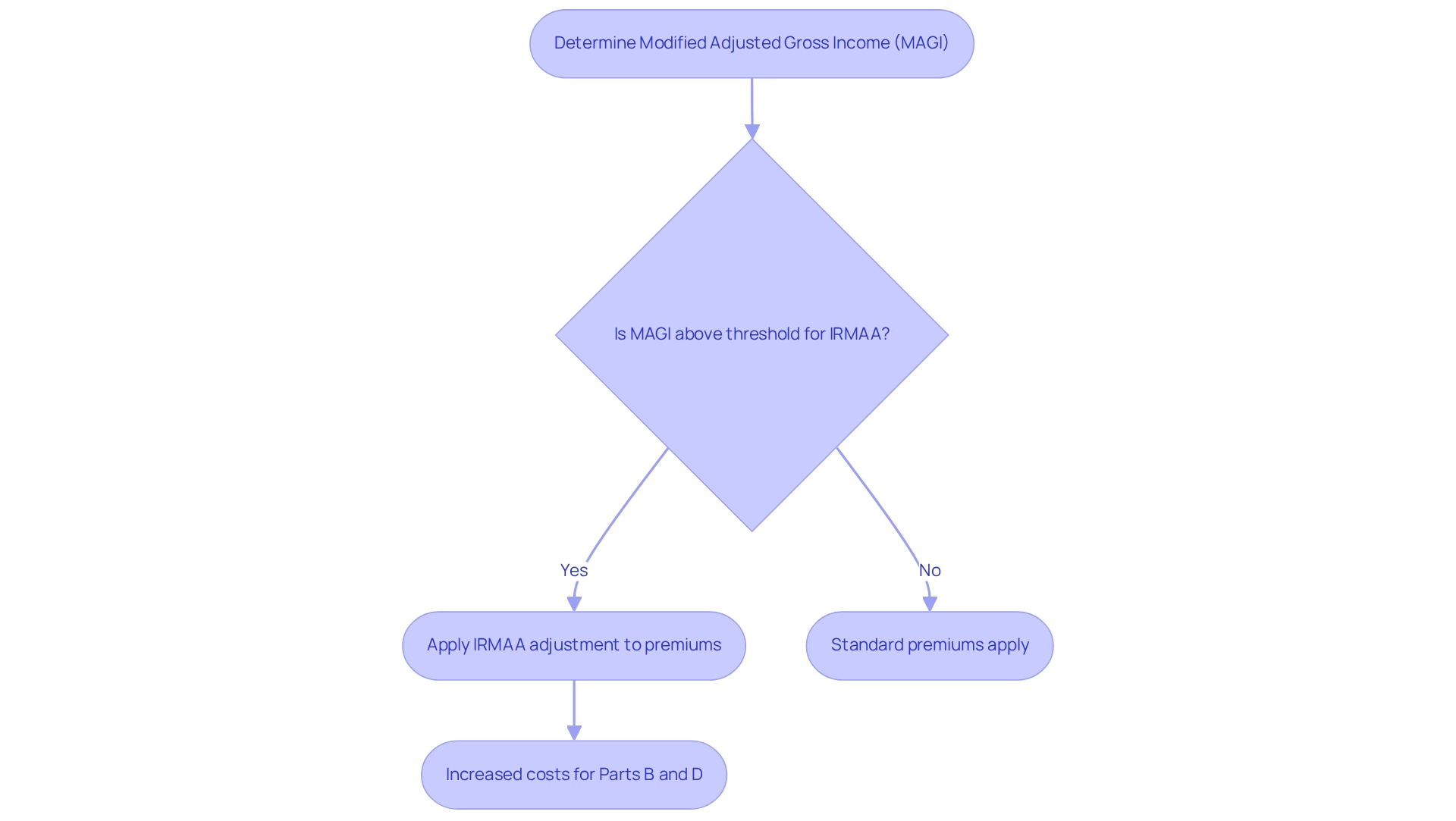
The Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA) represents an additional fee imposed on certain beneficiaries of the healthcare program, supplementing their standard premiums for Parts B and D. Established under the Modernization Act of 2003, this adjustment ensures that higher-income individuals contribute a more equitable share towards the costs of their healthcare coverage. Notably, this adjustment is determined based on the beneficiary’s modified adjusted gross earnings (MAGI) from two years prior, underscoring the necessity for higher earners to comprehend how their earnings impact their healthcare costs, especially considering the 2025 IRMAA brackets.
In 2025, approximately 8% of Medicare recipients—over 5.2 million individuals—will be affected by the income-related adjustment. This financial modification is critical, as beneficiaries’ premiums typically cover only about 25% of the expenses related to Part B and around 15% for Part D, even with surcharges for those with elevated earnings. The complexities of the IRMAA highlight the financial strain faced by high-earning retirees, necessitating a collective effort to navigate these challenges in retirement financial planning.
Real-world examples illustrate the significant expenses that IRMAA can impose on beneficiaries, prompting many to seek guidance from financial advisors to understand how various revenue streams influence healthcare premiums. This aligns with the case study titled ‘Financial Planning for Healthcare Premiums,’ which emphasizes the importance of recognizing revenue sources. Such a proactive approach is essential for preparing for potential increases in healthcare costs, particularly as income levels fluctuate. Ultimately, the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount plays a vital role in the healthcare system, promoting fairness in funding while simultaneously presenting challenges for those impacted.
Detail the 2025 IRMAA Income Brackets
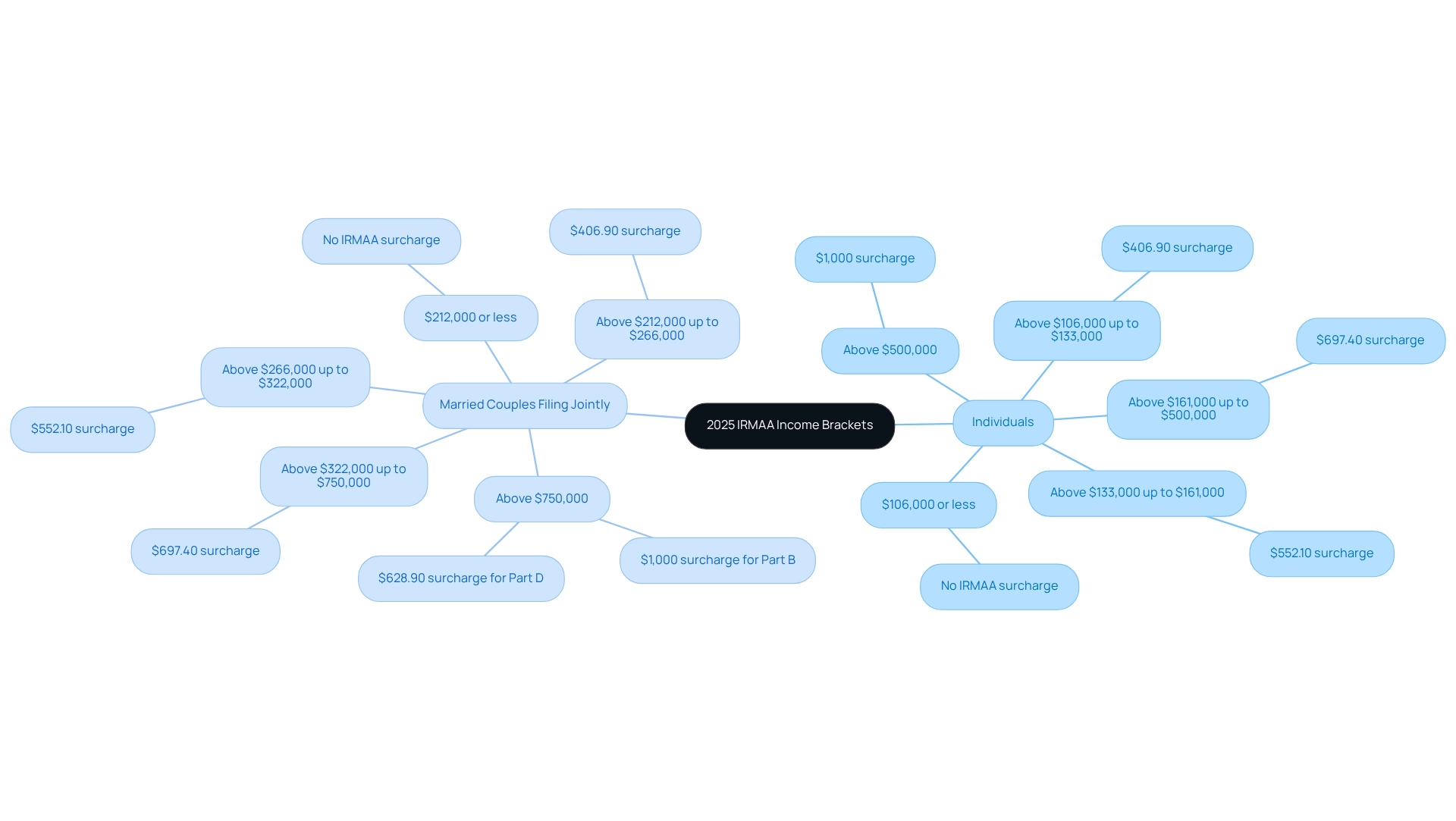
The additional revenue tiers for the 2025 IRMAA brackets are designed to apply extra fees on beneficiaries of the health insurance program based on their Modified Adjusted Gross Earnings (MAGI) from two years earlier. The brackets are as follows:
-
Individuals:
- $106,000 or less: No IRMAA surcharge
- Above $106,000 up to $133,000: $406.90 surcharge
- Above $133,000 up to $161,000: $552.10 surcharge
- Above $161,000 up to $500,000: $697.40 surcharge
- Above $500,000: $1,000 surcharge
-
Married Couples Filing Jointly:
- $212,000 or less: No IRMAA surcharge
- Above $212,000 up to $266,000: $406.90 surcharge
- Above $266,000 up to $322,000: $552.10 surcharge
- Above $322,000 up to $750,000: $697.40 surcharge
- Above $750,000: $1,000 surcharge for Part B and $628.90 for Part D.
These brackets illustrate the additional premiums that beneficiaries will incur based on their income levels, significantly affecting their overall Medicare costs. Notably, the additional fee for Medicare Part B is greater than that for Part D, which is established by the health insurance provider. As David Fei, a financial expert, points out, individuals with a MAGI surpassing $106,000 in 2023 can anticipate paying an additional charge on top of their standard Part B premium. This modification indicates the continuing pattern of rising additional fees, which are generally assessed each year but may be altered for substantial earnings variations. Understanding the 2025 IRMAA brackets is crucial for beneficiaries to effectively anticipate their healthcare expenses. Insights from the case study titled ‘What are the 2025 Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount Brackets and How Do They Affect Medicare Premiums?’ further emphasize the impact of these surcharges on beneficiaries, highlighting the importance of being aware of one’s financial status in relation to these brackets.
Explain How IRMAA is Calculated and Factors Influencing It
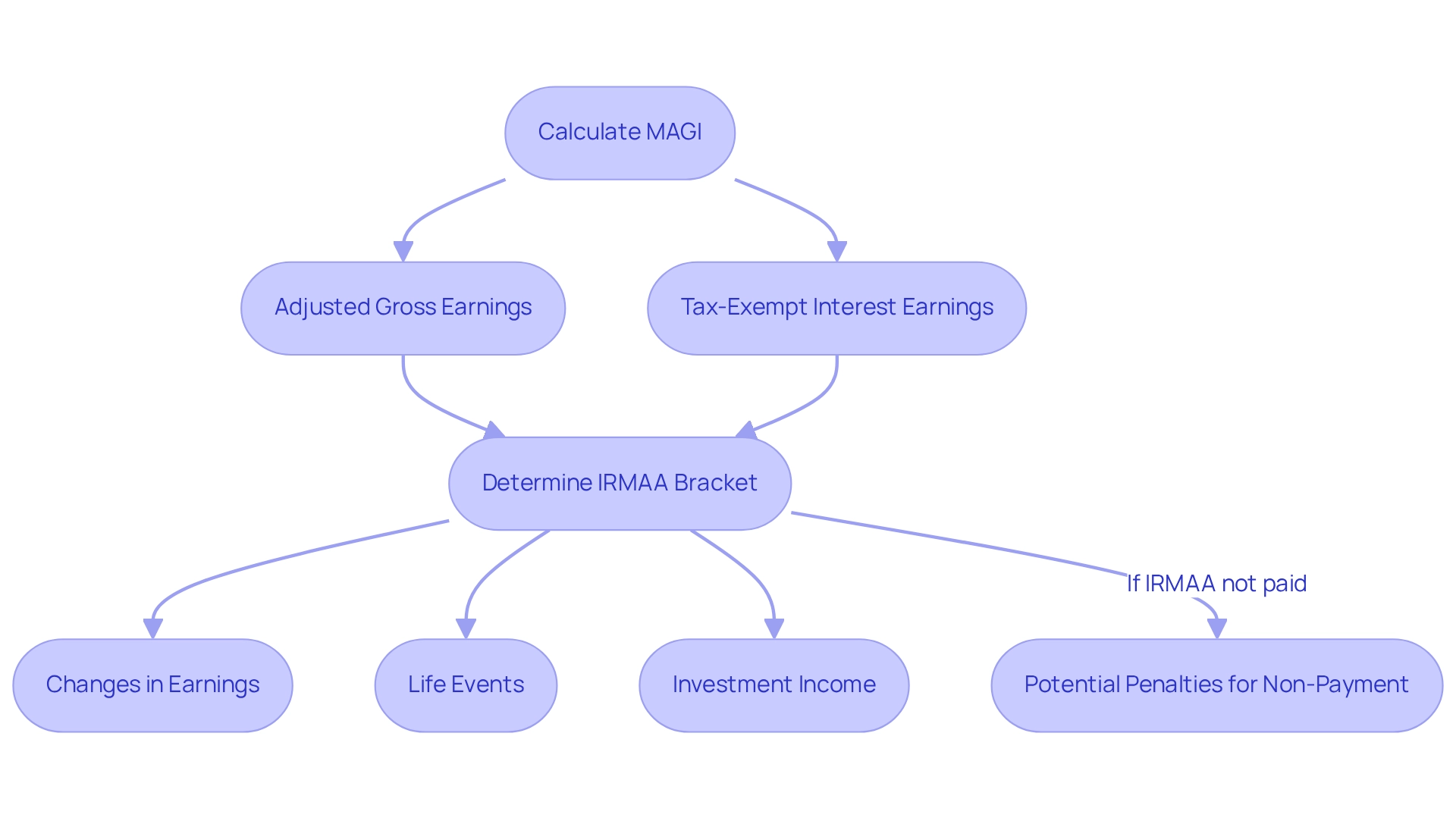
The Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount, or Adjustment Amount, is determined based on a beneficiary’s modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from two years prior. For instance, the earnings reported on your 2023 tax return will dictate your additional premium for 2025. This calculation encompasses two critical elements: Adjusted Gross Earnings (AGE), which reflects your total earnings after specific deductions, and Tax-Exempt Interest Earnings, which are added back to your AGE to establish your MAGI.
Several factors can influence your Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount. Changes in earnings play a significant role; a notable increase can elevate you to a higher adjustment bracket. For example, if your MAGI exceeded $106,000 on your 2023 taxes, you should anticipate an additional charge alongside your standard Part B premium due to the 2025 IRMAA brackets. Furthermore, the threshold for the 2025 IRMAA brackets is projected to reach $216,000 if inflation remains stable, which is a crucial consideration for recipients planning for future income shifts. Life events also impact your adjustment amount. Major changes, such as retirement, marriage, or divorce, can alter your income and, consequently, your adjustment amount. Additionally, investment income, including profits from capital gains and dividends, can affect your modified adjusted gross income, potentially leading to increased charges.
Understanding these factors is essential, as adjustment fees are recalculated annually based on income from two years earlier, with the possibility of reductions if income decreases. Beneficiaries must recognize that failing to pay surcharges can incur penalties, including interest fees and potential disruptions to Medicare coverage. Addressing any discrepancies with the Social Security Administration promptly is crucial to avoid adverse outcomes.
Provide Strategies to Manage or Reduce IRMAA Costs
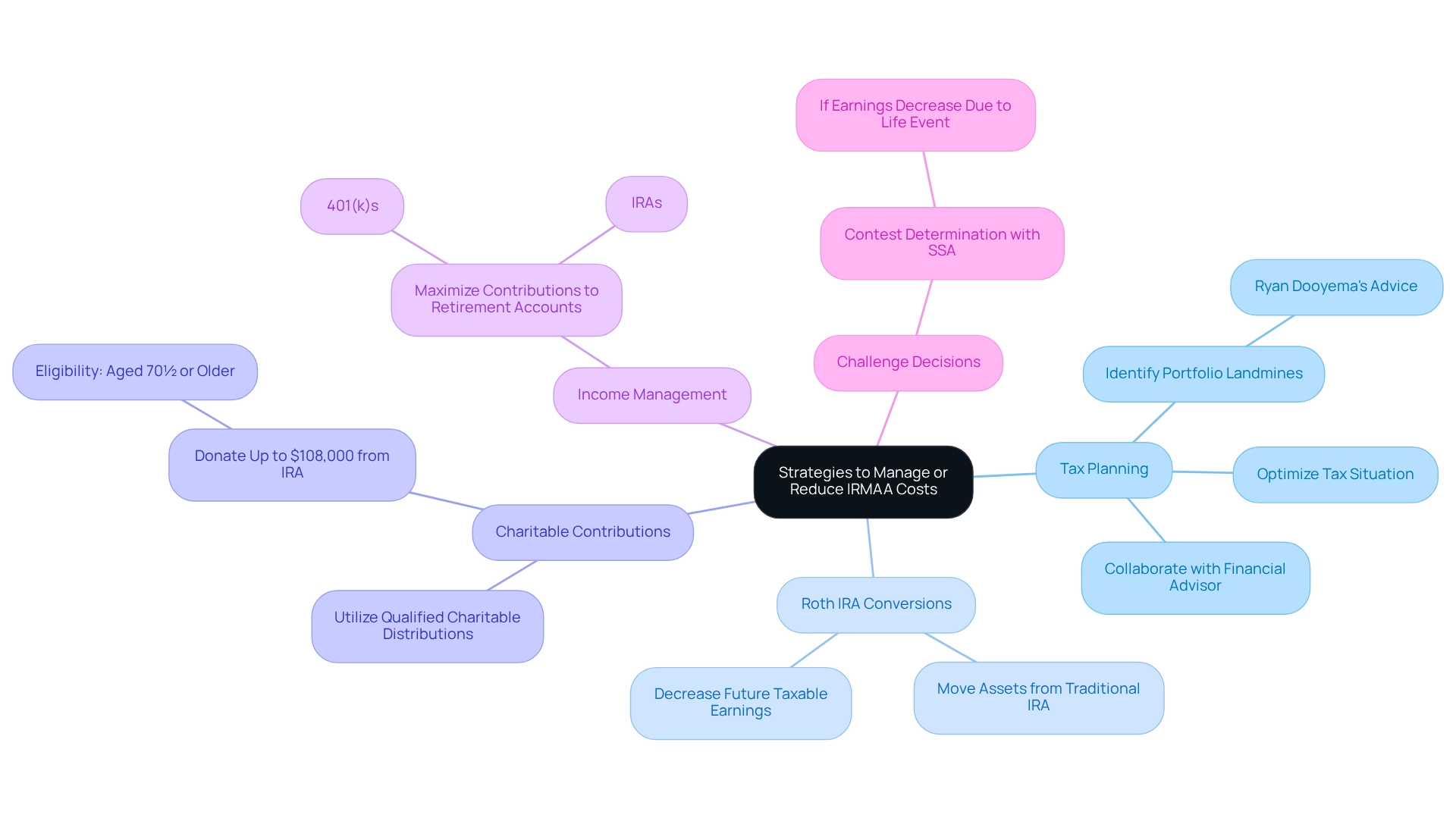
To effectively manage or reduce IRMAA costs, consider the following strategies:
-
Tax Planning: Collaborate with a financial advisor to optimize your tax situation, which may help lower your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI). As Ryan Dooyema advises, “Make sure you know where the landmines are in your clients’ portfolios.”
-
Roth IRA Conversions: Moving assets from a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA can decrease future taxable earnings, potentially lessening related impacts.
-
Charitable Contributions: Utilizing qualified charitable distributions can effectively lower your MAGI, thereby decreasing your income-related monthly adjustment amount obligations. Notably, individuals aged 70½ or older can donate up to $108,000 to qualified charities directly from their IRA in 2025, making this a powerful strategy.
-
Income Management: For those still in the workforce, maximizing contributions to retirement accounts such as 401(k)s or IRAs can reduce taxable earnings.
-
Challenge Decisions: If your earnings have decreased due to a major life event, you have the choice to contest your determination with the Social Security Administration.
Applying these strategies can enable beneficiaries to reduce their additional income-related Medicare charges and manage their Medicare expenses more efficiently under the 2025 IRMAA brackets. A significant percentage of beneficiaries are utilizing Roth IRA conversions as part of their tax planning strategies, demonstrating the effectiveness of proactive financial management in reducing expenses associated with 2025 IRMAA brackets. Additionally, effective income planning can help individuals stay below IRMAA thresholds, as highlighted in the case study “Strategic Income Planning for Retirement,” reinforcing the importance of these strategies.
Conclusion
The complexities surrounding the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA) are paramount for higher-income Medicare beneficiaries. IRMAA is implemented to ensure that affluent individuals contribute their fair share towards Medicare coverage, with significant financial implications for over 5.2 million individuals projected to be affected in 2025. Understanding IRMAA’s purpose, the specific income brackets for 2025, and the calculation methods is essential for effective financial planning during retirement.
The income brackets established for 2025 illustrate the increasing costs associated with Medicare premiums for those whose income exceeds certain thresholds. The surcharges vary significantly, underscoring the necessity for beneficiaries to be proactive in managing their income levels to avoid unexpected financial burdens. Additionally, factors influencing IRMAA, such as life events and changes in income, necessitate a strategic approach to financial management.
Beneficiaries can take actionable steps to mitigate IRMAA costs, including:
- Tax planning
- Roth IRA conversions
- Charitable contributions
These strategies not only help lower the modified adjusted gross income but also empower individuals to navigate their healthcare expenses more effectively. By being informed and proactive, higher-income retirees can better manage their Medicare costs, ensuring that they can enjoy their retirement without undue financial stress. Understanding and addressing the implications of IRMAA is a vital component of comprehensive retirement planning, emphasizing the importance of awareness and strategy in navigating the Medicare landscape.

