Overview
The article centers on effective strategies for implementing outcomes measurement in healthcare, underlining the critical need for systematic evaluation of health service results. It articulates this by delineating essential approaches, such as:
- Establishing clear objectives
- Utilizing standardized tools
- Integrating measurement into clinical practice
- Fostering collaboration among stakeholders
These strategies collectively enhance the quality and effectiveness of healthcare delivery, ultimately driving improved patient outcomes.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of healthcare, the measurement of outcomes has emerged as a pivotal component for enhancing patient care and ensuring the efficacy of medical interventions. By systematically evaluating the results of healthcare services, organizations can gain crucial insights into treatment effectiveness, patient satisfaction, and overall care quality. This article delves into the significance of outcomes measurement, exploring the methodologies that healthcare providers can adopt to assess and improve their practices.
From establishing clear objectives and utilizing standardized tools to fostering collaboration among diverse stakeholders, a comprehensive approach to outcomes measurement not only promotes transparency but also drives a culture of continuous improvement in healthcare delivery. As the industry shifts towards data-driven decision-making, understanding the nuances of outcomes measurement becomes essential for optimizing patient health and achieving better healthcare outcomes.
Define Outcomes Measurement in Healthcare
In healthcare, outcomes measurement represents a systematic evaluation of the results derived from services and interventions, with a keen focus on their impact on individual health status. This process encompasses various metrics that assess treatment effectiveness, client satisfaction, and overall care quality. Key result measures include mortality rates, readmission rates, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs). By establishing these metrics for outcomes measurement, medical providers can effectively evaluate the effectiveness of their services, identify areas needing enhancement, and ensure that care adheres to established best practices. The World Health Organization defines a result measure as a change in health linked to a medical intervention, underscoring the necessity for accurate and pertinent metrics in assessing medical effectiveness.
In the context of Medicare, it is essential to understand how providers navigate treatment pathways using ICD, NDC, and HCPCS codes. These frameworks assist in defining interventions and tracking individual journeys from diagnosis through various lines of therapy. By examining Medicare claims data, stakeholders can gain insights into the treatments being authorized by Medicare Part D Plans and the associated expenses, thereby enhancing the understanding of provider interventions and consumer outcomes.
The Agency for Research and Quality (AHRQ) offers quality indicator tools for data analytics and surveys on safety culture, which can serve as a reliable foundation for discussing the significance of systematic assessment in health results. Moreover, the CMS Hospital Performance Reports illustrate practical applications of outcomes measurement, emphasizing trends and differences in hospital performance influenced by location and demographic disparities. These reports have been transformed into an interactive website, allowing users to explore national trends and comparisons of hospital performance, ultimately enhancing comprehension of hospital quality and care for individuals, while emphasizing outcomes measurement as part of the growing trend toward transparency and accountability in healthcare. This shift not only fosters a culture of continuous improvement but also aligns with the broader objective of optimizing health outcomes. As noted by the Dartmouth Atlas of Healthcare, despite recognized advantages, many individuals do not receive recommended therapies, such as beta-blockers following a heart attack, highlighting the tangible effects of results measurement in enhancing care quality and adherence to optimal practices.
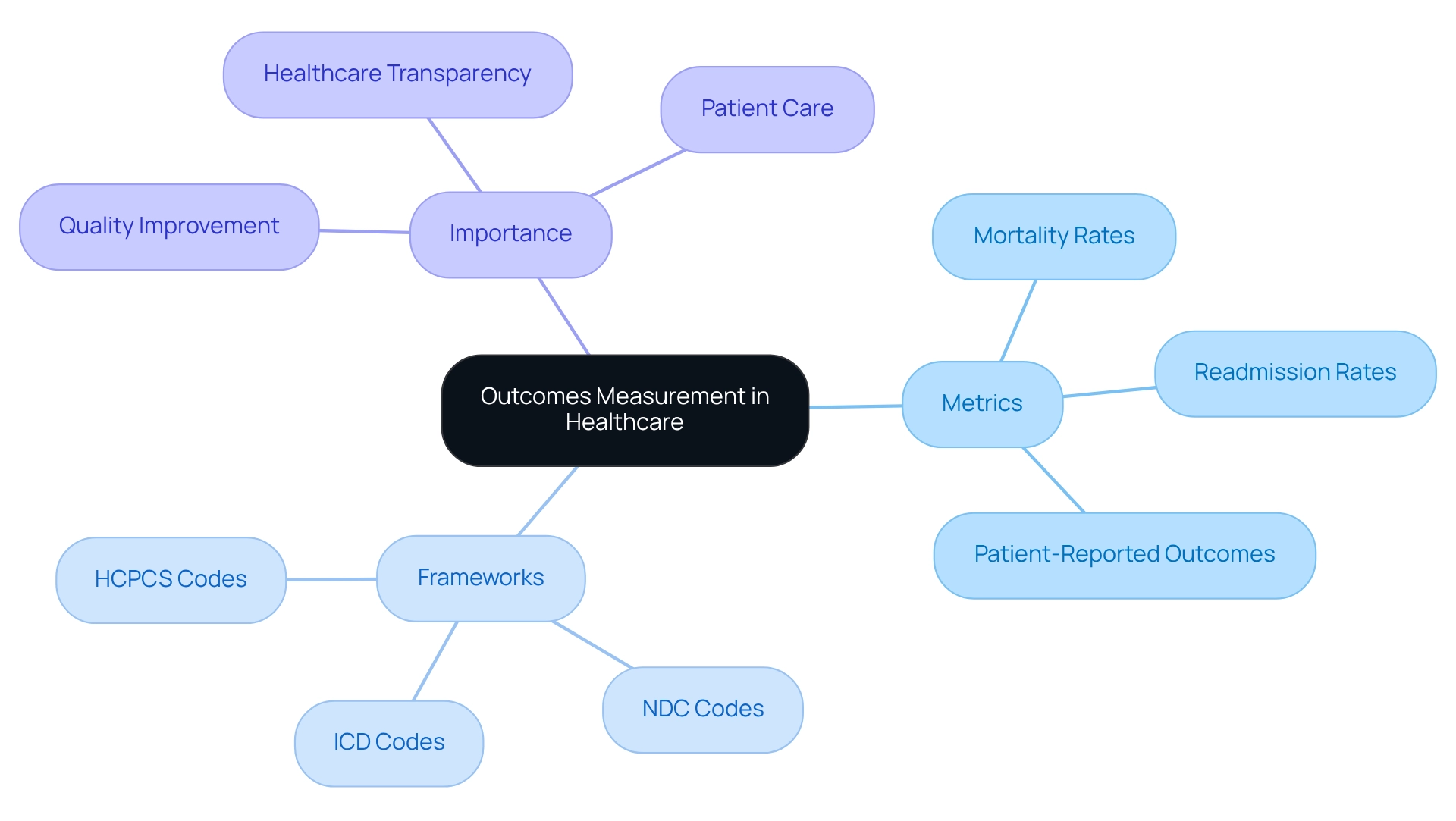
Implement Effective Strategies for Measuring Outcomes
To implement effective strategies for assessing results, healthcare organizations should consider the following approaches:
-
Establishing clear objectives is paramount. Define the most relevant outcomes for your client population and align them with organizational goals. This alignment ensures that measurement efforts are focused and meaningful, ultimately enhancing care for individuals.
-
Utilizing standardized tools is also essential. Employ validated measurement tools and frameworks to ensure consistency and reliability in data collection. For example, the Patient-Reported Results Measurement Information System (PROMIS) standardizes how results are evaluated, facilitating comparability across various contexts. As highlighted by CMS in a 2018 report, standardized measurement tools are crucial for achieving reliable assessments, such as hospital star ratings.
-
Integrating measurement into clinical practice is another vital step. Incorporate outcomes measurement as a routine part of clinical workflows. Integrating measurement tools into electronic health records (EHRs) enables real-time information collection and analysis, enhancing the process and increasing responsiveness to individual needs. CareSet’s integration of more than 100 external data sources illustrates the significance of comprehensive data in improving measurement effectiveness, especially in understanding treatment pathways and provider interventions across Medicare A, B, and D benefits.
-
Training staff is equally important. Provide comprehensive training for healthcare providers on the significance of outcomes measurement and how to effectively use the available tools. This training promotes a culture of quality enhancement and responsibility, enabling staff to prioritize outcomes for those they serve.
-
Monitoring and adapting practices are crucial for ongoing improvement. Regularly review gathered information to identify trends and areas for enhancement. Utilizing this information to adapt clinical practices ensures continuous enhancement of care provided to individuals. Notably, as of 2025, an estimated 91% of population health platforms are projected to incorporate artificial intelligence capabilities, which will further improve predictive accuracy and reduce false positives in risk identification, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of interventions. However, it is important to recognize that 67% of medical organizations struggle with quality issues that hinder their population health initiatives, highlighting the necessity of the proposed strategies.
By implementing these strategies, medical organizations can significantly enhance their measurement processes, ultimately leading to improved health for individuals and more effective service delivery, supported by insights from CareSet’s comprehensive Medicare information solutions.
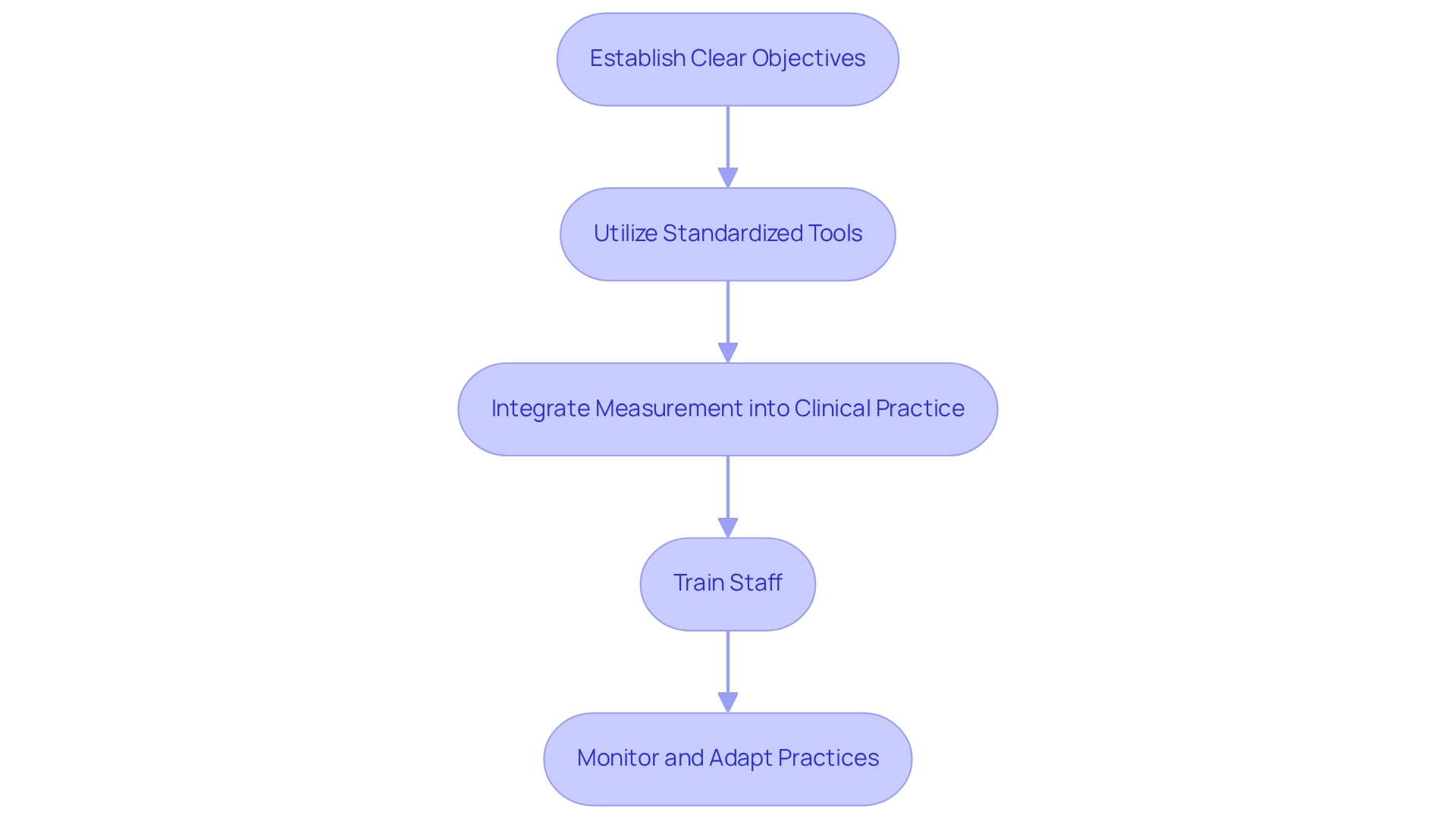
Ensure Data Transparency and Integration in Measurement Practices
Ensuring clarity and integration of information in results assessment involves several key practices:
-
Adopt Open Information Policies: Promoting the sharing of results information among stakeholders—including individuals receiving care, providers, and payers—cultivates trust and responsibility in service delivery. This collaborative approach is crucial for enhancing care and outcomes.
-
Employ Interoperable Systems: Establishing systems that enable smooth information exchange across different medical platforms is essential. Such integration provides a comprehensive perspective on outcomes, enabling informed decision-making and improving care coordination. Notably, 88% of hospitals participated in electronically transmitting and receiving patient health information in 2021, underlining the current involvement in information sharing among healthcare organizations.
-
Regular Audits and Quality Checks: Conducting routine evaluations of information collection methods ensures precision and thoroughness. This practice helps identify discrepancies or gaps that could compromise outcomes measurement, thereby maintaining the integrity of the data while involving individuals in information sharing by actively engaging them in the collection process and granting access to their health details, which empowers them to take control of their care. This engagement not only enhances the quality of the information gathered but also promotes patient-centered care.
-
Leverage Advanced Analytics: Utilizing sophisticated analytical tools to examine integrated information sets can uncover insights that enhance care and outcomes. By harnessing the power of information, medical organizations can gain deeper insights into treatment trends and individual requirements, ultimately resulting in improved care delivery. CareSet’s integration of over 100 external data sources exemplifies the capabilities necessary for comprehensive insights in this area, as demonstrated in our case study focusing on the 4th line of therapy for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) treatment options. This method not only boosts provider involvement but also enables pharmaceutical and biotech firms to create data-informed strategies that enhance patient outcomes measurement.
The ongoing assessment of interoperability will guide future initiatives and evaluate policy effects, emphasizing the significance of these practices in achieving successful outcomes measurement in health. Furthermore, insights from the Epic Systems Community Connect case study reveal potential areas for enhancement in vendor-client relationships, emphasizing the necessity for direct support in IT implementations within the medical field.
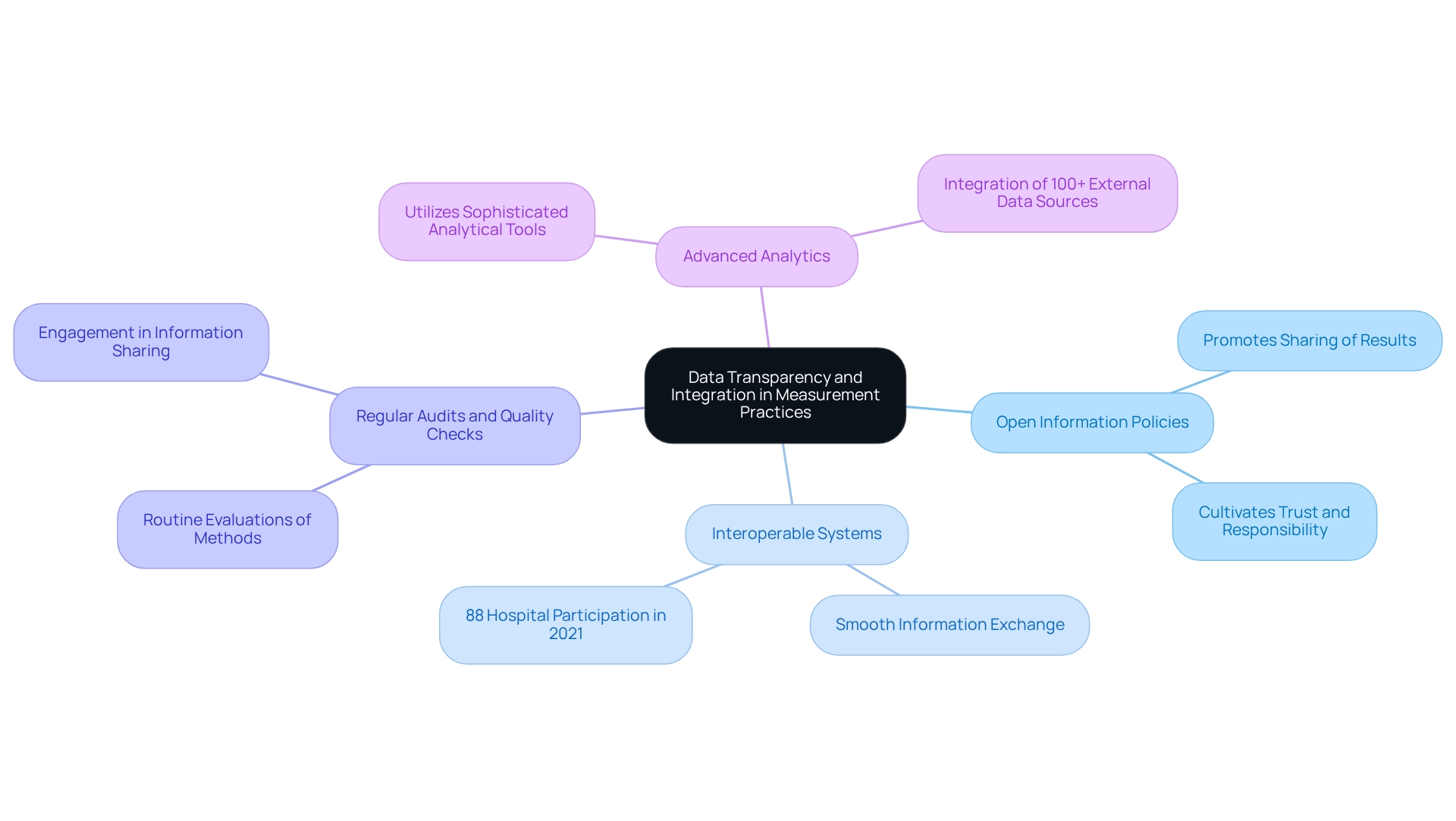
Foster Collaboration Among Stakeholders for Improved Outcomes
Encouraging cooperation among parties is essential for improving medical results. Effective strategies to enhance collaboration include:
- Engage Diverse Stakeholders: Involving a broad spectrum of stakeholders—healthcare providers, patients, payers, and policymakers—in the measurement process is vital. This diverse input enhances the relevance and thoroughness of results, particularly when leveraging CareSet’s extensive Medicare data insights from over 62 million beneficiaries and 6 million providers.
- Establish Collaborative Frameworks: Developing formal partnerships and frameworks that clearly define roles, responsibilities, and communication channels among stakeholders is crucial. Such clarity streamlines efforts and enhances accountability, ensuring that all parties are aligned towards common goals. Understanding the roles and perspectives of different stakeholders is essential for effective results measurement.
- Facilitate Regular Communication: Organizing consistent meetings and updates to discuss progress in results measurement, share insights, and address challenges fosters a collaborative culture. Open lines of communication promote continuous improvement, supported by data-driven insights from CareSet that empower stakeholders to make informed decisions.
- Share Best Practices: Encouraging stakeholders to exchange successful strategies and lessons learned from their results measurement initiatives can inspire innovative approaches. This knowledge sharing significantly enhances overall effectiveness, particularly when informed by CareSet’s analytics that highlight successful case studies.
- Utilize Technology for Cooperation: Applying collaborative technologies and platforms allows stakeholders to effortlessly share information, insights, and resources. This technological integration enhances coordination and improves the quality of results measurement, facilitating stakeholders’ effective use of CareSet’s information solutions.
To boost the chances of team success, selecting individuals who embody essential traits that promote collaboration is crucial. By employing these strategies, medical organizations can create a more integrated approach to outcomes measurement, which ultimately leads to improved patient well-being and more effective service delivery. CareSet exemplifies the importance of collaboration in healthcare analytics, reinforcing the need for effective stakeholder engagement through comprehensive data insights.
Conclusion
Outcomes measurement in healthcare is essential for enhancing patient care and ensuring the effectiveness of medical interventions. By systematically evaluating treatment effectiveness, patient satisfaction, and overall care quality, healthcare organizations can pinpoint areas for improvement and align their practices with established best practices. The implementation of standardized tools and clear objectives is crucial for reliable data collection. Integrating these measures into clinical workflows cultivates a culture of continuous quality improvement.
Moreover, ensuring data transparency and integration significantly enhances the outcomes measurement process. By adopting open data policies and utilizing interoperable systems, stakeholders can share insights that drive informed decision-making and improve care coordination. Engaging patients in this process not only empowers them but also enriches the quality of collected data, ultimately promoting patient-centered care.
Collaboration among diverse stakeholders is equally vital in the pursuit of improved healthcare outcomes. By fostering partnerships and maintaining open channels of communication, organizations can leverage the collective knowledge of providers, patients, payers, and policymakers. This collaborative approach enriches the outcomes measurement process and cultivates a community dedicated to enhancing patient health through data-driven strategies.
In conclusion, the effective measurement of healthcare outcomes is critical for optimizing patient health and improving the quality of care. By implementing strategic approaches, ensuring data transparency, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, healthcare organizations can drive significant improvements in their practices. This ultimately leads to better patient outcomes and a more effective healthcare delivery system.


