Overview
The 2-midnight rule, established by CMS, dictates that inpatient admissions are typically deemed appropriate for Medicare reimbursement when a physician expects a patient will require hospital care for at least two midnights. This regulation aims to reduce unnecessary admissions and enhance the quality of care provided. The significance of this rule cannot be overstated, as it establishes clear criteria for compliance and outlines the implications for reimbursement. Furthermore, it provides healthcare providers with strategies to optimize adherence, collectively underscoring the rule’s critical role in guiding hospital admissions and ensuring financial stability.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of healthcare, the 2-Midnight Rule emerges as a crucial regulation that influences patient admissions and Medicare reimbursements. Established by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in 2014, this rule is designed to streamline inpatient admissions by defining explicit criteria for when hospital stays are deemed necessary.
As healthcare providers navigate the complexities of this regulation, grasping its implications is essential—not only for optimizing reimbursement but also for ensuring that patients receive appropriate care.
This article explores the following:
- The definition and purpose of the 2-Midnight Rule
- The criteria for its application
- The financial implications of compliance
- Strategies for healthcare organizations to refine their practices in the face of evolving regulations
Define the 2-Midnight Rule and Its Purpose
Established by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in 2014, the 2-midnight rule determines that inpatient admissions are typically deemed appropriate for Medicare Part A reimbursement when a physician anticipates that an individual will require hospital care for at least two midnights. The 2-midnight rule was introduced as a regulation to reduce unnecessary hospital admissions and ensure that individuals receive care aligned with their medical needs. By providing clear criteria for inpatient status, the rule empowers healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding admissions and billing practices. This clarity not only improves patient care but also maximizes resource use within healthcare facilities, as demonstrated by the 2-midnight rule; for instance, Tenet Health reported an increase in admissions by 50 to 100 basis points due to the implementation of this guideline within Medicare Advantage.
Furthermore, the Office of Inspector General (OIG) has initiated audits to ensure compliance with the rule, particularly focusing on whether short stays have been incorrectly billed as inpatient rather than outpatient. This examination emphasizes the importance of adhering to the 2-midnight rule, as failing to comply could result in financial repercussions for hospitals. As Hammons noted, the benefits of the system’s built-out utilization review and physician adviser program play a crucial role in reducing the number of self-downgrades, further supporting the rule’s effectiveness.
Specific diseases defined by ICD that are commonly diagnosed and treated under this rule include conditions such as pneumonia, heart failure, and certain surgical procedures. Understanding these circumstances aids in delineating the categories of cases that may justify inpatient admission under the 2-midnight rule. Moreover, individuals transition from diagnosis to treatment utilizing Medicare benefits—Medicare Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, Part B covers outpatient services, and Part D provides prescription drug coverage. This navigation is essential for ensuring that individuals receive comprehensive care throughout their treatment journey, as the 2-midnight rule serves as an important framework for justifying hospital admissions and ultimately aims to enhance outcomes while maintaining the integrity of Medicare billing practices.
By examining provider interventions and patient journeys through the lens of ICD, NDC, and HCPCS codes, stakeholders can gain deeper insights into treatment pathways and improve adherence to Medicare regulations. The CMS oversight case study highlights the ongoing efforts to enforce compliance with the 2-midnight rule, reinforcing its significance in the healthcare landscape.
Outline Criteria for the 2-Midnight Rule Application
To effectively apply the 2-midnight rule, healthcare providers must adhere to several critical criteria.
- Physician Expectation: The admitting physician must reasonably anticipate that the individual will require hospital care extending beyond two midnights. This expectation is pivotal in justifying inpatient admissions.
- Medical Necessity: Inpatient care must be warranted based on the individual’s condition, as determined by clinical judgment. Documentation of medical necessity is essential to support the admission decision.
- Documentation: Comprehensive and accurate records of the individual’s condition, treatment plan, and anticipated length of stay are crucial. This documentation serves as evidence to substantiate the inpatient admission and is vital for reimbursement processes. Notably, hospitals must report Clinical Quality Measures (CQMs) for a three-month quarter to meet the requirements of the EHR Incentive Program, further emphasizing the importance of thorough documentation.
- Observation Status: If the physician anticipates the individual to require care for under two midnights, the individual should be categorized under observation status rather than inpatient. This distinction is important for adherence and reimbursement.
Incorporating these criteria is essential, especially considering that the estimated savings for FY 2014 from the HAC payment provision were $26 million, highlighting the financial implications of following the specified timeframe. Furthermore, the incorporation of discharge status code 69 into the GROUPER logic for MS-DRGs 280, 281, and 282 is essential for recognizing individuals diagnosed with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) who were discharged alive to designated disaster alternative care sites. This underscores the significance of precise documentation in ensuring suitable management of individuals. By diligently adhering to these standards, healthcare providers can enhance their compliance with the 2-midnight rule, thus optimizing reimbursement and improving care outcomes. Furthermore, hospitals that have effectively adopted these criteria have noted improved documentation practices, resulting in better alignment with regulatory expectations and enhanced care management. A case study assessing the effect of new policies on hospital admissions and care reveals that these policies aim to enhance care by ensuring that admissions are based on medical necessity while also decreasing unnecessary hospital stays.
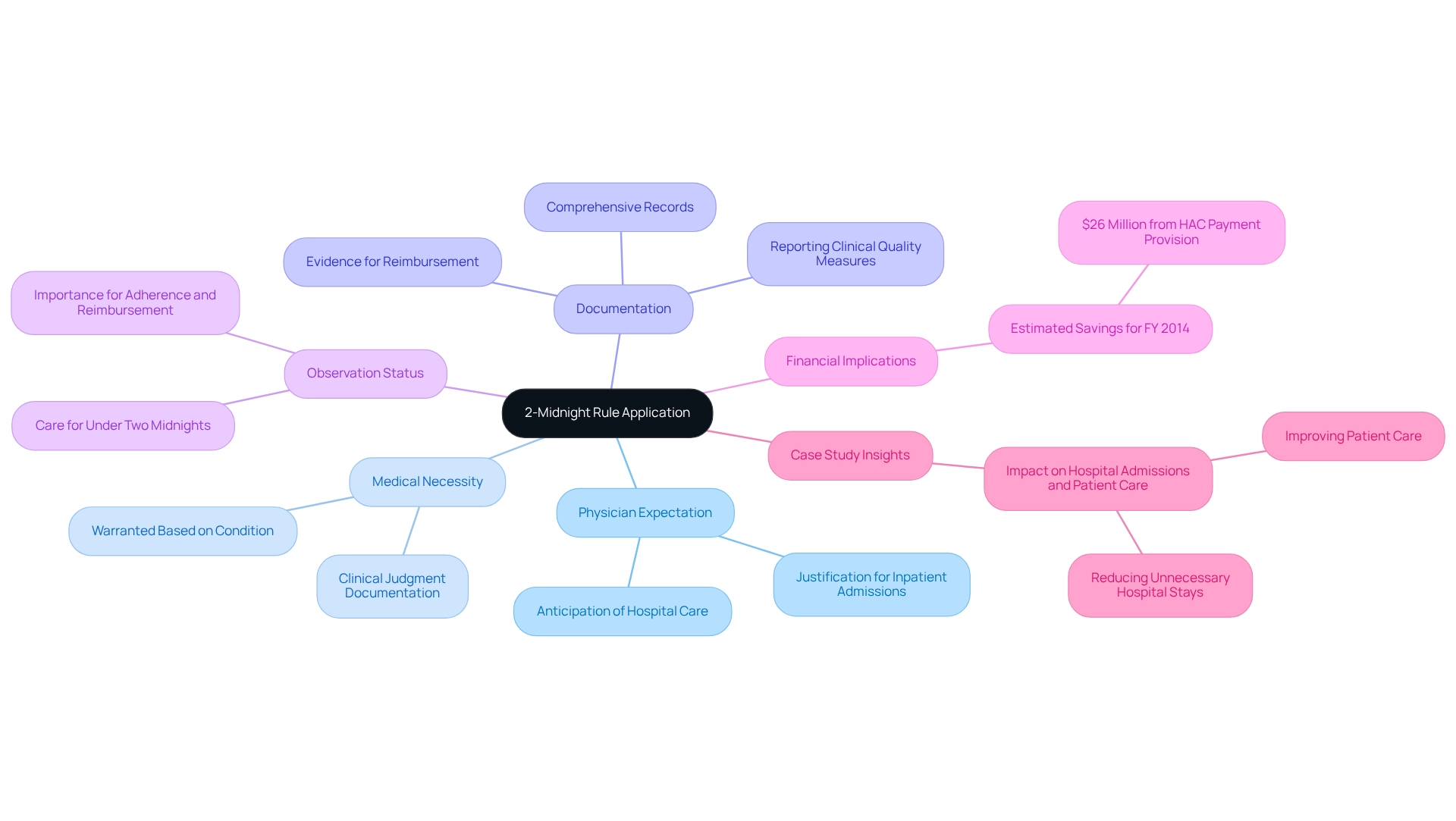
Analyze Reimbursement Implications of the 2-Midnight Rule
The Midnight Rule carries substantial implications for Medicare reimbursement. When a patient qualifies as an inpatient under this rule, hospitals can access higher reimbursement rates compared to outpatient services. However, misclassification can lead to significant financial repercussions, including claim denials, increased scrutiny, and financial penalties.
Claim denials are a primary concern; Medicare may reject claims for inpatient admissions that do not satisfy the 2-midnight rule, resulting in considerable revenue loss. Statistics indicate that hospitals face a notable percentage of claim denials linked to this rule, underscoring the need for precise documentation. CareSet integrates more than 100 external data sources for its analysis, highlighting the complexity and necessity of accurate data in this context, empowering healthcare stakeholders with insights from over 62 million beneficiaries and 6 million providers.
Increased scrutiny is another challenge. Hospitals may encounter heightened audits and reviews from Medicare contractors, which can deplete resources and jeopardize financial stability. This scrutiny is particularly pronounced in cases where patterns of misclassification are detected. Notably, the expected issue date for the audit report is in fiscal year 2025, adding urgency to the need for compliance.
Ongoing breaches of the 2-midnight rule can lead to financial penalties, resulting in fines and reduced reimbursement rates for subsequent claims, exacerbating the financial pressure on healthcare facilities.
For example, a recent case study titled ‘Hospital Strategies for Managing Two-Midnight Policies’ emphasized how hospitals are adjusting their approaches to handle payer policies associated with the 2-midnight rule. By reinforcing denial management practices and optimizing documentation, these institutions aim to mitigate observation denials in Medicare Advantage while maintaining stability in traditional Medicare. This targeted approach reflects the critical need for hospitals to navigate complex payer policies effectively.
As Saum Sutaria, MD, Chairman and CEO with Tenet, stated, “At some point, there has to be a solution to this because it’s just wasted administrative time and cost.” Grasping these implications is crucial for healthcare providers to skillfully navigate the complexities of Medicare reimbursement, ensuring adherence and protecting financial well-being.
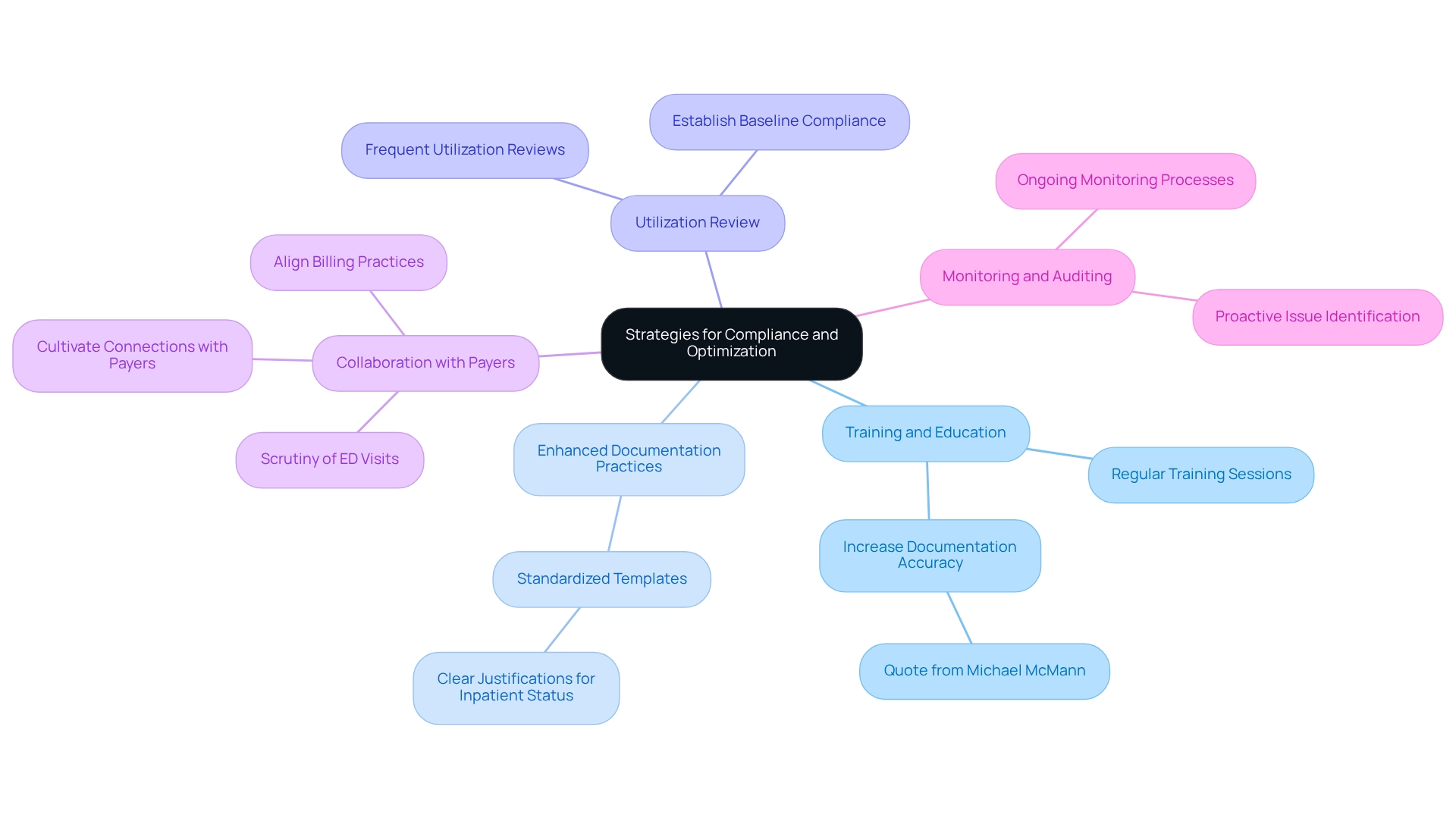
Implement Strategies for Compliance and Optimization
Healthcare providers can adopt several effective strategies to ensure compliance with the 2-midnight rule and optimize reimbursement.
- Training and Education: Implement regular training sessions for staff on the criteria and documentation requirements related to the 2-midnight rule. This ensures that all team members understand the significance of accurate documentation and compliance. As Michael McMann, Vice President of Client Management Physician Services, emphasizes, “You need to be informing providers to make sure they’re increasing the accuracy of their documentation to make sure that a Level IV visit is actually supported by what they’ve documented.”
- Enhanced Documentation Practices: Create standardized templates for documenting patient admissions. These templates should contain clear justifications for inpatient status, in accordance with the two-midnight guideline to enhance communication and assist with billing.
- Utilization Review: Conduct frequent utilization reviews to evaluate adherence to the 2-midnight rule. This process assists in recognizing areas requiring enhancement in admission practices, ensuring that documentation meets regulatory standards. The initial cycle sought to establish baseline adherence to documentation standards, emphasizing the significance of continuous efforts in this area.
- Collaboration with Payers: Cultivate robust connections with payers to elucidate their requirements concerning the two-midnight guideline. This collaboration can help align billing practices and reduce misunderstandings that may lead to claim denials. Notably, approximately half of the payers are now closely scrutinizing ED visits, making this collaboration even more critical.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Establish ongoing monitoring and auditing processes to proactively identify potential regulatory issues. This approach allows providers to address concerns before they escalate into claim denials or financial penalties.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare providers can significantly improve their adherence to the 2-midnight rule, reduce the risk of claim denials, and optimize their reimbursement processes. For instance, the introduction of standardized documentation practices, such as the SAMPLE history-taking process in emergency departments, aimed to standardize documentation practices in fast-paced environments. The deployment of the SAMPLE tool resulted in enhanced documentation methods, improving communication among healthcare professionals and ultimately contributing to greater safety and care for individuals. This case study demonstrates the positive effect of organized documentation on adherence and reimbursement results.
Additionally, Dr. Ronald Hirsch will conduct a session on the basics of Medicare for utilization review professionals, covering payment processes and patient costs, which could serve as a valuable resource for further education on compliance issues.
Conclusion
The 2-Midnight Rule is integral in shaping hospital admissions and Medicare reimbursement practices. By establishing explicit criteria for inpatient admissions, this rule aims to enhance patient care while enabling healthcare providers to adeptly navigate the complexities of Medicare billing. It is essential for healthcare professionals to grasp the definition, purpose, and application of this regulation, as it directly influences patient outcomes and the financial stability of healthcare organizations.
Compliance with the 2-Midnight Rule transcends mere regulatory obligation; it is a strategic imperative. By adhering to the specified criteria, prioritizing accurate documentation, and employing targeted improvement strategies, healthcare providers can optimize their reimbursement processes and reduce the risks linked to claim denials. The financial ramifications of misclassification underscore the necessity of comprehensive training and collaboration with payers, ensuring that all staff members are well-prepared to meet the rigorous demands of the rule.
Ultimately, adept navigation of the 2-Midnight Rule reflects the dedication of healthcare organizations to deliver appropriate care while safeguarding their financial health. As the healthcare landscape evolves, remaining informed and proactive in compliance efforts will be crucial for providing quality patient care and maintaining operational efficiency. Embracing these principles will not only enhance healthcare delivery but also cultivate a culture of accountability and excellence within the industry.


