Overview
This article presents essential insights for effectively managing Medicare claims. It emphasizes the importance of understanding Medicare Parts A and B, the submission processes, and the roles of Medigap and retiree plans. By detailing the claims submission and processing steps, it highlights the significance of clean submissions and the impact of evolving healthcare policies on reimbursement practices. Ultimately, the goal is to improve operational efficiency for healthcare providers.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Medicare claims presents a significant challenge for both healthcare providers and beneficiaries. The intricate interplay between Medicare Parts A and B necessitates a thorough understanding of claims management fundamentals, which is essential for securing timely reimbursements and minimizing denials. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the importance of Medigap policies and retiree health plans further complicates the financial dynamics of patient care.
This article explores the core components of Medicare claims, outlines the processing steps involved, and examines the impact of supplemental insurance options. By providing valuable insights, we aim to enhance your understanding and optimize your strategies in this critical area of healthcare.
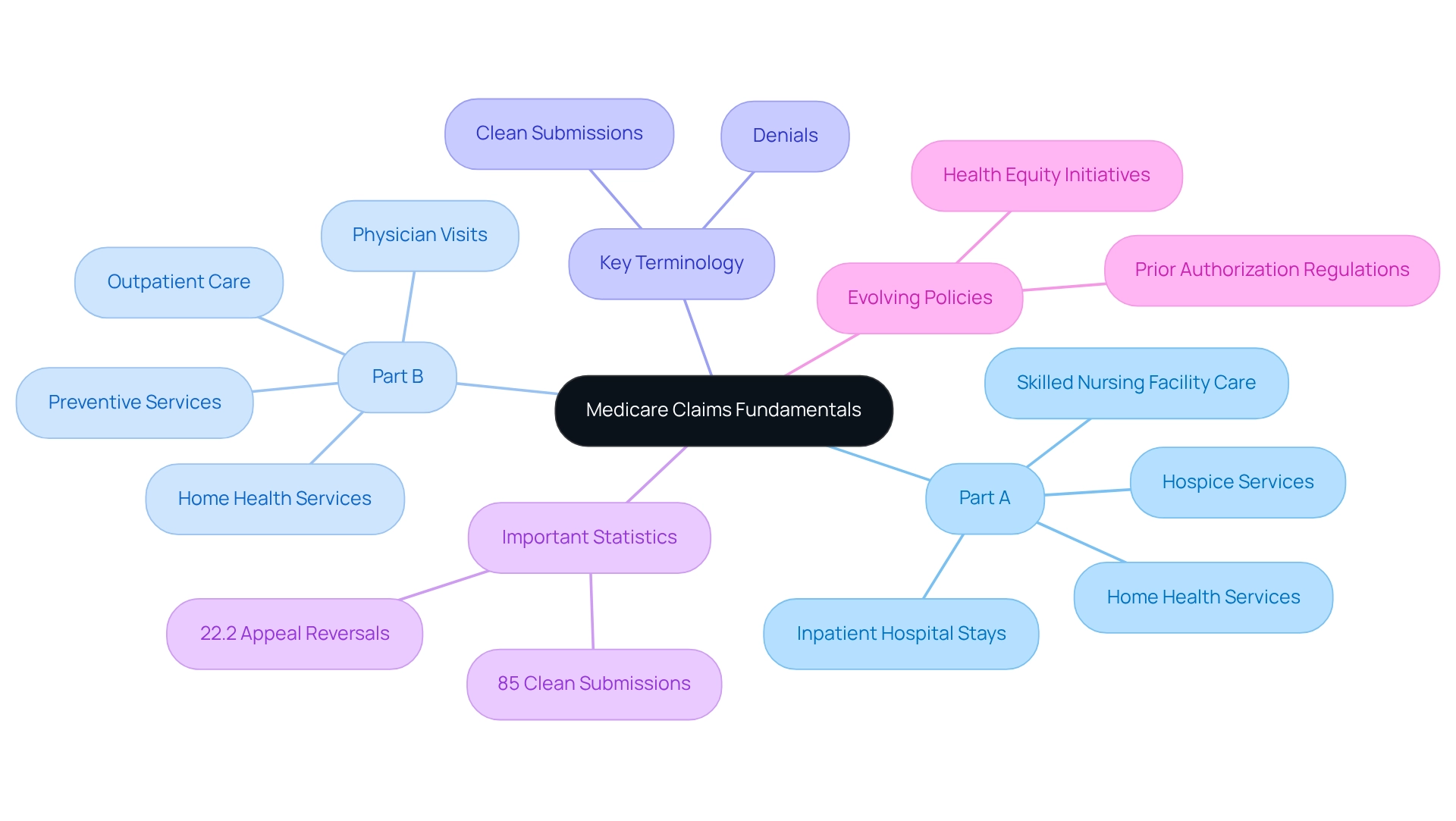
Clarify Medicare Claims Fundamentals
Medicare claims represent the appeals for payment that healthcare providers submit to Medicare for services rendered to beneficiaries. A comprehensive understanding of the two primary components of Medicare—Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance)—is crucial for the effective management of Medicare claims requests. Part A encompasses coverage for inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice services, and certain home health services, whereas Part B addresses outpatient care, physician visits, preventive services, and some home health services.
Grasping key terminology is imperative; ‘clean submissions’ denote Medicare claims that meet all processing requirements, while ‘denials’ refer to submissions that have been rejected. In 2025, the percentage of clean submissions made to Medicare claims serves as a vital metric, reflecting the effectiveness of management practices. Recent statistics reveal that this percentage stands at 85%, underscoring the importance of upholding high standards in submissions. Furthermore, understanding the timelines for filing Medicare claims—typically within 12 months of service—is essential for ensuring timely reimbursement. Common reasons for denials of Medicare claims include incorrect modifiers, failure to meet submission deadlines, and inaccuracies in patient information. Recent statistics indicate that the proportion of appeals for Medicare claims leading to reversed initial decisions was 22.2% for specific hospital outpatient services, highlighting the significance of meticulous submission practices.
Moreover, the evolving healthcare environment necessitates an understanding of the implications of prior authorization regulations. New rules require Advantage plans to assess the effects of these regulations on individuals with social risk factors. This initiative aims to address health equity challenges, ensuring that prior authorization procedures do not disproportionately impact at-risk groups, ultimately influencing management practices for reimbursements. As the healthcare landscape transforms, over three-quarters of practitioners report that payer policy modifications are occurring more frequently than in previous years. This underscores the importance for healthcare professionals to stay informed about the fundamentals of Medicare claims and insurance submissions, particularly regarding Parts A and B, to adeptly navigate the complexities of submission oversight.
CareSet’s monthly updates on health insurance programs further enhance provider engagement by delivering insights into drug utilization and patient treatment pathways. These updates empower healthcare strategies with data from over 62 million beneficiaries and 6 million providers, fostering informed decision-making in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Explore the Processing of Medicare Part A and B Claims
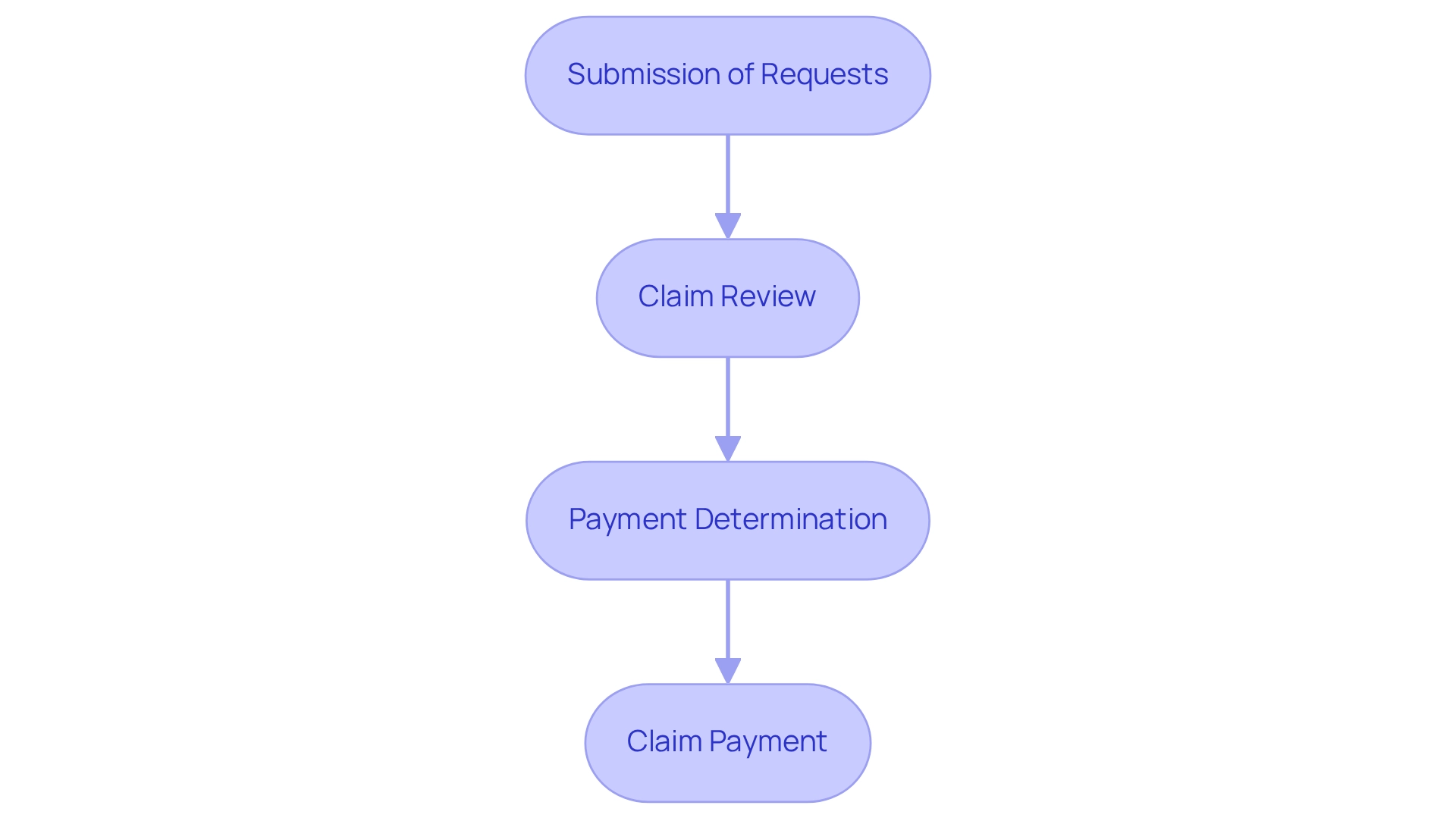
The processing of Medicare Part A and B claims encompasses several critical steps that ensure both accuracy and efficiency.
-
Submission of Requests: Providers have the option to submit requests electronically or via paper forms, specifically utilizing the CMS-1500 for Part B submissions. The Administrative Simplification Compliance Act (ASCA) promotes the use of standard transactions within the healthcare industry, thereby encouraging electronic submissions.
-
Claim Review: Administrative Contractors (MACs) meticulously examine submitted claims to confirm their precision and adherence to established criteria.
-
Payment Determination: Following the review, the program assesses the payment amount based on the specific services rendered and the beneficiary’s coverage details.
-
Claim Payment: The insurance program directly reimburses the service supplier, while beneficiaries receive a Summary Notice (MSN) that details the covered services and any amounts they may owe.
Understanding these steps is crucial for service professionals, as it enables them to anticipate potential challenges and enhance their billing practices. CareSet’s monthly Medicare updates provide innovative insights into drug utilization and treatment pathways, thereby enhancing provider engagement and empowering pharmaceutical strategies.
Current trends indicate a shift towards electronic submissions, which are typically processed faster than paper documents. For instance, electronic submissions are generally processed within 14 days, while paper submissions can take up to 30 days. As federal healthcare program per capita expenditures continue to rise, with forecasts suggesting greater growth rates between 2020 and 2030, effective processing of requests becomes increasingly essential for health organizations. Claire Ernst, the director of governmental affairs at the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), states, “The federal health insurance program is available for individuals 65 years or older and those younger than 65 with certain health conditions.”
By implementing successful strategies for Medicare claims submission and staying informed about the latest processing trends, providers can significantly improve their operational efficiency and ensure timely reimbursements. CareSet’s comprehensive approach not only addresses immediate data needs but also fosters long-term strategic growth for its partners in the healthcare industry, positioning them to optimize the lifecycle management of pharmaceutical products.
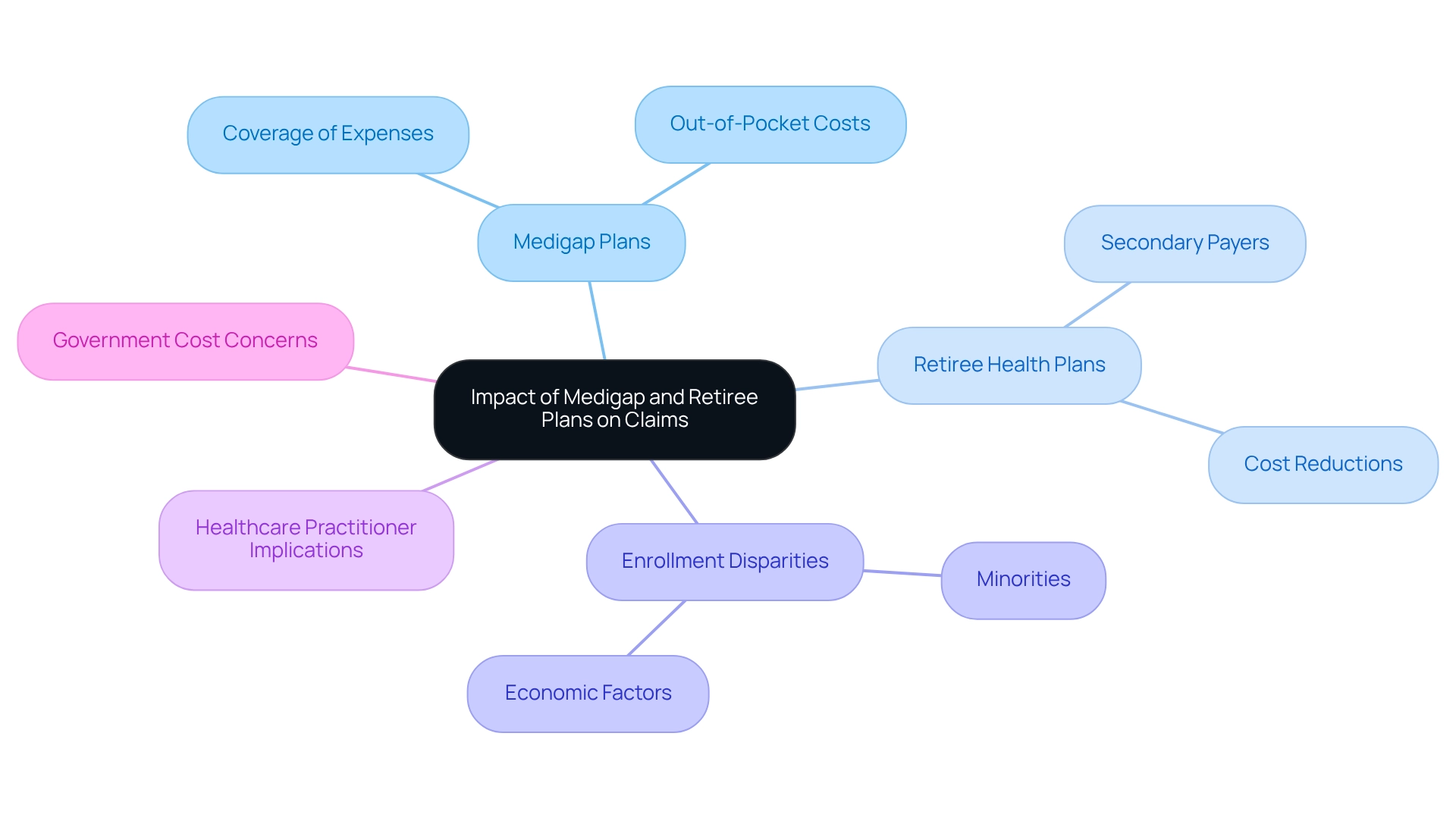
Examine the Impact of Medigap and Retiree Plans on Claims
Medigap plans, also known as Supplement Insurance, are essential in covering expenses that Original health insurance does not, such as copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. When beneficiaries have both health insurance and a Medigap plan, the insurance pays its share first, followed by the Medigap plan, which can significantly lower out-of-pocket costs. Furthermore, retiree health plans often act as secondary payers to government health programs, addressing additional expenses that may arise. Understanding how these plans interact is vital for healthcare practitioners to ensure accurate billing and assist patients with their financial responsibilities. In 2025, statistics show that around 14 million beneficiaries of the federal health program have Medigap coverage, highlighting its prevalence and importance in managing healthcare expenses.
Expert insights indicate that beneficiaries with retiree health plans tend to experience reduced out-of-pocket costs, as these plans can cover expenses that the federal health program does not fully address. However, the complexity of the Medigap market, with its diverse coverage options, presents challenges for consumers attempting to compare their choices effectively. As Nancy Ochieng points out, recipients in traditional Medicare without supplemental coverage are more likely to be under 65 and have lower incomes, underscoring the financial implications for these individuals.
A comprehensive analysis of Medicare claims illustrates the impact of Medigap arrangements on patient treatment pathways and provider behaviors. For example, research reveals that minority groups, particularly Black and Hispanic beneficiaries, have lower enrollment rates in Medigap plans compared to their White counterparts. This disparity is linked to socioeconomic factors and health disparities that hinder access to necessary coverage. The challenges faced by these groups in enrolling in Medigap plans underscore the need for targeted strategies to improve access. Additionally, concerns have been raised regarding the financial implications of low stop-loss thresholds in Medigap plans, which may lead to increased costs for the government. These limits can result in higher overall expenditures, as beneficiaries may incur substantial out-of-pocket costs that the government ultimately covers. As the Medicare landscape evolves, understanding how retiree health plans and Medigap policies interact with Medicare claims will be essential for healthcare providers seeking to optimize patient care and financial outcomes.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of Medicare claims is essential for both healthcare providers and beneficiaries, as it significantly impacts the financial dynamics of patient care. A thorough understanding of the fundamentals of Medicare’s Parts A and B is crucial, particularly in managing clean claims and minimizing denials. A solid grasp of key terminology and submission timelines enhances the efficiency of claims management, ultimately leading to timely reimbursements.
The processing of Medicare claims involves several critical steps, from submission to payment determination. Providers must stay informed about current trends and best practices. The shift towards electronic submissions not only accelerates processing times but also reinforces the necessity for accurate claim submissions to ensure operational efficiency. By leveraging resources like CareSet’s monthly updates, providers can optimize their strategies and navigate the evolving landscape of Medicare effectively.
Furthermore, the impact of Medigap and retiree health plans cannot be overlooked. These supplemental insurance options play a vital role in alleviating the financial burden on beneficiaries, yet the complexities of these policies present challenges in understanding coverage. The disparities in enrollment rates among different demographic groups highlight the need for targeted strategies to improve access to Medigap policies. As the healthcare environment continues to evolve, equipping providers with the knowledge and tools to navigate Medicare claims and supplemental insurance options will be crucial in optimizing patient care and financial outcomes.


