Overview
This article delves into the critical factors and steps essential for the precise calculation of carboplatin dosage. It underscores the importance of individual patient characteristics, particularly renal function, in determining safe and effective dosing. By detailing the application of the Calvert formula for dose calculation, the article highlights the significance of estimating glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Furthermore, it emphasizes the necessity of customizing treatments based on patient demographics and responses to optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing toxicity.
Introduction
In the realm of oncology, the precision of chemotherapy dosing can mean the difference between life and death. Carboplatin, a cornerstone in cancer treatment—particularly for ovarian and lung cancers—exemplifies this critical balance.
Its dosing intricacies, influenced by factors such as renal function and individual patient characteristics, are paramount to maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing toxicity. Recent studies illuminate the nuances of carboplatin clearance and patient response variability, underscoring the necessity for healthcare providers to customize treatment plans that cater to each patient’s unique pharmacokinetics.
This article delves into the essential components of carboplatin dosing, exploring its calculation, the significance of tailored approaches, and the common challenges faced in clinical practice. It emphasizes the ongoing need for vigilance and informed decision-making in cancer care.
Understand Carboplatin and Its Dosing Importance
Carboplatin, a platinum-based chemotherapy agent, plays a pivotal role in managing various cancers, particularly ovarian and lung cancer. The precision of its administration is paramount, especially in carboplatin dose calculation, significantly influencing both the drug’s therapeutic efficacy and patient safety. Accurate administration through carboplatin dose calculation not only mitigates the risk of toxicity but also maximizes the potential benefits of therapy. Typically, the drug’s administration is guided by the area under the curve (AUC), which evaluates the substance’s concentration in the bloodstream over time. This pharmacokinetic insight is essential for healthcare professionals aiming to tailor care strategies that enhance individual outcomes while minimizing adverse effects, especially regarding carboplatin dose calculation.
A study published in the British Journal of Cancer in October 2023 highlighted the average clearance values of carboplatin across treatment cycles, indicating that variations in clearance can significantly impact dosing strategies. Understanding these values is critical for refining treatment plans, particularly in the context of carboplatin dose calculation tailored to individual needs. Additionally, the median duration to PSA progression on this chemotherapy was reported as 67 days, with a range extending from 15 to 418 days. This variability illustrates the necessity for customized administration strategies, as individual responses can differ markedly based on personal pharmacokinetics.
Real-world examples further illustrate the impact of carboplatin administration on clinical outcomes. Evidence-based administration guidelines for pediatric cancer patients have been developed to address the lack of pharmacological data for this vulnerable population. These guidelines are designed to enhance administration accuracy and improve clinical results, especially in scenarios where carboplatin dose calculation for therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is not feasible. The implications of these guidelines extend beyond infants, emphasizing the need for personalized carboplatin dose calculation strategies across diverse demographics to ensure optimal therapeutic effectiveness, with expert opinions reinforcing the critical nature of precise medication administration.
Oncologists emphasize that the accurate carboplatin dose calculation is vital for ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy, as incorrect dosages can lead to severe adverse effects or suboptimal therapeutic responses. David W. Pook noted that the limited sample size in ongoing research constrains the ability to achieve statistical significance and identify factors that could predict positive or negative reactions to treatment. This highlights the persistent challenges in developing effective administration protocols. Continued research and case studies underscore the significant influence that carboplatin administration has on cancer care outcomes, stressing the necessity for healthcare professionals to remain vigilant and well-informed about administration protocols, particularly the importance of carboplatin dose calculation in enhancing patient care.
Identify Key Factors Affecting Carboplatin Dosing
Several critical factors influence the carboplatin dose calculation, each playing a significant role in optimizing treatment outcomes.
Renal function is crucial for carboplatin dose calculation, particularly the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) which determines carboplatin clearance. Impaired renal function can lead to increased drug accumulation, heightening the risk of toxicity. Therefore, precise evaluations of kidney function are crucial for carboplatin dose calculation, as they directly influence medication administration, agent selection, and eligibility for clinical trials involving innovative substances. As Jan H. Beumer observes, “Estimation of kidney function in patients with cancer directly influences medication administration, agent selection, and eligibility for clinical trials of novel agents.”
While carboplatin dose calculation has traditionally been based on Body Surface Area (BSA), this method may overlook individual variations in drug metabolism. Adjustments based on patient-specific factors can enhance the carboplatin dose calculation accuracy, ensuring that treatment is tailored to the individual.
The carboplatin dose calculation is customized based on the target area under the curve (AUC), specific to the cancer type and the individual’s overall health. Typical AUC values for carboplatin dose calculation range from 4 to 6 mg/mL/min, and achieving these targets is crucial for effective treatment. Utilizing the AUC method has been associated with decreased hematological toxicity while maintaining similar antitumor activity in terms of response rate and survival.
Patient Demographics: Factors such as age, weight, and gender significantly influence drug metabolism and clearance. The CKD-EPI study population comprised 63% white, 32% black, and 1% Asian patients, emphasizing the significance of personalized treatment approaches based on demographic factors.
Current Guidelines: Oncologists stress the importance of incorporating kidney function evaluations into chemotherapy administration protocols. The case study titled ‘Importance of Accurate Kidney Function Estimates in Cancer Patients’ highlights the need for precise kidney function estimates to enhance clinical outcomes, underscoring the dangers of both overestimation and underestimation of kidney function in medication administration and clinical trial eligibility.
By thoroughly understanding these factors, healthcare professionals can make informed choices regarding carboplatin dose calculation, ensuring that each individual receives the most effective and safe treatment tailored to their unique clinical profile.
Calculate Carboplatin Dose Using the Appropriate Formula
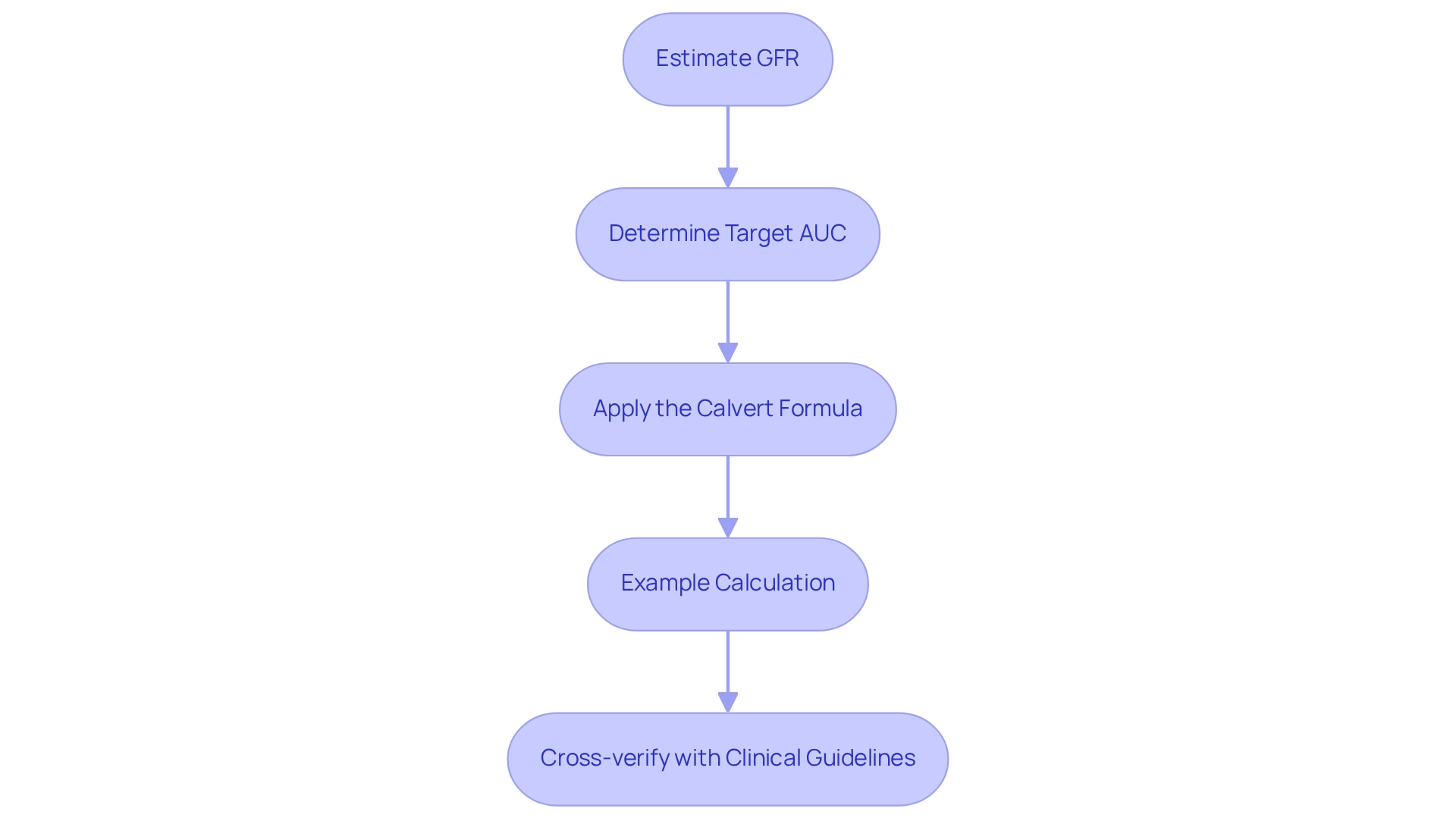
To accurately perform the carboplatin dose calculation, it is essential to follow these critical steps utilizing the Calvert formula:
- Estimate GFR: Begin by estimating the patient’s Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) using the Cockcroft-Gault equation or another validated method. This value is crucial for assessing renal function, which directly influences carboplatin dose calculation.
- Determine Target AUC: Establish the target Area Under the Curve (AUC) based on the specific treatment protocol. Typical target AUC values range from 4 to 6 mg/mL/min, depending on the clinical scenario.
- Apply the Calvert Formula: Implement the formula:
Carboplatin Dose (mg) = Target AUC (mg/mL/min) x (GFR + 25)
In this equation, GFR is expressed in mL/min, and the addition of 25 accounts for non-renal clearance, ensuring a more accurate dose calculation. - Example Calculation: For instance, if a patient has a GFR of 60 mL/min and the target AUC is set at 5 mg/mL/min:
Carboplatin Dose = 5 x (60 + 25) = 5 x 85 = 425 mg
This calculated dose should be cross-verified with clinical guidelines and adjusted as necessary based on the patient’s response and any observed side effects.
Recent studies emphasize the complexities of carboplatin administration, particularly its dependence on renal function and the narrow therapeutic index associated with this cytotoxic agent. The original Calvert formula remains a preferred method for administering medication, especially in carboplatin dose calculation, validated by research analyzing various eGFR equations and their implications for treatment cycles. Precise evaluation of GFR is crucial for carboplatin dose calculation, as even minor changes can result in substantial differences in dosing—about 8 mg for AUC-2 individuals compared to 21 mg for those at AUC-5/6. This highlights the importance of standardized kidney function evaluations in oncology to guarantee safe and effective chemotherapy administration, particularly in the context of carboplatin dose calculation. As noted by M. Rosner, accurate GFR estimation is crucial in this context, highlighting the importance of carboplatin dose calculation and precise methodologies. Furthermore, the case study titled ‘Guidelines for Kidney Function Assessment in Chemotherapy’ highlights the absence of agreement on preferred methodologies, thereby promoting standardized approaches such as carboplatin dose calculation to improve safety and efficacy of care. Moreover, recent discoveries confirm the uniform administration of the drug in adult individuals with normal kidney function, endorsing the ongoing application of carboplatin dose calculation through the Calvert formula.
Troubleshoot Common Carboplatin Dosing Issues
When performing carboplatin dose calculation and administration, healthcare providers may encounter several common issues that can significantly influence results.
-
Imprecise GFR Estimates: Employing suitable techniques for calculating glomerular filtration rate (GFR) tailored to the specific group of individuals is essential. Inaccurate estimates can lead to underdosing, resulting in treatment failure, or overdosing, which increases the risk of toxicity. Recent research indicates that chemotherapy medication mistakes, particularly those related to dosage, are prevalent and can greatly impact patient safety. CareSet’s analysis of Medicare data can help identify trends in dosing errors, enabling providers to refine their practices.
-
Variability in Individual Response: Close monitoring of individuals for signs of toxicity or inadequate therapeutic response is crucial. Individual tolerance and side effects should guide dose adjustments, given the wide variability in responses to carboplatin. Utilizing Medicare data enhances understanding of individual demographics and reactions, aiding in the development of more customized care strategies.
-
Renal Function Changes: Renal function may fluctuate, especially in individuals with comorbidities. Regular reassessment of GFR is necessary to ensure that medication administration remains appropriate and effective throughout the treatment course. CareSet’s data leadership provides insights into how renal function affects medication administration across various patient groups.
-
Protocol Deviations: Adherence to established dosing protocols is vital. Deviations from these protocols can result in inconsistent treatment outcomes, undermining the efficacy of the carboplatin dose calculation in therapy. A case study on the implementation of a computerized physician order entry (CPOE) system for chemotherapy highlights how technology can assist in reducing medication errors and enhancing safety. By utilizing Medicare data, healthcare providers can better understand the implications of protocol adherence on healthcare outcomes.
-
Client Education: Informing clients about potential side effects and the importance of promptly reporting any adverse reactions is essential. This proactive approach can help reduce complications and improve the overall safety of care. Engaging patients through informed discussions, supported by data insights from CareSet, empowers them to take an active role in their care journey.
By recognizing these issues and implementing effective strategies for carboplatin dose calculation, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the safety and efficacy of carboplatin therapy, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. CareSet’s expertise in Medicare data analysis can further support healthcare professionals in understanding treatment patterns and improving dosing accuracy.
Conclusion
The intricacies of carboplatin dosing underscore its pivotal role in cancer treatment, particularly for ovarian and lung cancers. Critical factors influencing dosing include renal function, body surface area, and patient demographics, emphasizing the necessity of personalized treatment plans. Such tailored approaches are essential for optimizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing toxicity. The Calvert formula serves as a cornerstone for accurate dose calculations, empowering healthcare providers to adapt their strategies based on individual patient needs and responses.
Furthermore, the challenges surrounding carboplatin dosing—ranging from inaccurate GFR estimates to variations in patient responses—illustrate the importance of vigilance and adherence to established protocols. Addressing these issues through regular monitoring and patient education significantly enhances treatment outcomes, ensuring patients receive the most effective care.
Ultimately, ongoing research and evolving guidelines in carboplatin dosing reflect a commitment to improving cancer care. By prioritizing individualized treatment strategies and remaining informed about the latest developments, healthcare professionals can adeptly navigate the complexities of chemotherapy dosing. This proactive approach leads to better patient safety and enhanced therapeutic results. The journey toward precision in oncology is ongoing, necessitating that practitioners remain engaged in their approach to carboplatin therapy.

