Overview
The essential eligibility checks for Medicare coverage encompass:
- Age requirements
- Citizenship status
- Social Security qualifications
- Documentation needs
These elements are crucial for ensuring access to health insurance for seniors and individuals under 65 who are eligible. Understanding these checks is vital for avoiding gaps in coverage and financial penalties. Moreover, it plays a significant role in navigating the complexities of enrollment and maintaining access to necessary healthcare services. By grasping these essential criteria, individuals can better prepare themselves for the Medicare process and ensure they receive the benefits they deserve.
Introduction
As individuals approach the significant milestone of turning 65, the complexities of Medicare eligibility and enrollment come into sharp focus. This crucial age not only marks a transition into retirement but also serves as a gateway to essential healthcare coverage.
Understanding the various pathways to qualify for Medicare—whether through age, disability status, or prior health coverage—is vital. Additionally, factors such as income verification and documentation requirements add layers of complexity that can significantly impact beneficiaries’ access to necessary services.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, staying informed about policy changes and available assistance programs becomes increasingly important for individuals navigating this critical phase of their lives.
This article delves into the key aspects of Medicare eligibility, providing insights and guidance to empower individuals in making informed decisions about their healthcare options.
Age Requirement: Understanding the 65-Year Threshold
To be eligible for health insurance for seniors, individuals must pass eligibility checks at the age of 65, a pivotal milestone that coincides with the typical retirement age in the United States. This age threshold is not merely a formality; it serves as a critical indicator for registration. Significantly, approximately 59% of individuals signed up for health insurance in Rhode Island are participating in a health plan, underscoring the growing trend of recipients opting for these options as they age.
Those already receiving Social Security benefits will be automatically enrolled in Part A and Part B of the program upon reaching 65, ensuring a seamless transition into coverage. Conversely, individuals not receiving Social Security must proactively apply during the Initial Enrollment Period, which spans three months before and three months after their 65th birthday. This proactive approach is essential to prevent any gaps in coverage during this transitional phase.
The significance of turning 65 transcends mere eligibility; it marks a crucial juncture in healthcare planning. A statistical analysis from the Centers for Health Services and Medicaid revealed that understanding the age dynamics of enrollment can yield valuable insights into the types of coverage held by beneficiaries. This analysis is particularly pertinent for healthcare stakeholders, as it illuminates the pathways patients traverse from diagnosis to treatment, including interventions defined by NDC and HCPCS codes. Moreover, as the population ages, the proportion of individuals automatically registered in the healthcare program at age 65 continues to rise, highlighting the vital importance of this milestone in shaping healthcare access and planning strategies.
Specific diseases defined by ICD that providers diagnose and treat significantly influence this context, as they directly affect the interventions and treatment pathways available to patients. Insights from CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data solutions can empower strategies by analyzing treatment approvals and provider interventions, ultimately enhancing patient care and fostering business success.
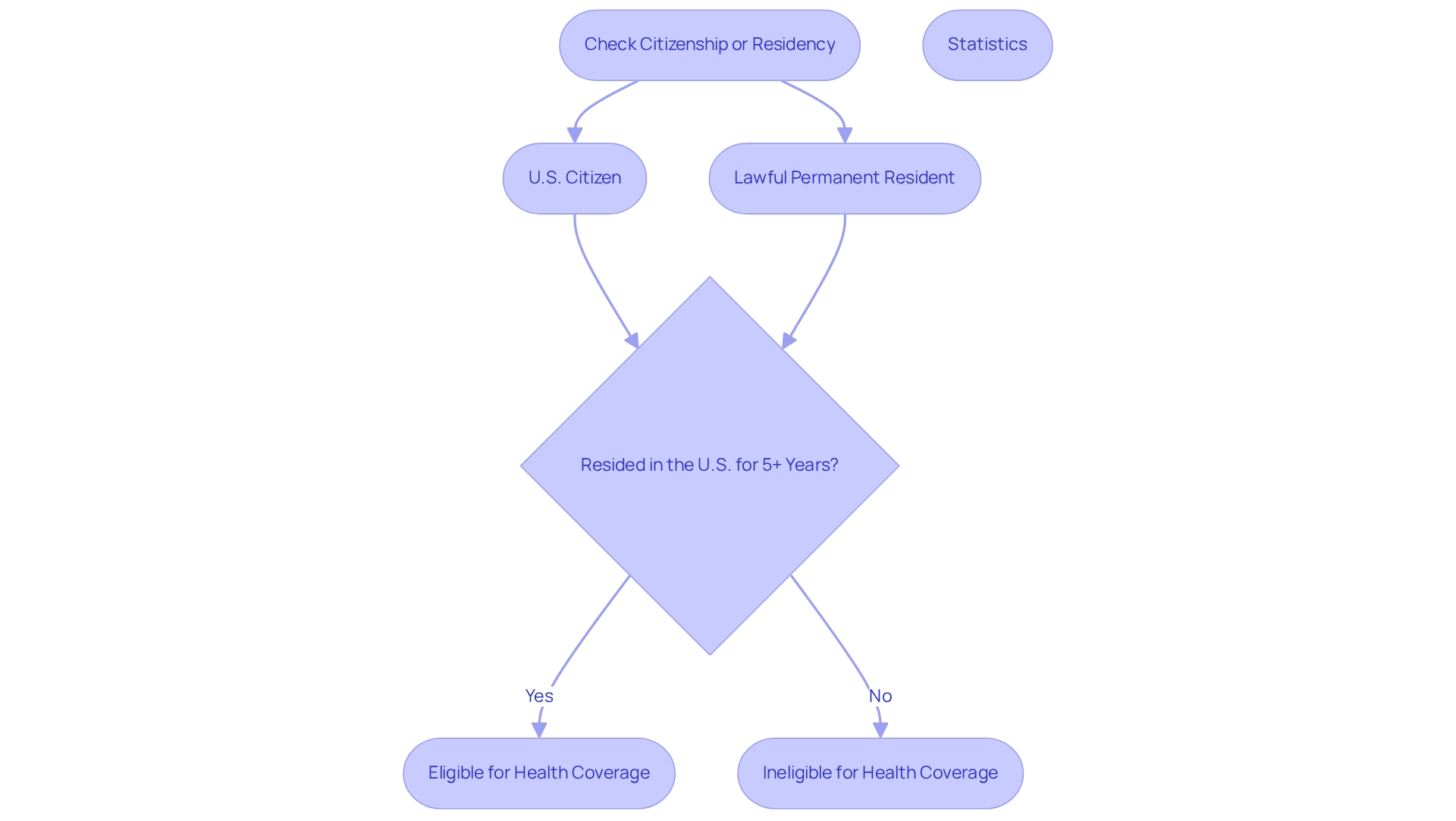
Citizenship and Residency: Confirming Your Status
To qualify for the government health program, individuals must pass eligibility checks, which require them to be U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents who have resided in the United States for a minimum of five consecutive years. This residency requirement is vital, as it ensures that healthcare benefits are accessible to those who have established a significant connection with the country. Non-citizens must provide documentation that verifies their legal status and the duration of their residency when applying for health coverage. Notably, statistics reveal that a significant proportion of health plan recipients are U.S. citizens, with approximately 59% of those in Rhode Island enrolled in Advantage plans, reflecting broader participation trends. Humana holds an 18% share of the Advantage market, and together with UnitedHealthcare, they dominate this sector, accounting for nearly half of all Advantage beneficiaries. This underscores the importance of understanding eligibility checks and coverage options.
Experts emphasize that residency criteria are essential eligibility checks that influence enrollment decisions and the benefits available to individuals. Those who fail to meet these residency criteria may encounter obstacles in obtaining critical healthcare services. As discussions within the healthcare community progress into 2025, the impact of residency on health insurance benefits remains a focal point, highlighting the necessity for clear eligibility guidelines. Additionally, individuals seeking assistance can utilize a complimentary tool to connect with a health insurance advisor, who can help determine the type and level of coverage needed, thereby easing the navigation of these intricate requirements.
CareSet’s dedication to data quality guarantees that clients receive timely and relevant insights from an extensive dataset comprising over 62 million beneficiaries and 6 million providers. This data empowers healthcare stakeholders to understand treatment pathways, provider interventions, and treatment authorization within the insurance framework, ultimately enhancing patient care and facilitating strategic development for partners in the healthcare sector.
Social Security Qualification: Meeting the Necessary Criteria
Eligibility for health insurance is intricately linked to Social Security benefits. Individuals qualify if they are entitled to receive Social Security retirement benefits or Railroad Retirement benefits. Typically, those who have worked and contributed to Social Security for a minimum of 10 years (40 quarters) are eligible. Moreover, individuals under 65 who have been receiving Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) for 24 months automatically qualify for health coverage. This relationship underscores the importance of understanding one’s Social Security status when preparing for eligibility checks during health insurance enrollment.
Statistics reveal that a significant percentage of individuals qualify for health coverage through Social Security, underscoring the program’s critical role in providing essential healthcare support. As of December 2023, approximately 7.4 million people were receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI), highlighting the importance of Social Security benefits in assisting vulnerable populations and enhancing access to healthcare. The SSI program has seen a steady increase in recipients since its inception, emphasizing its vital function in delivering financial support.
Understanding the intricacies of treatment pathways is essential for effectively navigating the healthcare landscape. By examining provider interventions and patient journeys through ICD, NDC, and HCPCS frameworks, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into how patients transition from diagnosis to treatment and ultimately to recovery. This knowledge is crucial for Pharmaceutical Market Access Managers as they strategize around Part D Plan approvals, which significantly influence the treatments covered and the associated costs.
Neglecting to register for the program on time can lead to substantial out-of-pocket medical expenses and late registration penalties, making it imperative for individuals to be proactive about their registration. Financial advisors stress that understanding Social Security benefits is vital for effective healthcare planning, particularly as the landscape evolves in 2025. Real-world examples illustrate how Social Security qualifications directly impact eligibility checks for healthcare, reinforcing the necessity for individuals to remain informed about their benefits and enrollment timelines. Additionally, the projected deficit of Social Security revenue in 2097 is anticipated to reach -4.61% of taxable payroll, with an expected shortfall over the next 75 years at 3.50% of taxable payroll, underscoring the significance of these benefits in relation to healthcare eligibility.
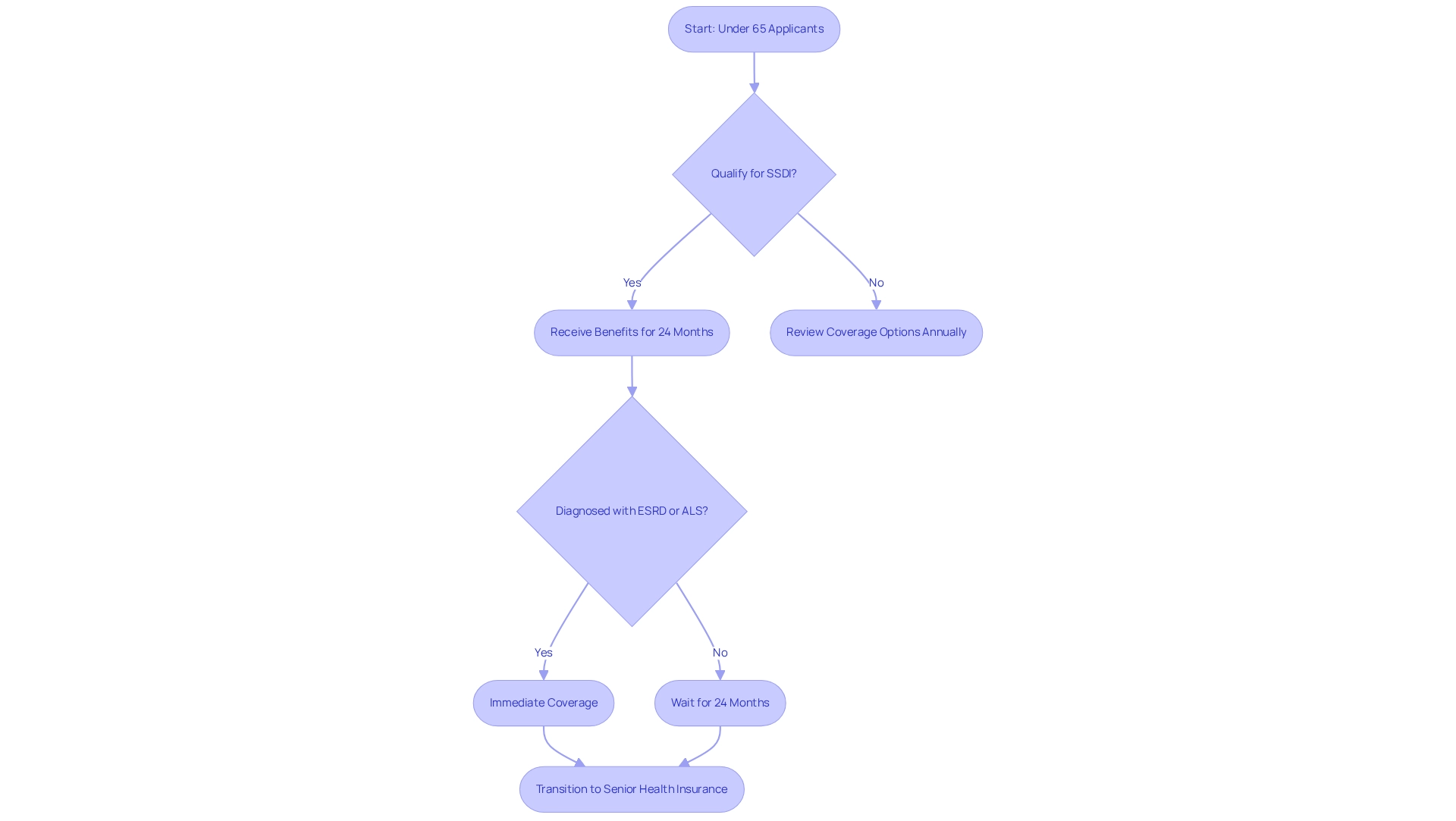
Disability Status: Eligibility for Under-65 Applicants
Individuals under 65 can qualify for health coverage primarily through Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) after receiving benefits for at least 24 months. This pathway is crucial for those facing significant health challenges, as it allows timely access to essential medical care. Notably, individuals diagnosed with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) qualify for government health insurance without the 24-month waiting period, ensuring immediate support for their healthcare needs.
As of 2025, approximately 19% of recipients of the federal health insurance program are under 65, largely due to SSDI eligibility. This demographic shift underscores the importance of understanding the nuances of healthcare registration for younger beneficiaries. For instance, SSDI beneficiaries typically transition to health insurance for seniors automatically after the waiting period; however, they must remain vigilant about their coverage options during the yearly open enrollment period to secure the best plan for their needs. It is imperative for individuals to review their options annually to ensure optimal coverage.
Understanding the treatment pathways defined by ICD, NDC, and HCPCS codes is vital for effectively navigating the healthcare system. These frameworks clarify how providers diagnose and treat conditions, guiding patients from diagnosis through various lines of therapy. Treatments approved under Part D Plans can vary, and comprehending the associated costs is essential for beneficiaries. Case analyses illustrate the impact of healthcare access on individuals under 65. For example, a recent analysis indicated that prompt enrollment in the program significantly improved health outcomes for SSDI recipients, enabling them to manage chronic conditions more effectively. Disability advocates emphasize the importance of this access, asserting that it can be transformative for those reliant on these benefits for their healthcare. As one supporter stated, “Access to healthcare is not merely an advantage; it’s a crucial support for many people confronting health issues.”
Navigating from diagnosis to treatment across insurance plans A, B, and D benefits necessitates an understanding of the specific coverage options available for various treatments. In summary, qualifying for health coverage with SSDI involves important eligibility checks for many individuals under 65, and grasping the eligibility criteria and enrollment procedures is essential for maximizing healthcare access and outcomes. Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize the Part D coverage gap, commonly referred to as the ‘donut hole,’ which can significantly impact younger recipients’ prescription drug coverage.
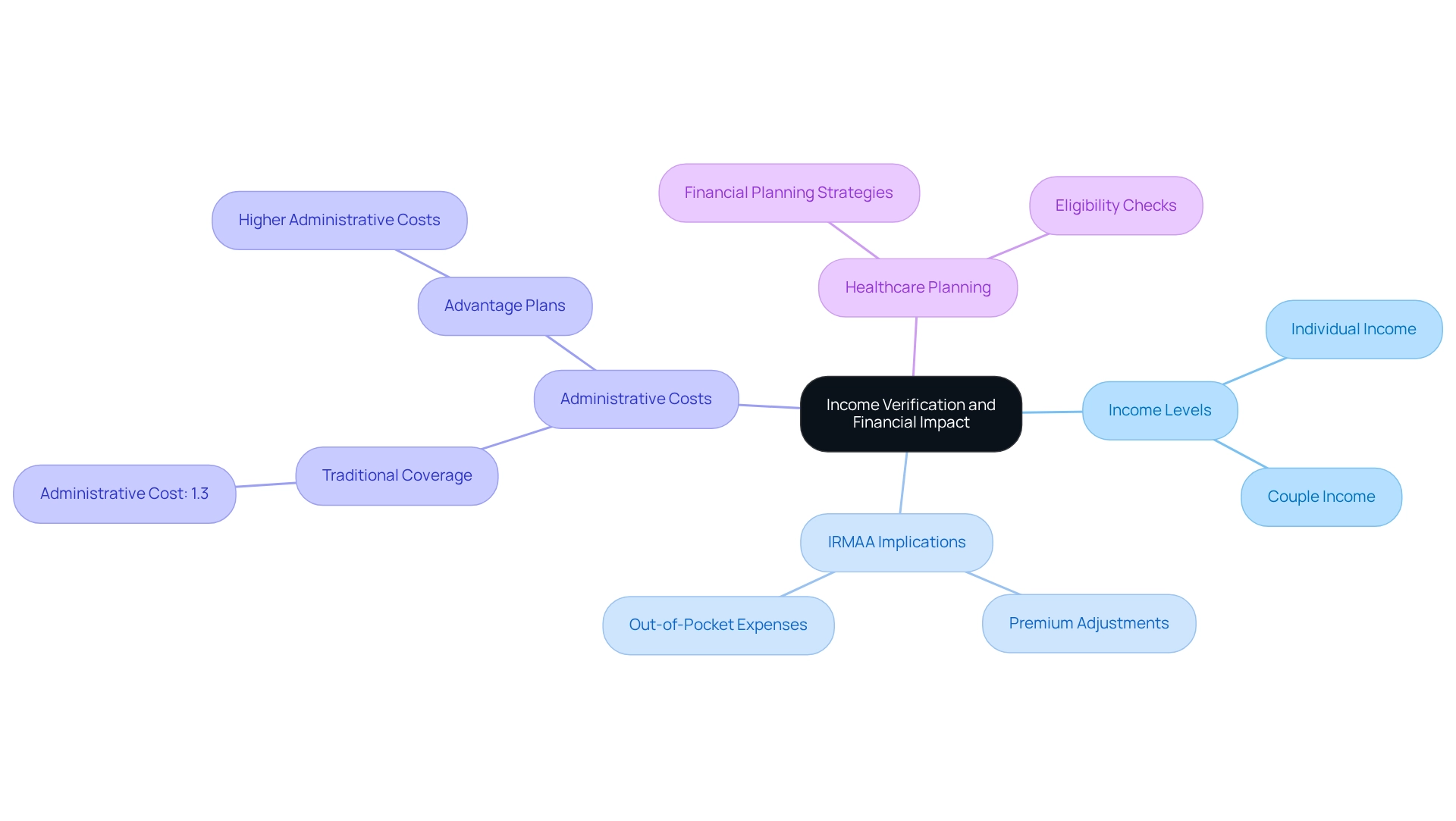
Income Verification: Assessing Your Financial Situation
Income Verification: Evaluating Your Financial Status
While qualification for the program does not depend on income, individuals’ financial conditions significantly influence their premium costs and out-of-pocket expenses. Higher-income individuals may face the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA), which raises premiums for Parts B and D. In 2023, individuals earning over $103,000 and couples earning more than $206,000 are subject to these increased expenses. Understanding the IRMAA and its connection to Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) is essential for recipients to effectively manage their healthcare expenses.
A recent case study on administrative expenses within the program reveals that traditional coverage maintains lower administrative costs at just 1.3% of total spending, in stark contrast to the higher costs associated with Advantage plans. This efficiency highlights the importance of grasping the financial implications of various healthcare plans, particularly how these expenses can affect premium adjustments based on income.
Furthermore, insights from healthcare economists indicate that approximately 30% of individuals enrolled in these programs are affected by IRMAA, underscoring the necessity for eligibility checks to ensure accurate income verification processes. As recipients assess their financial situations, they must recognize how their income levels can influence their healthcare expenses, preparing them for potential changes in their premiums. This proactive strategy not only aids in financial planning but also enhances overall patient care and access to essential services. For any corrections regarding prescription drug coverage, individuals should reach out to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
Incorporating CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data insights can empower stakeholders to better understand these financial implications and navigate the complexities of eligibility checks and income verification. By leveraging data from over 62 million beneficiaries and 6 million providers, CareSet can deliver valuable insights that enhance financial planning and patient care strategies.
Prior Health Coverage: Evaluating Your Insurance History
Individuals with previous health insurance coverage through an employer or other sources must carefully evaluate their insurance history before signing up for Medicare-related programs. Delaying registration in Part B of the health insurance program without credible coverage can lead to substantial late registration fees. In 2022, approximately 2.5 million people, or about 5 percent of Part D participants, faced late registration penalties, underscoring the financial repercussions of postponing health coverage enrollment. It is important to note that while this statistic pertains to Part D, similar penalties apply to Part B registration as well.
Understanding the eligibility checks related to prior coverage is essential for a seamless transition into Medicare. For example, a case study involving a client who retired at age 68 and opted for 12 months of COBRA coverage illustrates the risks associated with delaying Part B registration. After being diagnosed with cancer, he discovered that his COBRA plan would not cover his treatment costs due to his failure to enroll in Part B on time. This situation underscores the importance of prompt actions to avoid costly penalties and ensure adequate health coverage, particularly as individuals approach retirement.
Healthcare policy experts emphasize that while late enrollment penalties were designed to encourage timely enrollment, many individuals remain unaware of these penalties or how to avoid them. As Keith D. Lind points out, “Although these penalties were created to motivate individuals to sign up quickly for the program, some individuals ultimately incur late-enrollment fees because they are unaware of them or do not understand how to evade them.”
Integrating insights from CareSet, understanding one’s previous insurance history can be significantly enhanced by utilizing comprehensive healthcare data solutions. By performing eligibility checks on their insurance background and seeking guidance from a healthcare consultant, individuals can navigate the complexities of enrollment more effectively and protect against unexpected costs. CareSet’s data insights empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their coverage options, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and financial security.
Medicare Savings Programs: Exploring Financial Assistance Options
Savings Programs (MSPs) are indispensable in alleviating the financial burdens that low-income individuals face regarding health insurance, encompassing premiums, deductibles, and co-payments. These programs comprise various categories, notably the Qualified Beneficiary (QMB) initiative, which covers both Part A and B premiums, and the Specified Low-Income Beneficiary (SLMB) initiative, specifically aiding with Part B premiums. Eligibility for these programs hinges on income and resource limits, underscoring their critical role for those struggling to afford healthcare costs. As we look toward 2025, MSPs are undergoing significant transformations, with notable expansions across different states. For instance, Maine’s recent enhancement of its healthcare Savings Program, financed through Medicaid, has facilitated greater financial assistance for low-income residents, thereby improving access to essential healthcare services. This initiative illustrates the positive impact that MSPs can have on the lives of low-income beneficiaries, enabling them to obtain necessary medical care without the burden of excessive costs.
Current statistics reveal that a considerable percentage of low-income individuals utilize MSPs; however, many remain unaware of their eligibility for these programs. Despite policy modifications introduced in 2010, participation rates have not seen substantial improvement, with estimates suggesting that only about 20% of qualified individuals are enrolled. This highlights the urgent need for ongoing outreach and education efforts. Healthcare advocates emphasize the crucial role of MSPs in mitigating financial strain for beneficiaries, asserting that these programs are vital for ensuring equitable access to healthcare.
As of 2025, a variety of financial assistance options are available for Medicare beneficiaries, including state-specific programs and federal initiatives aimed at boosting participation in MSPs. These resources may provide support for premiums, deductibles, and co-payments, tailored to the needs of low-income individuals. Insights from financial aid program specialists indicate that increasing awareness and simplifying the application process are essential steps for improving access for low-income populations. By leveraging these resources, beneficiaries can navigate the complexities of healthcare coverage more effectively, ensuring they receive the care they require. As Alex Prosser from Healthgrades aptly notes, providing accessible information is crucial for positively influencing health and well-being, particularly for those dependent on MSPs.
Enrollment Periods: Understanding Timelines for Coverage
Medicare registration is regulated by distinct timeframes that individuals must navigate to secure their coverage effectively. The Initial Enrollment Period (IEP) is a critical timeframe, spanning three months before a person turns 65 and extending three months after their birthday. Additionally, General Registration Periods and Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs) are available for those who meet specific criteria, such as losing employer-sponsored coverage.
Understanding these timelines is essential, as missing registration deadlines and failing to complete eligibility checks can result in significant gaps in coverage and potential financial penalties. Statistics indicate that a notable percentage of individuals fail to meet these deadlines, underscoring the necessity for awareness and proactive planning. For instance, in Ohio, approximately 21% of the state population is insured by a government health program, highlighting the extent of individuals affected by registration issues. This statistic emphasizes the broader implications of participation difficulties within the state.
Practical examples illustrate the consequences of gaps in health insurance coverage due to registration errors. A case study examining county-level differences in health plan participation reveals that while some counties boast participation rates as high as 80%, others fall below 30%. This disparity reflects not only demographic factors but also varying levels of understanding regarding registration periods. In 2024, 37% of individuals utilizing the program reside in counties where at least 60% are enrolled in Advantage plans, a significant increase from just 3% in 2010, suggesting a shift towards these plans in metropolitan areas.
Expert insights underscore the importance of comprehending these registration timelines. Healthcare policy experts assert that beneficiaries must grasp the nuances of the health insurance program through eligibility checks to avoid unnecessary complications and ensure uninterrupted coverage. Furthermore, with the recent approval of Illinois SB0056, which allows individuals aged 65 to 75 with current supplement plans to purchase any supplement policy from any authorized partner starting January 1, 2026, it is crucial for stakeholders to remain informed about forthcoming changes in healthcare policies.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, staying aware of eligibility checks and compliance periods becomes increasingly vital for all parties involved. CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data insights can empower stakeholders to navigate these complexities effectively, ensuring they possess the necessary information to make informed decisions. Moreover, it is imperative to recognize that approximately 25% or more of the populace in regions such as New Hampshire, Vermont, West Virginia, and Maine are enrolled in health coverage, highlighting the importance of understanding registration timelines across various areas. To ensure compliance with registration deadlines, stakeholders should consider adopting proactive strategies and utilizing available resources to remain informed about changes in healthcare policies.
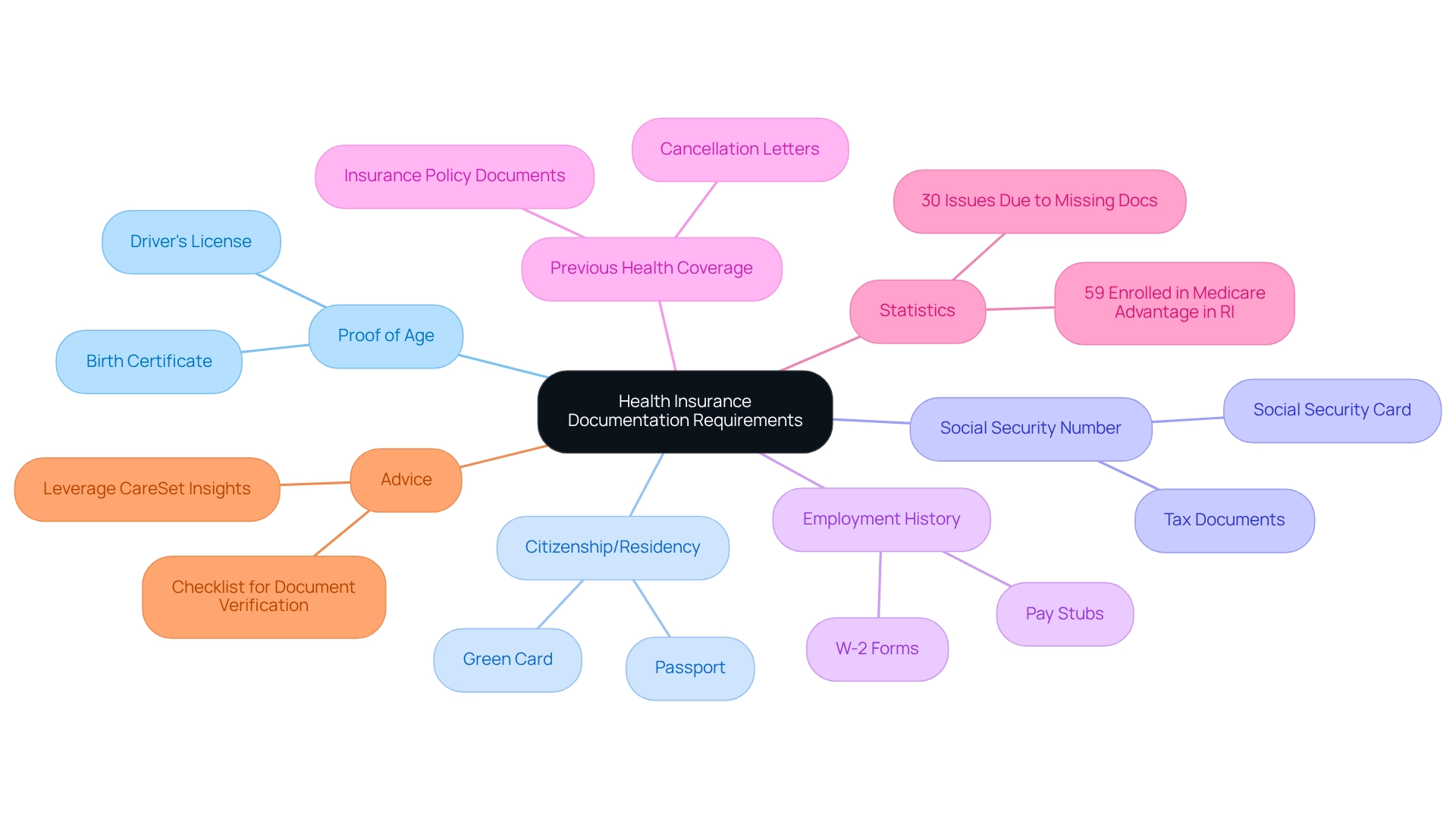
Documentation Requirements: Ensuring You Have What You Need
Applying for health insurance necessitates the submission of specific documentation to complete eligibility checks. Essential documents include proof of age, such as a birth certificate, alongside evidence of citizenship or legal residency status and a Social Security number. Additionally, applicants may need to provide details about their employment history and any previous health insurance coverage. Adequately preparing and submitting these documents is vital; statistics indicate that approximately 30% of applicants encounter issues due to missing documentation, which can delay the admission process.
In 2025, the landscape of healthcare documentation requirements continues to evolve, with healthcare professionals underscoring the importance of thoroughness in applications. Real-world examples demonstrate that incomplete submissions can lead to complications, highlighting the necessity for meticulous attention to detail. As noted by a healthcare enrollment specialist, “Ensuring all required documents are in order not only facilitates a smoother enrollment process but also enhances overall access to benefits.”
As the Advantage landscape expands—evidenced by the fact that 59% of enrollees in Rhode Island are now part of such plans—understanding the documentation requirements becomes increasingly essential. This statistic reflects the growing importance of ensuring that applicants are well-informed about the necessary documentation to access these plans. Case studies reveal that the payment methodologies of the program, particularly concerning Advantage plans, have significant financial implications, with an estimated $83 billion in higher spending projected for 2024. This scrutiny reinforces the necessity for accurate and complete documentation and eligibility checks to ensure beneficiaries receive the quality care they deserve.
To ensure your documentation is complete before applying for health coverage, consider creating a checklist of required documents and verifying that each item is in order. Additionally, leveraging CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data insights can empower healthcare stakeholders to streamline the documentation process, ensuring that all necessary information is readily available. This proactive approach can help prevent delays and ensure a smoother enrollment experience.
Policy Changes: Keeping Up with Medicare Eligibility Updates
Medicare policies and eligibility criteria are often subject to frequent changes driven by legislative updates and healthcare reforms. For recipients and potential applicants, staying informed about these changes is essential to fully comprehend their rights and responsibilities within the program. Recent statistics reveal that a significant percentage of recipients remain unaware of recent policy changes, underscoring the need for proactive engagement with available resources. A 2023 report indicates that while 85% of individuals enrolled in the program express satisfaction with their care, those under 65 with disabilities encounter greater challenges in accessing healthcare, highlighting the necessity for targeted interventions.
To navigate these complexities, individuals should routinely review official resources related to the program, such as Medicare.gov, and seek guidance from healthcare professionals. Engaging with these resources not only aids in understanding current eligibility checks but also empowers recipients to adapt effectively to new policies. CareSet’s comprehensive healthcare data insights can empower stakeholders by providing valuable information on policy changes and their implications. By utilizing CareSet’s data, stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding eligibility checks and coverage options. Expert insights emphasize that careful deliberation among all stakeholders is required when considering potential changes and their implications for recipients, healthcare providers, and the federal budget. As we approach 2025, recent alterations in healthcare policies will continue to influence the landscape, making it essential for stakeholders to remain alert and knowledgeable.
Real-world examples illustrate how recipients are adjusting to these updates, showcasing the impact of legislative changes on eligibility checks. For instance, the shifting demographics of Medicaid reveal a greater proportion of Black or Hispanic individuals compared to the general population, which may affect future policy considerations for the program. By staying updated on Medicare policy changes, recipients can ensure they make informed decisions regarding their coverage and access to care. Furthermore, understanding that 42% of Medigap policyholders hold a bachelor’s degree or higher may indicate a higher level of awareness among certain demographics regarding policy changes, further emphasizing the need for targeted communication strategies. Stakeholders can leverage CareSet’s insights to effectively tailor their communication strategies, ensuring that all beneficiaries are informed and engaged.
Conclusion
As individuals approach the milestone of 65, understanding Medicare eligibility becomes paramount. Key factors such as age, citizenship, residency, and prior health coverage play critical roles in determining access to Medicare benefits. Turning 65 not only marks a significant life transition but also serves as a pivotal moment for healthcare planning. This emphasizes the need for proactive enrollment to avoid penalties and gaps in coverage.
Furthermore, the importance of Social Security qualification and the nuances of disability status cannot be overlooked. For those under 65, pathways to Medicare through Social Security Disability Insurance are vital, ensuring timely access to essential healthcare services. The discussion surrounding income verification and Medicare Savings Programs underscores the financial considerations that can influence beneficiaries’ access to care.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, staying informed about policy changes and enrollment periods is crucial. The complexities surrounding documentation requirements and the implications of prior health coverage necessitate careful planning and awareness. Engaging with available resources and expert guidance empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their Medicare options.
Ultimately, navigating the intricacies of Medicare eligibility requires diligence and understanding. By remaining proactive and informed, individuals can secure their healthcare coverage and ensure they are prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead as they transition into this new phase of life.


