Overview
The article highlights the pivotal role of Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) in enhancing patient care by delivering essential insights into prescribing patterns and patient demographics. By emphasizing the significance of data analysis, it identifies high-risk patients and problematic prescribing behaviors, ultimately fostering improved patient safety and care outcomes. This approach not only underscores the importance of PDMPs but also encourages further exploration of how these programs can be leveraged to optimize healthcare practices.
Introduction
In the ongoing battle against prescription drug abuse, Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) have emerged as vital tools for healthcare providers. These programs offer comprehensive insights into prescribing patterns and patient histories, significantly curbing misuse while enhancing patient safety and care outcomes.
However, the implementation of PDMPs presents challenges, including:
- Compliance
- Data sharing
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
This article delves into the multifaceted role of PDMPs, exploring their effectiveness, the impact of legal mandates, and the importance of training healthcare providers.
Through a blend of data analysis and expert insights, the discussion highlights how PDMPs can be optimized to navigate the complexities of prescription management, ensuring that patient care remains paramount.
CareSet: Comprehensive Medicare Data Insights for PDMP Effectiveness
CareSet excels in analyzing Medicare claims data, a vital resource for enhancing the effectiveness of pdmps. By providing detailed insights into prescribing patterns and demographics, CareSet enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions that align with pdmps. This data-driven methodology is instrumental in identifying high-risk patients and problematic prescribing behaviors, ultimately leading to improved patient safety and care outcomes.
For instance, a recent examination of opioid prescription patterns over a 30-week pre- and post-implementation timeframe highlighted crucial areas where prescription monitoring programs could enhance their focus to reduce misuse and guarantee compliance with prescribing guidelines. The findings emphasize that while prescription drug monitoring programs can effectively reduce misuse, they may inadvertently limit appropriate care, highlighting the need for a balanced approach.
Furthermore, CareSet’s extensive Medicare information solutions offer insights from more than 62 million beneficiaries and 6 million providers, enabling a nuanced understanding of treatment pathways for individuals. Case studies show that clinicians frequently face obstacles to using prescription monitoring programs, such as time limitations and the difficulty of retrieving the information. CareSet tackles these challenges with intuitive designs and efficient access, boosting clinician involvement with pdmps, and consequently enhancing the quality of care. This aligns with the findings from the case study titled ‘Barriers to PDMPs Utilization,’ which emphasizes the importance of overcoming these obstacles to optimize PDMPs prescribing practices.
Expert opinions further reinforce the significance of Medicare claims information in refining the effectiveness of pdmps. Analysts emphasize that ongoing work is essential to determine the optimal configuration of clinical decision support systems (CDSS) for opioid prescribing, ensuring that prescribing patterns are appropriately modified and patient outcomes are enhanced. As Robert P. Pierce noted, “Further work is needed to determine the optimal configuration of opioid CDSS so that opioid-prescribing patterns are appropriately modified and encounter outcomes are improved.” Through its thorough examination, CareSet not only meets urgent information requirements but also promotes long-term strategic development in the healthcare environment, particularly in relation to pdmps.
Impact of PDMPs on Prescription Drug Abuse Reduction
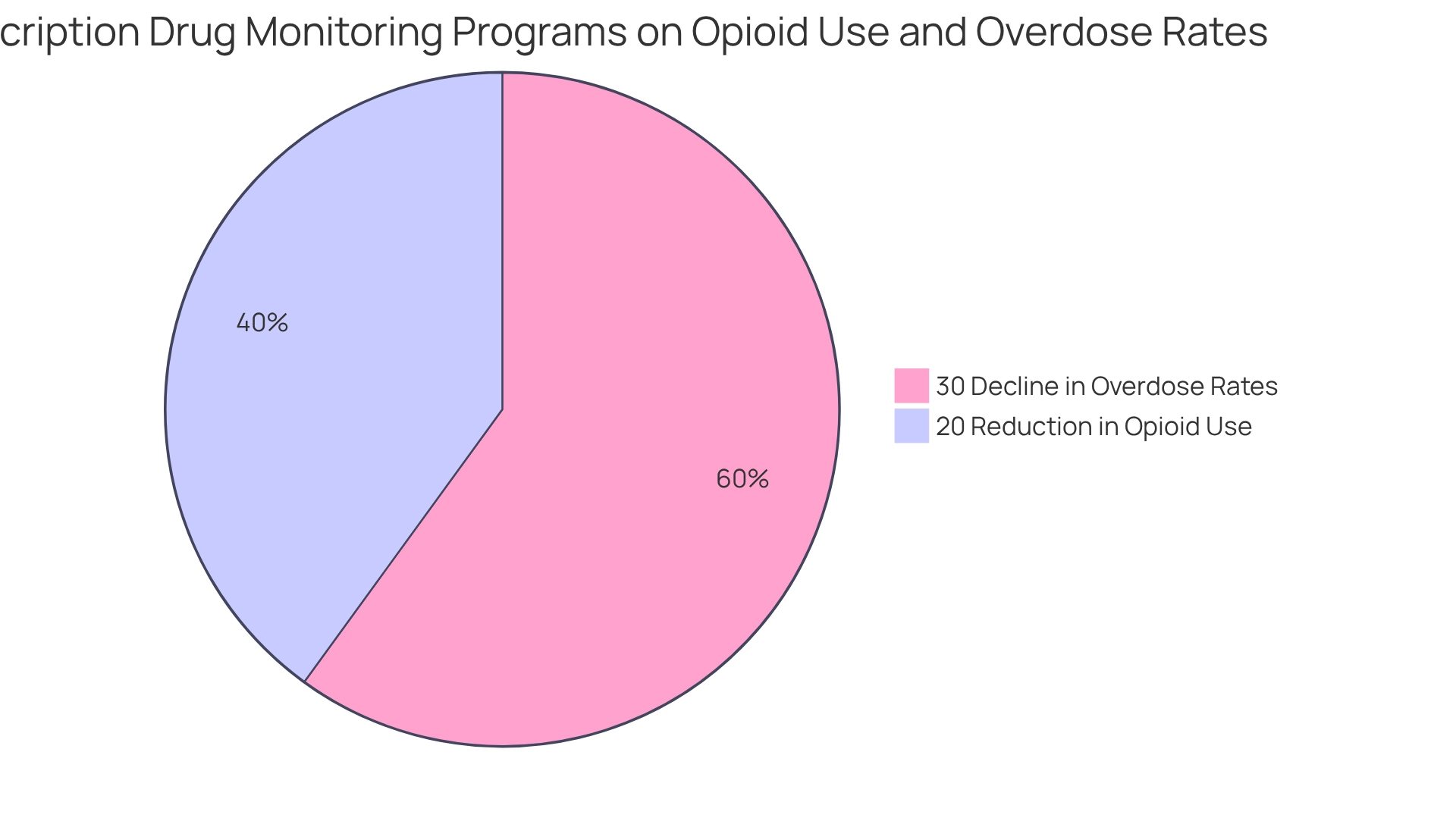
Medication Monitoring Programs serve as vital instruments in the fight against drug misuse, particularly in the context of opioid abuse. By meticulously overseeing orders for regulated medications, these programs furnish healthcare professionals with critical information that can dissuade improper prescribing practices. Recent statistics indicate that states with effectively implemented monitoring programs have witnessed a substantial decrease in opioid consumption and related overdose incidents. For instance, states mandating prescription drug monitoring program evaluations reported a significant reduction in opioid-related fatalities, underscoring the effectiveness of these initiatives in bolstering public health.
A 2025 analysis revealed that states with comprehensive monitoring systems experienced a 20% reduction in opioid use compared to those without such frameworks, based on a study conducted from February to August 2016. Furthermore, research suggests that these programs can lead to a 30% decline in opioid overdose rates, particularly in regions with high medication distribution levels. These findings illustrate that drug monitoring programs not only assist in curbing medication misuse but also play a pivotal role in enhancing individual safety.
Case studies focusing on the Veterans Affairs (VA) system illustrate that improved training and streamlined access to monitoring information significantly enhance physician engagement with these initiatives. By incorporating PDMP data into electronic medical records (EMRs), healthcare providers can more effectively track patient prescriptions, thereby mitigating the risk of misuse. The VA’s experience highlights how targeted policies can amplify the impact of prescription drug monitoring programs on opioid prescribing practices, emphasizing the importance of understanding facilitators to inform policy development.
Expert insights further underscore the significance of prescription drug monitoring programs. Physicians have noted that while the mandated use of these programs may pose administrative challenges, practices that integrate regular checks into their workflows can effectively mitigate these issues. This proactive approach not only fosters compliance but also enhances the overall efficacy of prescription drug monitoring programs in combating prescription drug abuse.
In conclusion, the evidence strongly advocates for the implementation of robust prescription drug monitoring programs as a crucial strategy in addressing the opioid crisis. States that have successfully embraced these initiatives serve as exemplary models for others seeking to improve patient care and safety.
Legal Mandates and Compliance Requirements for PDMPs
Legal mandates for prescription drug monitoring programs vary significantly by state, yet they generally necessitate that healthcare providers consult the program prior to prescribing controlled substances. Adherence to these mandates is not merely a formality; it is crucial for the effectiveness of pdmps.
Healthcare providers must be acutely aware of their state’s specific requirements, which encompass:
- Registration
- Information submission
- Usage protocols
Non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties and ultimately undermine the program’s objectives. Therefore, ongoing education and training for providers are essential to ensure compliance with these legal obligations, thereby enhancing the overall effectiveness of pdmps.
Interstate Data Sharing: Enhancing PDMP Effectiveness
Interstate information exchange among pdmps is crucial for enhancing the efficiency of medication oversight. By enabling states to share medication information, healthcare professionals gain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s medication history, regardless of where medications are processed. This capability is essential for identifying individuals who may engage in ‘doctor shopping’ or misuse medications, ultimately improving patient safety.
Initiatives like PMP InterConnect exemplify this information-sharing approach, connecting participating state PDMPs to facilitate the secure transfer of prescription information across state lines. This platform not only enhances clinical decision-making but also strengthens efforts to address drug diversion and abuse nationwide by adhering to each state’s information access regulations. However, misconceptions regarding PMP InterConnect’s security have prevented some states from adopting its standards, underscoring the challenges that remain to be addressed.
The impact of interstate information sharing is substantial. For instance, in 2025, statistics indicate that states utilizing PMP InterConnect reported a notable increase in the identification of potential medication misuse cases. Furthermore, healthcare leaders emphasize that exchanging medication information across states fosters collaboration and enhances the overall efficiency of pdmps, which leads to improved patient outcomes. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is actively working to eliminate barriers to integration, developing standards and implementation guidance to support both in-state and interstate exchange of pdmps data. By working together, states can create a more comprehensive and efficient system for overseeing medications, ultimately enhancing patient care and safety within the healthcare environment. CareSet’s integration of over 100 external information sources further highlights the importance of thorough information sharing in bolstering the effectiveness of pdmps.
Integration of PDMPs with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Integrating pdmps with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is essential for enhancing the availability and functionality of medication information. This integration allows healthcare providers to access pdmps information seamlessly within their EHR systems, thereby eliminating the cumbersome task of navigating multiple platforms. Research demonstrates that the integration of EHR with pdmps significantly increases the frequency of queries, leading to more informed prescribing decisions. For example, a recent pilot initiative revealed that clinicians with integrated access to pdmps were notably more adept at identifying potential prescription misuse, which enhances safety outcomes.
Expert opinions further underscore the advantages of this integration. Healthcare IT experts assert that linking pdmps with EHRs not only streamlines workflows but also enhances the quality of care by providing clinicians with comprehensive medical histories at their fingertips. By 2025, statistics indicate that healthcare systems adopting EHR integration with pdmps report heightened query rates, correlating with improved patient care outcomes. CareSet’s integration of over 100 external information sources bolsters this trend, offering a robust framework for analysis.
Additionally, Dr. Hannah T. Neprash emphasizes, “However, we plan to address this limitation in subsequent analyses of the PRINCE trial interventions, by linking e-prescribing information derived directly from the EHR itself,” highlighting the critical role of direct data integration.
Case studies further illustrate the positive impact of EHR integration with pdmps on prescribing decisions. One notable study titled ‘Future Directions for PDMP Integration’ identified barriers to PDMP integration, including cost and interoperability challenges. However, it also emphasized the substantial benefits of increased query rates and improved safety for individuals in pdmps. The findings suggest that while EHR integration promotes PDMP usage, ongoing research is vital to thoroughly assess its effect on care.
In conclusion, the integration of pdmps with EHRs represents a significant advancement in healthcare, allowing systems to refine prescribing decisions and ultimately enhance care for individuals.
Analyzing Opioid Prescription Trends Using PDMP Data
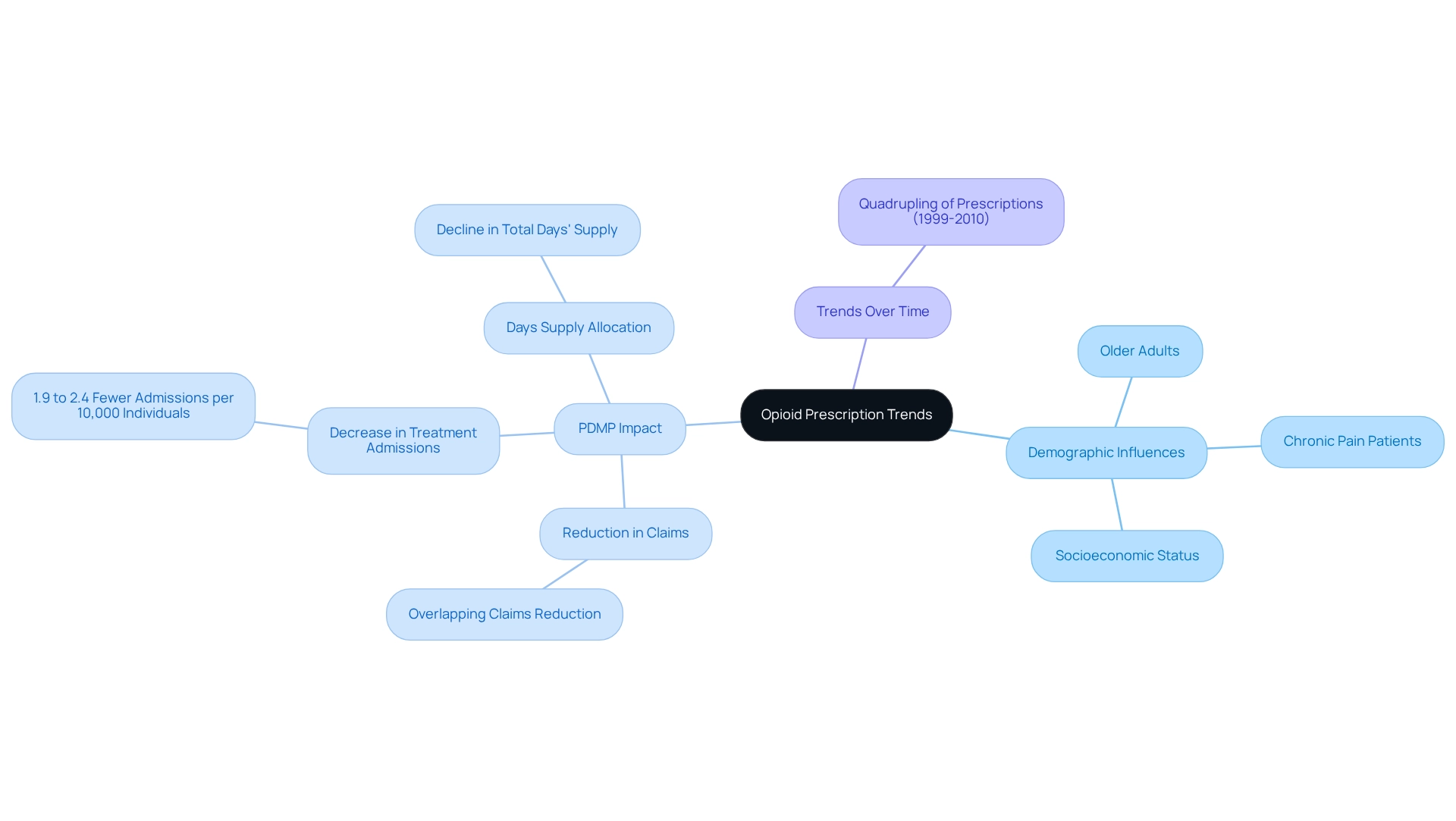
Examining opioid prescribing patterns through the lens of pdmps is crucial for understanding dispensing practices and their implications for public health. Analyzing medication volumes, patient demographics, and prescribing behaviors allows stakeholders to identify trends that may indicate misuse or over-prescribing. For instance, research reveals that opioid prescribing quadrupled from 1999 to 2010, underscoring a significant surge in usage. Moreover, a study investigating medication monitoring programs and overlapping opioid claims among Medicare Part D enrollees from 2007 to 2013 found that mandatory access to monitoring data led to a decrease in overlapping claims, signifying enhanced oversight of opioid medications.
Demographic analyses indicate that specific groups, such as older adults and individuals with chronic pain conditions, are more likely to receive high quantities of opioids, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to address these disparities. By 2025, ongoing evaluations of demographic factors influencing opioid usage trends—such as age, gender, and socioeconomic status—will be essential for tailoring public health initiatives. Notably, mandatory access to pdmps has been associated with a reduction in treatment admissions for opioid substance-use disorder, with findings indicating a decrease of 1.9 to 2.4 fewer treatment admissions per 10,000 individuals aged 12 and older, emphasizing the positive impact of pdmps on public health outcomes. Furthermore, Yarbrough’s findings suggest that the implementation of pdmps leads to a reduction in the overall days’ supply allocated for opioids, further reinforcing the effectiveness of these programs in regulating opioid use. Such insights not only inform clinical practices but also shape public health strategies aimed at curbing opioid misuse. As the landscape of opioid utilization continues to evolve, leveraging pdmps will be essential for stakeholders seeking to enhance care and optimize treatment outcomes.
Unintended Consequences of PDMP Implementation
PDMPS are strategically designed to mitigate prescription drug abuse; however, their implementation can yield unintended consequences. Research indicates that more stringent PDMP regulations may result in inadequate pain management for individuals with legitimate needs. Additionally, there is a growing concern that individuals might turn to illicit substances if they perceive their access to prescribed medications is restricted. Understanding these unforeseen outcomes is crucial for decision-makers and healthcare practitioners, as it enables the effective execution of PDMPs, which strike a balance between necessary oversight and the imperative of providing adequate care to individuals.
Training Healthcare Providers on Effective PDMP Utilization
Training healthcare providers on the effective utilization of PDMPs is essential for enhancing patient care. Providers must be skilled at accessing and interpreting PDMP information to make informed prescribing decisions. Ongoing education programs, such as workshops and online training modules, are vital for keeping clinicians updated on best practices and legal requirements surrounding PDMPs. These programs can provide practical advice on identifying warning signs in medication histories and utilizing PDMP information to shape treatment plans. Such training not only boosts provider confidence but also significantly contributes to improved patient outcomes.
Statistics indicate that approximately 10% of emergency department physicians in Washington State are noncompliant with legislation mandating PDMP use, underscoring the need for effective training initiatives. Furthermore, effective PDMP training initiatives for healthcare providers demonstrate that real-time access to prescription information can enhance the management of opioids, particularly among at-risk groups. This highlights the critical role of training in ensuring that healthcare providers can effectively utilize the data available to them.
Professionals in the area emphasize that upcoming improvements to prescription drug monitoring programs should incorporate user input to guarantee they address clinical requirements. As Chris Delcher, PhD, points out, “Further investigation is necessary to enhance comprehension of situations where prescription drug monitoring programs enhance care or differentially affect specific groups such as those with chronic pain or cancer.” By concentrating on optimal methods for interpreting PDMP data in clinical environments, healthcare providers can more effectively manage the complexities of care, ultimately resulting in safer prescribing practices and improved safety for individuals.
PDMPs and Their Role in Improving Patient Outcomes
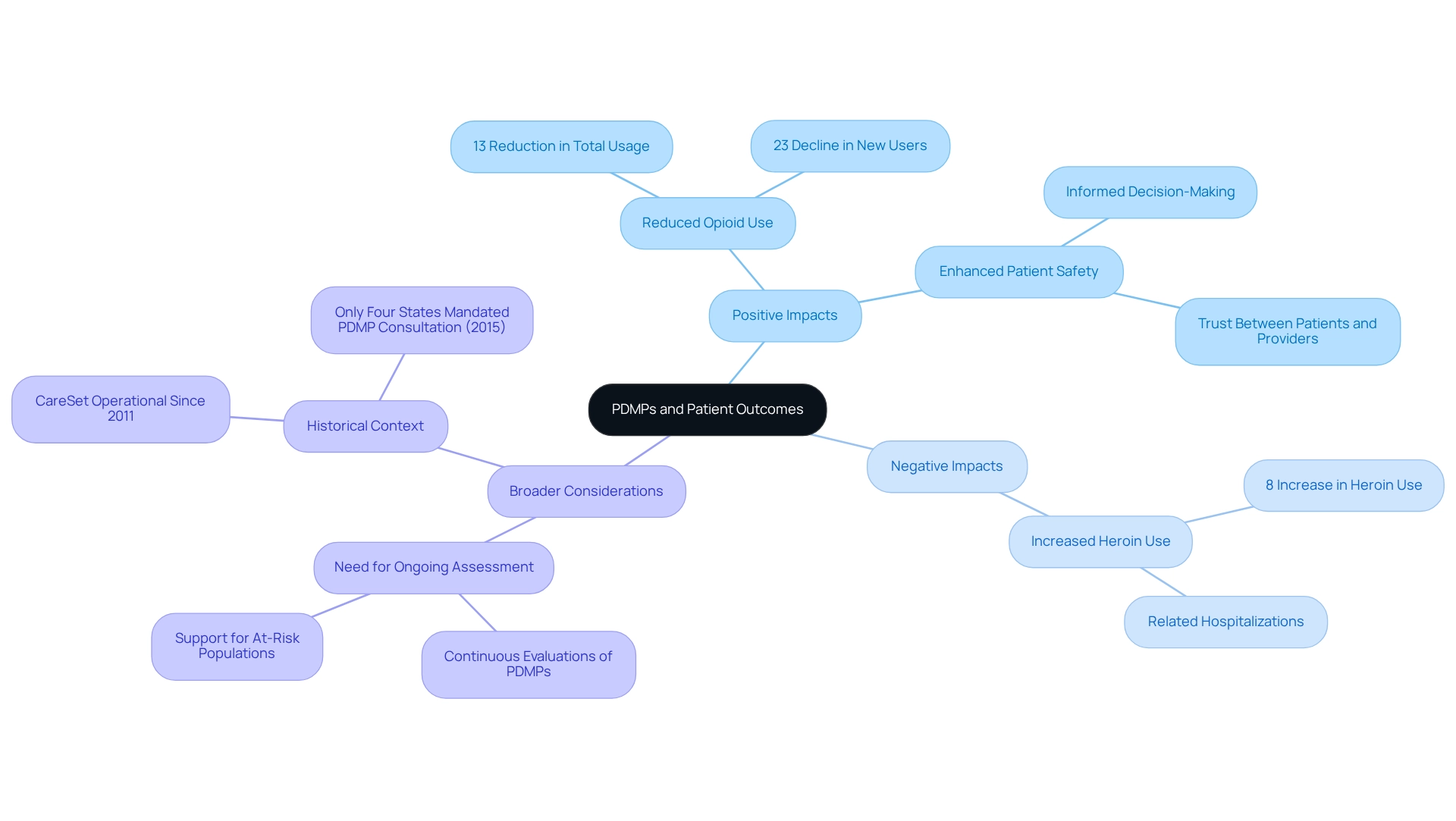
PDMPS play a critical role in enhancing healthcare outcomes by equipping medical professionals with vital information regarding an individual’s prescription history. By facilitating the identification of potential misuse or excessive prescribing, pdmps play a crucial role in ensuring that individuals receive care tailored to their unique needs. For instance, when clinicians access a comprehensive medication history, they can make informed decisions regarding pain management and substance use treatment. This proactive approach not only enhances patient safety but also fosters trust between patients and providers, which is essential for effective healthcare delivery.
Recent statistics reveal that pdmps have significantly decreased opioid use, with a 13% reduction in total usage and a 23% decline in new users. However, the implementation of these programs has also underscored the necessity for a balanced approach, as they are linked to an 8% increase in heroin use and related hospitalizations. This dual effect emphasizes the importance of pdmps in recognizing medication misuse while considering the broader context of substance use disorders.
Healthcare providers have indicated that accessing prescription histories through pdmps enhances their ability to provide safer and more effective care. As one expert remarked, “Until further action is taken, we are committing a great injustice to those suffering from pain, individuals with a mental illness, and those with a substance use disorder.” This statement highlights the critical need for ongoing assessment and improvement of PDMPs to better support at-risk populations. In 2025, continuous evaluations of pdmps effectiveness continue to affirm their vital role in promoting patient safety and trust, establishing pdmps as indispensable tools in modern healthcare. Notably, since CareSet has been operational since 2011, its extensive experience and data analysis provide valuable insights into pdmps, further reinforcing the significance of these initiatives in today’s healthcare landscape. Additionally, as of July 2015, only four states mandated prescribers to consult the PDMP before prescribing controlled medications, reflecting the evolving landscape of PDMP implementation and its relevance to current practices. The case study titled “Intended and Unintended Health Effects of Drug Monitoring Programs” further illustrates this dual impact, demonstrating that while such programs reduce opioid usage through medical prescriptions, they also contribute to increased illicit opioid use, indicating that supply-side restrictions alone are insufficient to address opioid misuse.
Current Research and Developments in PDMPs
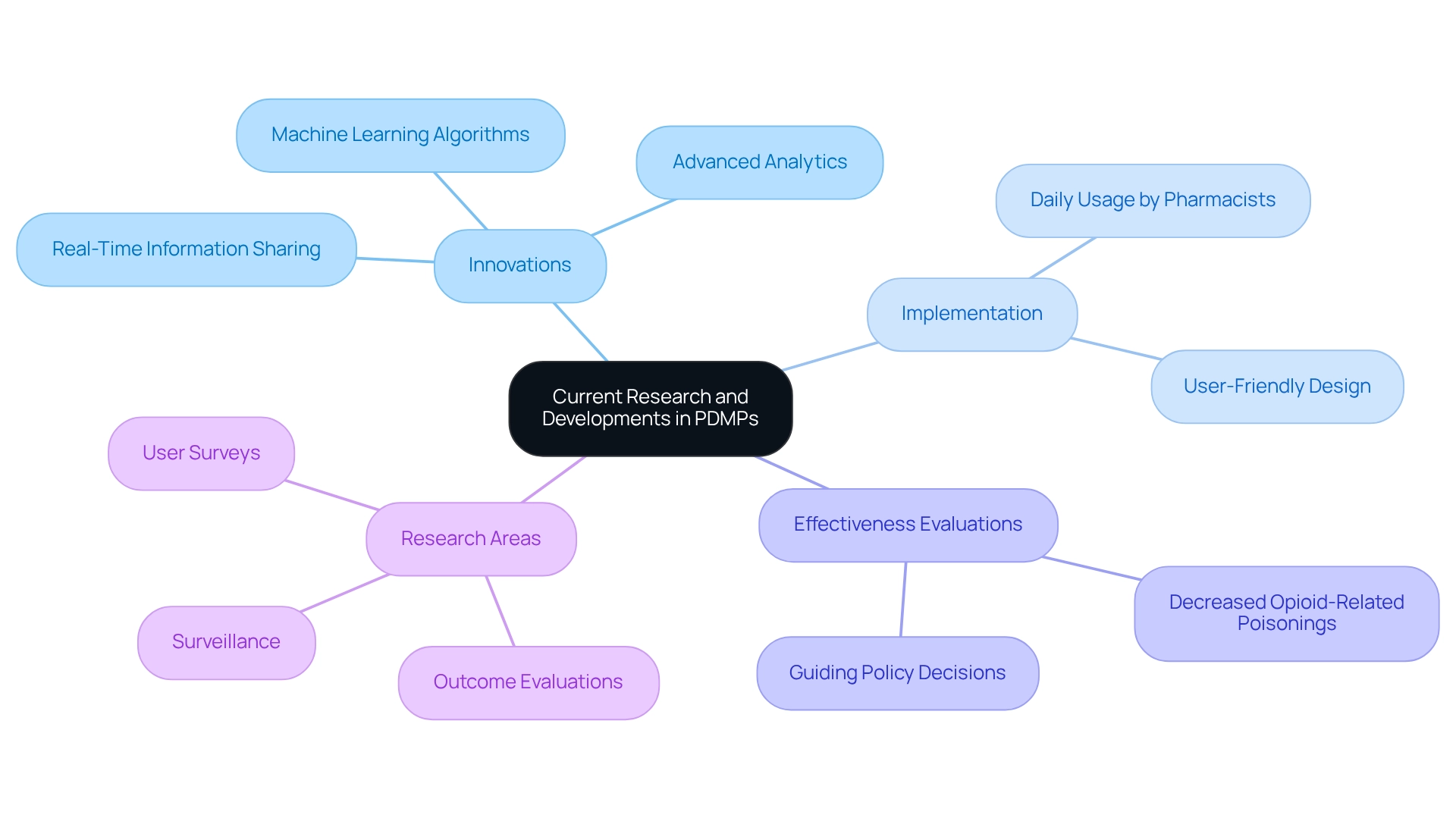
Current research and developments in pdmps are increasingly focused on enhancing their functionality to effectively combat prescription drug abuse. Innovations such as real-time information sharing and advanced analytics are at the forefront of these efforts, significantly enhancing pdmps. For instance, recent research has emphasized the use of machine learning algorithms to foresee high-risk prescribing behaviors by examining historical data, demonstrating a proactive approach to safety in healthcare.
Moreover, nearly every U.S. state has implemented prescription drug monitoring programs, with most pharmacists reporting daily usage across various practice settings, underscoring their integral role in healthcare. Evaluations of the effectiveness of pdmps are essential for guiding policy decisions and optimizing program implementation, ensuring that these tools remain relevant and impactful. Notably, characteristics of pdmps have been associated with decreased rates of opioid-related poisonings, demonstrating their efficacy in enhancing user safety.
A comprehensive review of literature from 2018 to 2019 revealed key themes in research on pdmps, including unintended consequences on opioid access and the effects on prescribing practices for benzodiazepines and stimulants. The synthesis of literature identified three main research focus areas:
- Outcome evaluations
- User surveys
- Surveillance
These insights are crucial for comprehending the evolving landscape of medication monitoring and the integration challenges across various specialties.
As healthcare providers and policymakers stay informed about these advancements, they can utilize pdmps to enhance patient care and safety, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. As one focus group participant noted, “An enhanced PDMP is worth the investment as long as the additional information provided is clear, concise, and easily interpretable by users.” This perspective emphasizes the importance of ensuring that pdmps are user-friendly and effective tools in the fight against prescription drug abuse.
Conclusion
Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) play a crucial role in combating prescription drug abuse, particularly concerning opioids. They equip healthcare providers with vital insights into prescribing patterns and patient histories, thereby enhancing patient safety and care outcomes. Evidence indicates that states with effective PDMPs witness significant reductions in opioid prescriptions and overdose incidents, underscoring their importance in promoting public health.
Nevertheless, challenges persist in the implementation of PDMPs, including adherence to legal mandates, interstate data sharing, and integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs). Comprehensive training for healthcare providers is essential to ensure they can effectively utilize PDMP data for informed prescribing decisions.
While PDMPs are instrumental in reducing misuse, it is imperative to acknowledge potential unintended consequences, such as the under-treatment of legitimate pain patients. A balanced approach is vital to ensure that PDMPs fulfill their objectives without compromising essential care.
In summary, PDMPs are indispensable tools in contemporary healthcare, critical for enhancing patient outcomes and addressing prescription drug abuse. By leveraging data-driven insights and fostering collaboration among providers, PDMPs can significantly elevate care quality and safety. The future of prescription management hinges on the successful integration of PDMPs into clinical practice, ensuring that patient safety and well-being remain paramount.


