Overview
The article delineates five critical steps for effective electronic data capture (EDC) in clinical trials:
- Defining the EDC system
- Selecting the appropriate platform
- Configuring the system
- Training stakeholders
- Monitoring performance
Each step is underpinned by comprehensive strategies and best practices that highlight the significance of compliance, user engagement, and ongoing evaluation. These elements are essential for enhancing data integrity and optimizing trial outcomes, ultimately driving successful clinical research initiatives.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, the transition from traditional paper-based data collection to Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems marks a significant advancement. These sophisticated software applications not only streamline the collection, management, and storage of trial data but also enhance accuracy and compliance, all while providing real-time access to critical information. As the industry faces the complexities of regulatory standards and the necessity for efficient data handling, the importance of EDC systems becomes increasingly pronounced.
This article explores the intricacies of EDC systems—covering their:
- Definition
- Selection
- Configuration
- Training
- Performance monitoring
Offering a comprehensive guide for organizations seeking to optimize their clinical trials and improve patient outcomes.
Define Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems
Electronic data capture clinical trials are represented by EDC platforms, which serve as advanced software applications that facilitate the electronic gathering, management, and storage of critical trial information. In stark contrast to traditional paper-based methods, electronic data capture clinical trials streamline the data collection process, enhance accuracy, and provide immediate access to essential information. By utilizing electronic Case Report Forms (eCRFs), these platforms amass comprehensive patient data, including demographic details, treatment protocols, and clinical outcomes.
The importance of electronic data capture clinical trials frameworks in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards is paramount. Alarmingly, recent statistics reveal that over 80% of clinical studies fail to meet regulatory requirements, resulting in delays in drug commercialization. The challenge is addressed by electronic data capture clinical trials through EDC frameworks that incorporate built-in checks to elevate data quality and enable trials to fulfill these critical standards. A notable case study illustrates how electronic data capture clinical trials utilize EDC frameworks to support compliance by generating robust audit trails, adhering to Good Clinical Practice guidelines, and maintaining the highest standards of data integrity. Electronic data capture clinical trials have reported significant improvements in compliance rates and data accuracy, underscoring their efficacy.
As clinical research continues to evolve, the benefits of electronic data capture clinical trials are expanding. These tools not only enhance data precision and compliance but also facilitate effective execution in electronic data capture clinical trials, ultimately driving better patient outcomes and improving study processes. Industry leaders emphasize that the analytical depth and precision provided by electronic data capture clinical trials tools markedly enhance strategic decision-making. As highlighted by the IMARC Team, “The depth of analysis, precision of information, and practical suggestions have significantly improved our strategic decision-making,” underscoring the vital role of EDC solutions in modern clinical studies.
Select the Appropriate EDC System
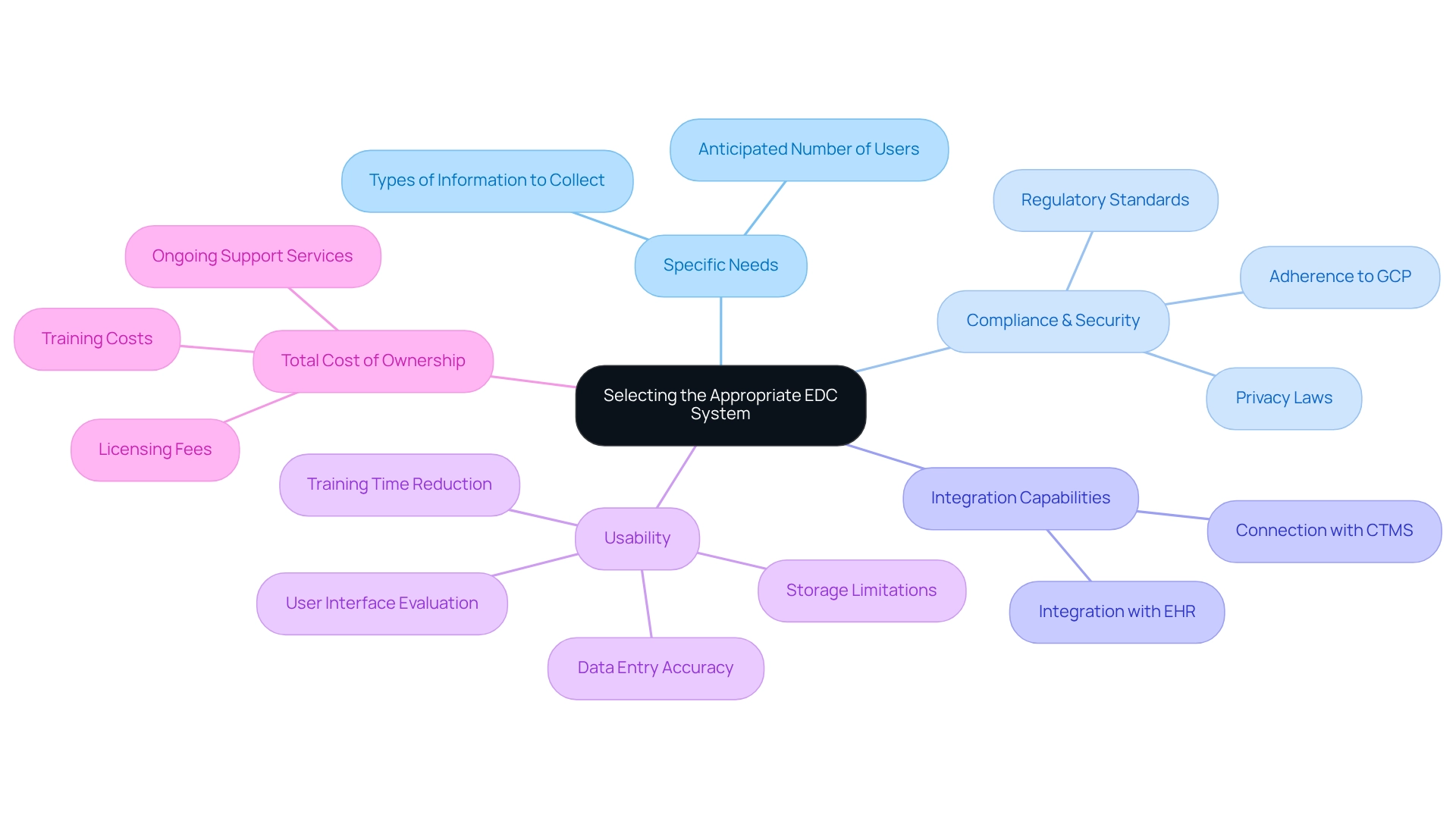
Choosing the appropriate platform for electronic data capture clinical trials is crucial for the success of clinical studies and requires careful consideration of several key factors. First, clearly outline the specific needs of your clinical trial, including the types of information to be collected and the anticipated number of users. Understanding these requirements is vital to ensure that the EDC framework can effectively support your study. For instance, REDCap offers flexibility by enabling information gathering in two modes: classic (one-time) and longitudinal (multiple times) per study subject.
Next, compliance and security are paramount. It is essential to confirm that the EDC platform adheres to regulatory standards such as Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and relevant privacy laws. High adherence rates for EDC frameworks with GCP are crucial, as they guarantee the integrity and reliability of the data collected. Additionally, assess the integration capabilities of the EDC system to ensure it can seamlessly connect with other clinical trial management systems (CTMS) and electronic health records (EHR). This ability is vital for optimizing data flow and enhancing overall study efficiency.
Usability is another critical factor. Evaluate the user interface and overall ease of use for all stakeholders involved in the trial. An intuitive platform can significantly reduce training time and improve data entry accuracy, which is essential for maintaining data integrity. It is important to consider challenges such as storage limitations and the need for manual uploads of data dictionaries, particularly with platforms like REDCap. Finally, consider the total cost of ownership, which encompasses licensing fees, training costs, and ongoing support services. A comprehensive cost assessment will help ensure that the selected system for electronic data capture clinical trials aligns with your budget while meeting your study’s objectives. Conducting a thorough review of these elements will facilitate the selection of an electronic data capture clinical trials system that not only complies with regulatory standards but also enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of your clinical studies. The term EDC, which stands for ‘electronic data capture’, refers to a web-based software application used in electronic data capture clinical trials to collect data from patients in clinical research. By prioritizing these factors, clinical study managers can make informed decisions that lead to successful outcomes. Furthermore, EDC frameworks should enable data entry and inquiry resolution for clinical study sites, further underscoring their importance in operational efficiency.
Configure the EDC System for Your Trial
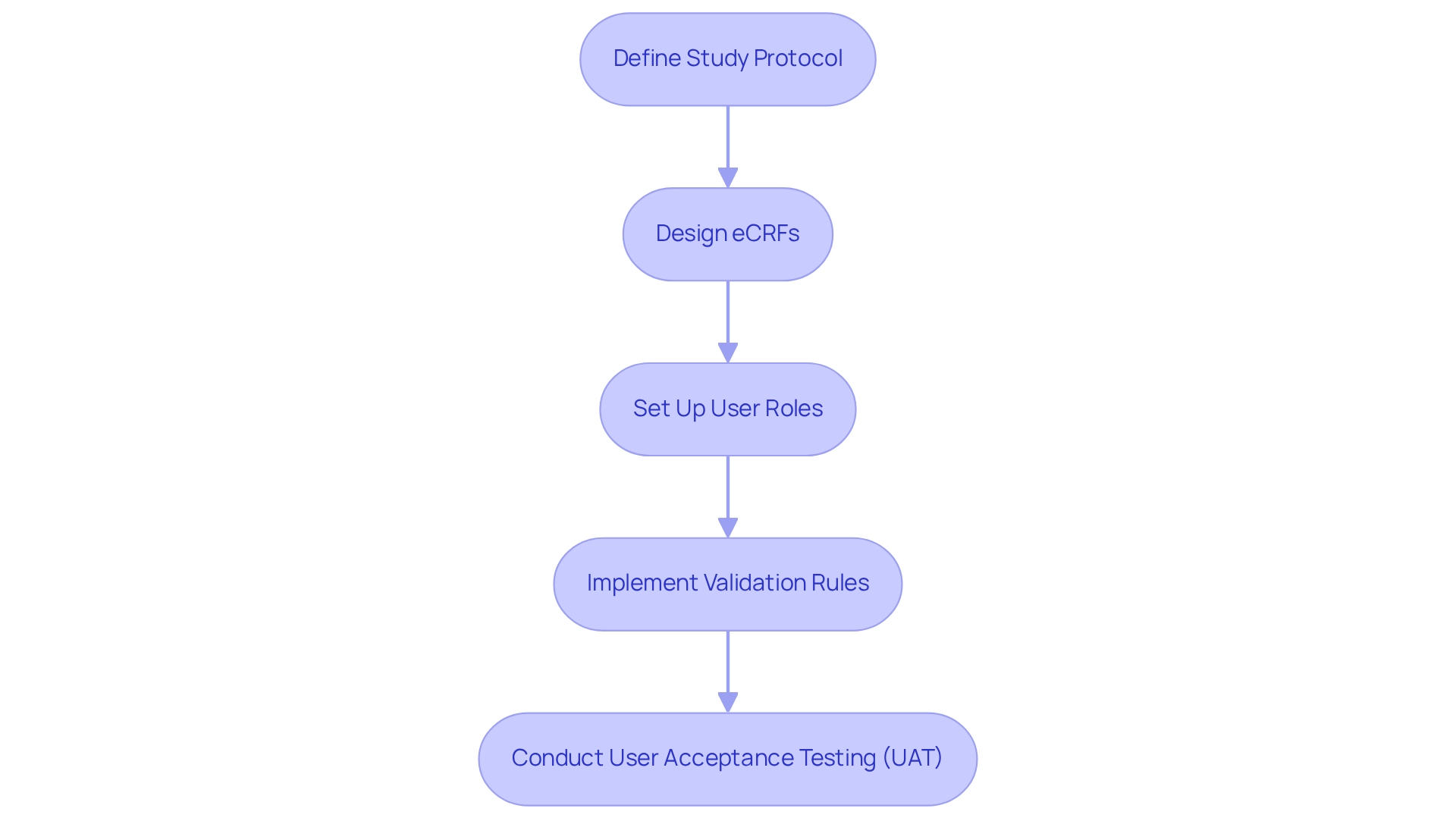
Configuring an electronic data capture clinical trials system is crucial for ensuring the success of clinical trials, which involves several essential steps that must be meticulously followed.
-
Define Study Protocol: The first step involves clearly outlining the study objectives, endpoints, and information collection methods. A well-defined protocol serves as the foundation for all subsequent configurations. As Illhoi Yoo, Associate Professor of Health Informatics, emphasizes, “The project requires approval from the IRB before gathering information can commence,” underscoring the significance of a solid protocol in ensuring compliance and integrity.
-
Design eCRFs: Next, create electronic Case Report Forms (eCRFs) tailored to the specific information points mandated by the study protocol. This customization guarantees that all necessary information is captured efficiently, enhancing the quality of data collected.
-
Set Up User Roles: It is vital to assign roles and permissions for all users, ensuring that entry personnel, monitors, and investigators possess appropriate access levels. Effective management of user roles is essential to maintaining information security and integrity throughout the trial process.
-
Implement Validation Rules: Establishing validation checks within the EDC system is imperative to minimize entry errors and ensure data integrity. Statistics indicate that pharmaceutical firms adopting comprehensive information management solutions can significantly reduce validation errors, thereby improving the overall quality of trial information. For instance, the case study titled “Graphical Data View and Stats Application” illustrates how graphical representations of data enable researchers to swiftly identify trends and anomalies, enhancing the data analysis process.
-
Conduct User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Prior to launching the system, conducting UAT is critical to detect any issues and confirm that the application functions as expected. This step allows for adjustments based on user feedback, ultimately increasing the likelihood of regulatory approval by 23% for companies that prioritize thorough testing. As Abu Saleh Mohammad Mosa, Director of Research Informatics, notes, “A well-defined study protocol is essential for effective EDC configuration.”
Proper configuration of the electronic data capture clinical trials system is essential for successfully executing clinical studies. By adhering to these steps, organizations can enhance their information management processes, leading to improved outcomes and more effective evaluations. Furthermore, insights from clinical study specialists emphasize the importance of a clearly outlined research protocol in EDC setup, ensuring that all elements of the study comply with regulatory standards and best practices.
Train Stakeholders on EDC Usage
Training stakeholders on the usage of electronic data capture clinical trials must encompass several critical components to ensure effective implementation and utilization.
-
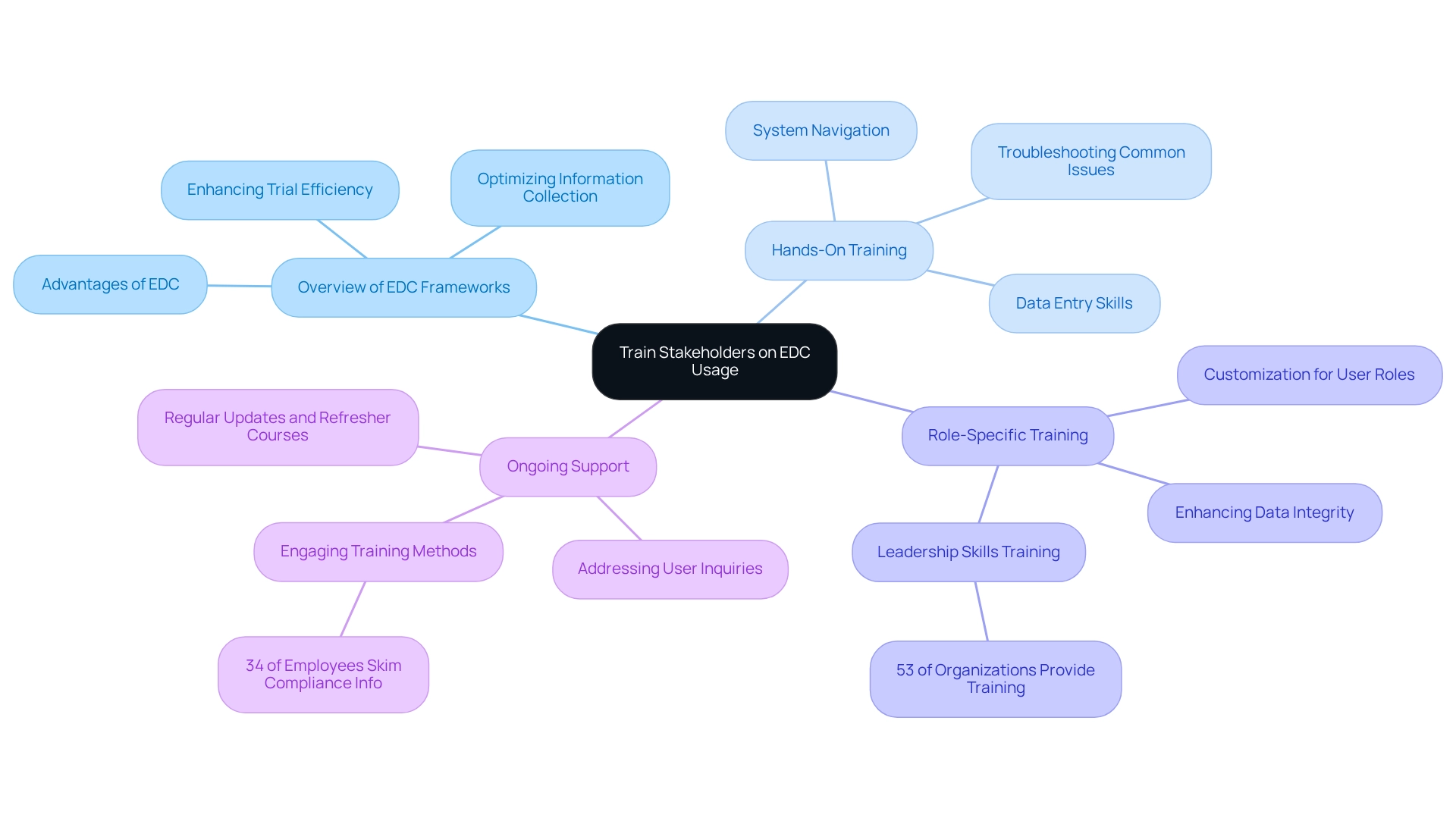
Overview of EDC Frameworks: Begin with a comprehensive introduction to EDC frameworks, emphasizing their advantages in optimizing information collection and enhancing trial efficiency. This foundational knowledge is crucial for stakeholders to appreciate the transformative potential of electronic data capture clinical trials.
-
Hands-On Training: Implement practical sessions that enable users to engage directly with the EDC platform. Focus on essential skills such as data entry, system navigation, and troubleshooting common issues. These elements are vital for fostering user confidence and ensuring a smooth transition to the new system.
-
Role-Specific Training: Tailor training sessions to meet the unique needs of various user roles. This customization ensures that data entry staff, monitors, and investigators are well-versed in their specific responsibilities, thereby enhancing overall data integrity and study outcomes. Notably, 53% of organizations recognize the value of leadership skills training, underscoring the necessity of structured programs to improve user effectiveness.
-
Ongoing Support: Establish a robust support framework that addresses user inquiries and challenges throughout the trial. Regular updates and refresher courses are essential for maintaining user proficiency and adapting to any changes, ultimately fostering a culture of continuous learning. Given that 34% of employees admit to skimming through compliance information, engaging training methods are crucial for ensuring thorough understanding and retention.
Statistics reveal that organizations offering leadership skills training experience significant improvements in employee engagement and performance. Additionally, aligning training objectives with broader employee experience goals can enhance the overall efficiency of EDC frameworks. Insights from a case study indicate that 92% of survey respondents believe that training goals should reinforce a positive employee experience, focusing on diversity, engagement, and a growth mindset. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can effectively address common challenges encountered during EDC training, such as varying levels of user experience and engagement. Experts emphasize that customized, role-specific training not only boosts user efficiency but also facilitates the successful implementation of electronic data capture clinical trials. As the Marketing Director at Philips Healthcare articulated, “The study was customized to our targets and needs with well-defined milestones,” highlighting the importance of tailored training in achieving desired outcomes.
Monitor and Evaluate EDC System Performance
Monitoring and assessing the performance of tools used in electronic data capture clinical trials is crucial for optimizing clinical trial outcomes. This process involves several key steps:
-
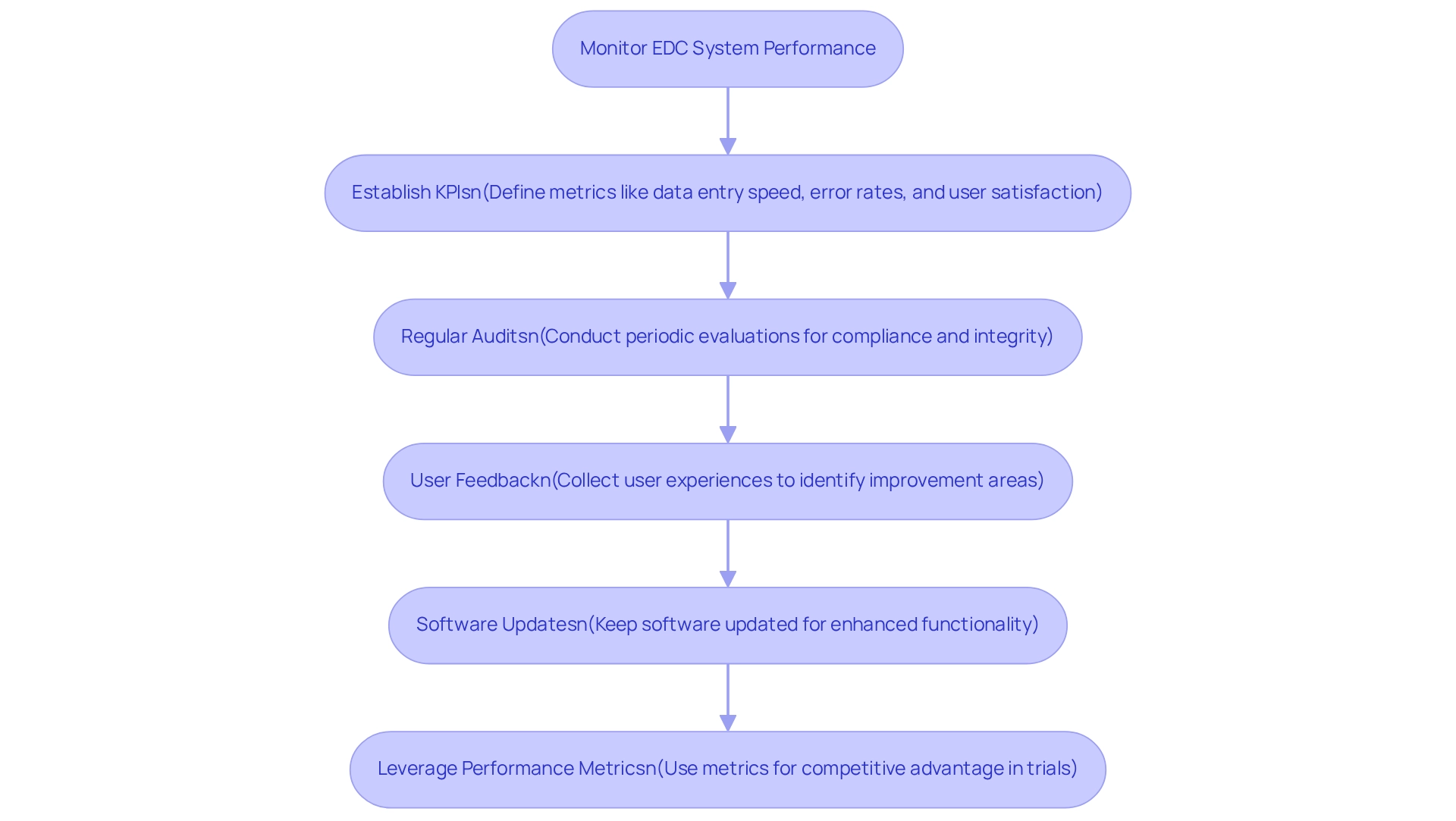
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Defining specific metrics is essential for assessing the system’s efficiency. Important KPIs include data entry speed, error rates, and user satisfaction. Broadly speaking, performance metrics can be grouped into ‘standard’ clinical metrics, applicable to various studies conducted by the same sponsor or site, and study-specific metrics, unique to a single trial. These indicators provide a clear picture of how well the EDC system is functioning and where improvements can be made.
-
Regular Audits: Conducting periodic evaluations of the gathered information ensures compliance with study protocols and regulatory requirements. This practice not only helps uphold information integrity but also identifies potential discrepancies that could affect trial results.
-
User Feedback: Actively gathering feedback from users is vital for identifying areas needing improvement. Grasping user experiences can reveal challenges encountered during data input and navigation, enabling focused improvements that enhance overall usability.
-
Software Updates: Keeping updated on software changes and new functionalities is essential for improving performance. Consistently incorporating these updates can result in enhanced functionality and user experience, ensuring that the EDC framework stays in sync with the changing requirements of clinical studies.
-
Leverage Performance Metrics: Utilizing performance metrics can provide a competitive advantage. For example, a case study named ‘Leveraging Metrics for Competitive Advantage’ explores how clinical study locations that effectively utilized these metrics in electronic data capture clinical trials were able to improve their market position and draw in more sponsors, resulting in expanded research opportunities.
By applying these strategies, stakeholders can guarantee that their electronic data capture clinical trials systems not only satisfy the immediate needs of clinical studies but also adjust to future challenges, ultimately promoting improved patient outcomes and more effective data management. Furthermore, the evolving landscape of clinical trial performance metrics underscores the importance of identifying relevant metrics to support effective decision-making.
Conclusion
The transition to Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems represents a transformative advancement in clinical research, streamlining data collection while enhancing accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. This article elucidates the critical components of EDC systems, encompassing their definition, selection, configuration, training, and performance monitoring. By providing organizations with essential tools, EDC systems optimize clinical trials and significantly improve patient outcomes.
Selecting the right EDC system is paramount, requiring a thorough assessment of user requirements, compliance, integration capabilities, usability, and cost. Equally important is the proper configuration of the EDC system, which is vital for effective data management and adherence to regulatory standards.
Training stakeholders on the usage of EDC systems is crucial for successful implementation. This encompasses hands-on experience and tailored instruction, ensuring data integrity and enhancing trial outcomes. Continuous support and learning opportunities are essential to keep users proficient and adaptable in an ever-evolving landscape.
Monitoring the performance of EDC systems through key performance indicators (KPIs) and user feedback facilitates ongoing evaluation and improvement. By leveraging these insights, clinical trial sites can enhance efficiency and maintain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the adoption of EDC systems is indispensable for navigating the complexities of clinical trials. These systems not only enhance data accuracy and compliance but also drive improved patient outcomes. This marks a significant step towards achieving more efficient and impactful research within the healthcare sector.


