Overview
This article delves into the 2024 Medicare deductible, which is established at $240 for Part B and $1,632 for Part A. Understanding these figures is crucial, as they significantly influence patient healthcare decisions and financial planning. Elevated out-of-pocket costs can deter patients from seeking essential medical care, underscoring the necessity for effective financial strategies to navigate these expenses. By addressing these deductibles, we can better equip patients to manage their healthcare costs and make informed decisions regarding their health.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Medicare can be daunting, particularly when it comes to understanding deductibles that significantly impact beneficiaries’ healthcare expenses. The 2024 figures reveal increases in both Medicare Part A and Part B deductibles, highlighting the growing financial implications for patients. These out-of-pocket costs not only shape the decisions beneficiaries make regarding care but also influence their overall health outcomes.
As these costs continue to rise, it becomes essential for individuals to develop effective strategies to manage these expenses, ensuring access to necessary medical services without jeopardizing their financial stability. This article delves into the nuances of Medicare deductibles, their implications for patient care, and practical strategies for effective financial planning in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Clarify Medicare Deductibles: Definitions and Importance
Healthcare costs encapsulate the out-of-pocket expenses that recipients must bear for medical services before the 2024 Medicare deductible comes into effect. For 2024, the Medicare Part B expenses will include a deductible of $240, up from $226 in 2023, which is referred to as the 2024 Medicare deductible.
Understanding this cost-sharing amount is crucial, as it directly influences beneficiaries’ financial responsibilities and their navigation through treatment pathways. Elevated out-of-pocket costs may affect how patients engage with medical providers and their decisions regarding treatment options.
This cost-sharing mechanism not only encourages responsible healthcare utilization but also significantly contributes to managing overall healthcare expenditures within the public health system. By analyzing claims data from the health insurance program, we can glean insights into how these costs impact patient experiences and treatment approvals under Part D, ultimately enhancing provider engagement and medication utilization strategies.
Examine 2024 Medicare Deductibles: Key Figures and Comparisons
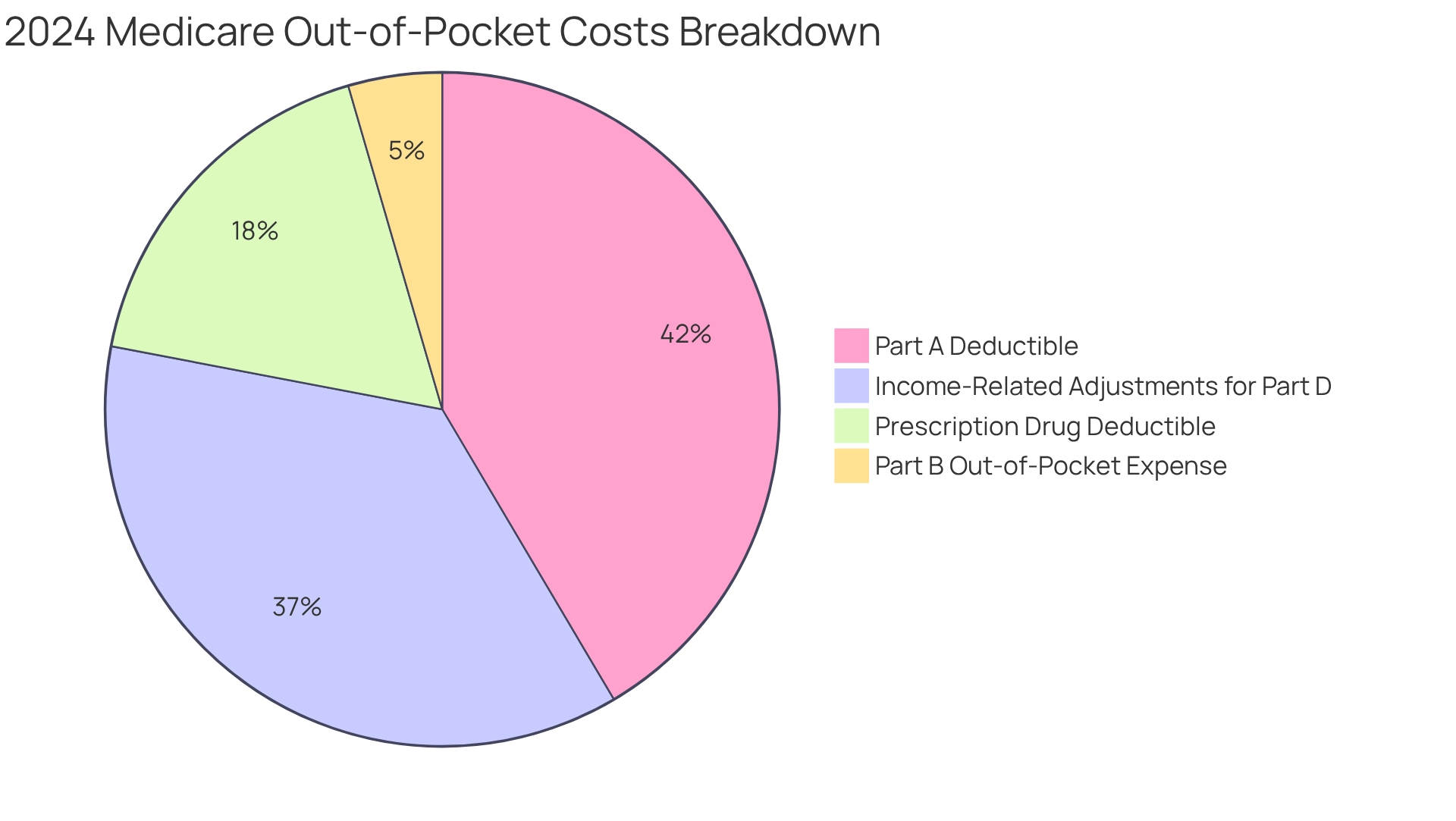
In 2024, the Medicare deductible for Part A is set at $1,632 per benefit period, which reflects a $14 increase from the previous year. Meanwhile, the Part B out-of-pocket expense will be $240, with an anticipated rise to $257 in 2025. These figures are critical for recipients as they plan their healthcare budgets.
Furthermore, the 2024 Medicare deductible for prescription drugs is capped at $545. For high-income recipients, the income-related monthly adjustment amounts for Part D range from $12.90 to $81.00, adding another layer of cost consideration for those affected.
Understanding these key figures allows beneficiaries to prepare effectively for their out-of-pocket costs and make informed decisions regarding their medical plans. Additionally, leveraging CareSet’s comprehensive medical data insights can empower Pharmaceutical Market Access Managers to navigate these changes adeptly, enhancing strategies related to Advantage and Prescription Drug Programs.
Historical trends indicate a gradual increase in out-of-pocket costs, underscoring the importance of staying informed about these changes to optimize healthcare expenditures. This context is vital for Pharmaceutical Market Access Managers as they adapt to the evolving healthcare landscape.
Analyze the Impact of Deductibles on Patient Care and Financial Planning
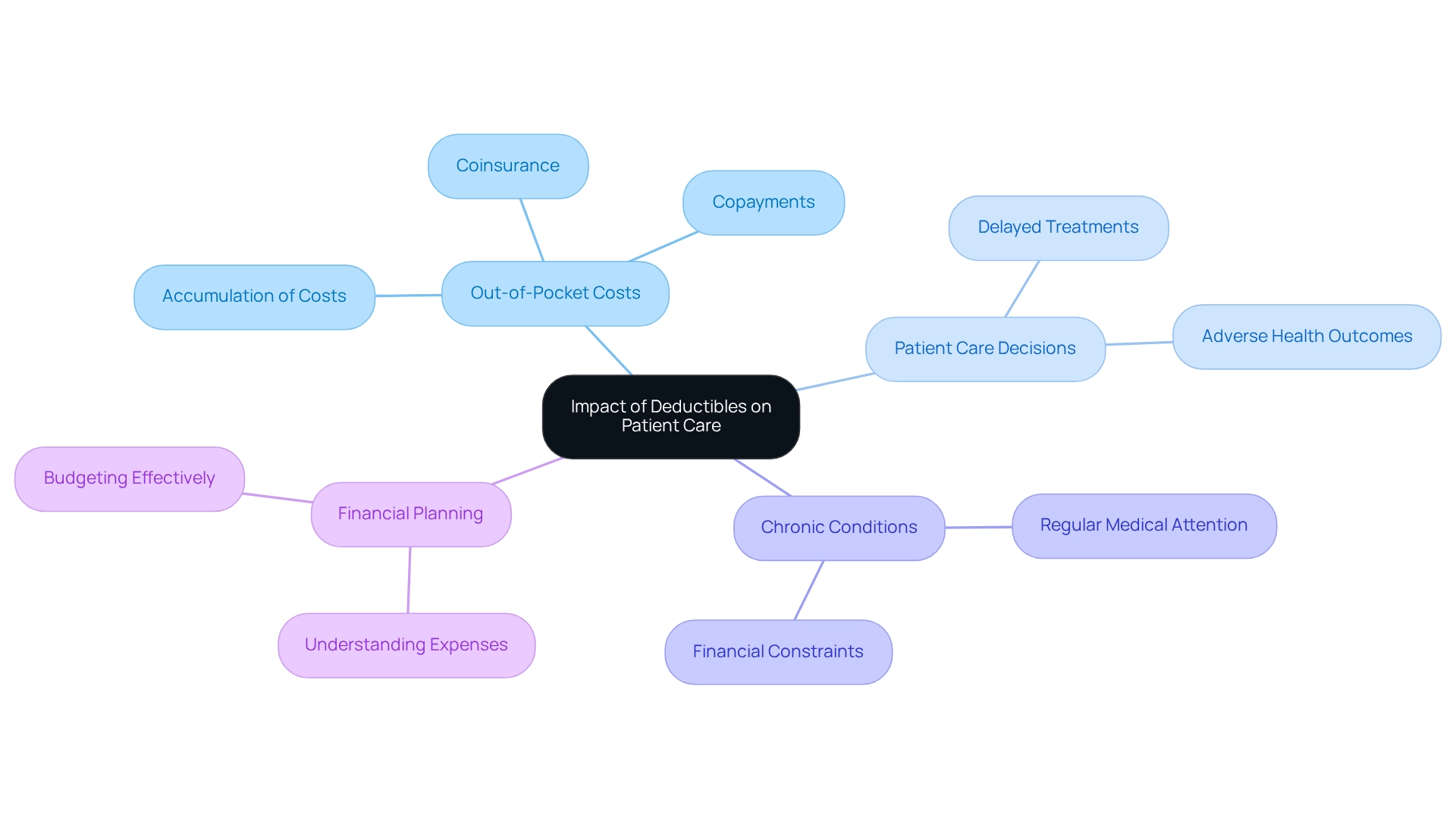
Out-of-pocket costs significantly influence patient care, shaping when and how individuals access medical services under Medicare A, B, and D. Elevated out-of-pocket expenses can deter patients from seeking essential care, leading to delayed treatments and potentially adverse health outcomes.
For instance, patients managing chronic conditions that necessitate regular medical attention may defer visits due to financial constraints. Consequently, it is crucial for recipients to strategically plan for these costs, as they can accumulate rapidly.
Effective financial planning involves understanding not only the out-of-pocket expenses but also the likelihood of additional costs such as coinsurance and copayments. By thoroughly analyzing these factors, recipients can make informed decisions regarding their healthcare and budget effectively, ensuring they navigate their treatment pathways with confidence.
Implement Strategies for Managing Medicare Deductibles and Costs
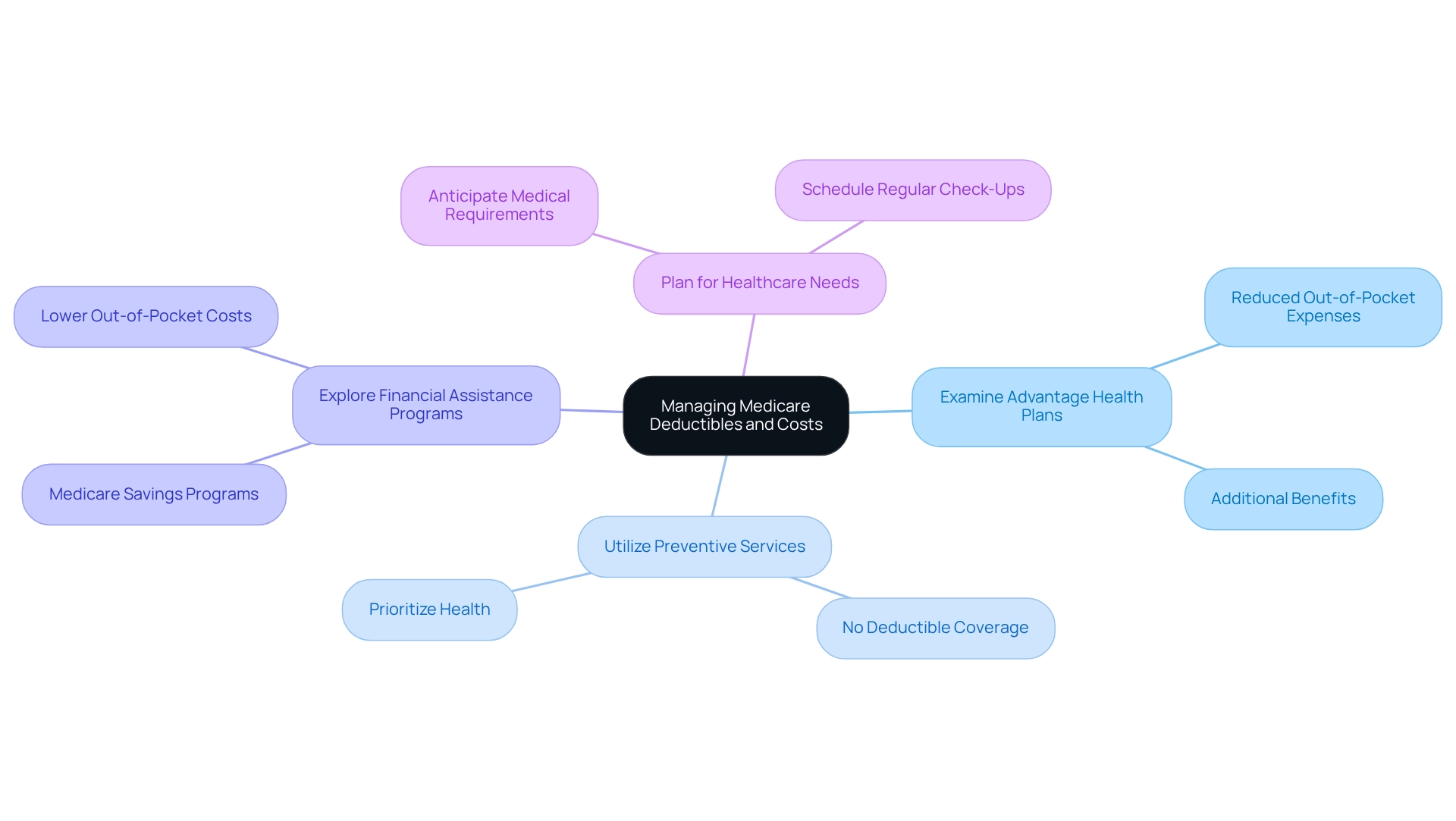
To manage healthcare expenses and related costs effectively, recipients should consider several strategies.
- Examine Advantage Health Plans: Certain plans offer reduced out-of-pocket expenses or additional benefits that can offset costs significantly.
- Utilize Preventive Services: Many preventive services are covered without a deductible, allowing recipients to prioritize their health without financial burden.
- Explore Financial Assistance Programs: Programs such as Medicare Savings Programs can assist in lowering out-of-pocket costs for individuals with limited income.
- Plan for Healthcare Needs: By anticipating medical requirements and scheduling regular check-ups, recipients can avoid unexpected expenses.
Implementing these strategies empowers beneficiaries to manage their healthcare expenses more effectively and ensures access to necessary care.
Conclusion
Understanding Medicare deductibles is essential for beneficiaries navigating their healthcare expenses, particularly with the 2024 increases in both Part A and Part B deductibles. The annual deductible for Part B has risen to $240, while Part A’s deductible stands at $1,632 per benefit period. These figures represent critical financial responsibilities that can significantly influence healthcare decisions and access to necessary treatments.
The implications of these deductibles extend beyond individual finances, affecting patient care and health outcomes. Higher out-of-pocket costs may deter beneficiaries from seeking timely medical attention, especially those managing chronic conditions. Such delays can lead to more severe health issues and increased long-term expenses. Therefore, it is crucial for beneficiaries to engage in proactive financial planning by understanding potential costs and exploring available strategies.
By reviewing Medicare Advantage plans, utilizing preventive services, and considering financial assistance programs, beneficiaries can mitigate the impact of these deductibles. Anticipating healthcare needs and making informed decisions empowers individuals to navigate their treatment pathways effectively while maintaining financial stability. As the landscape of Medicare evolves, staying informed about changes and implementing effective management strategies becomes vital for ensuring access to necessary healthcare services. The responsibility lies not only in understanding the numbers but also in taking actionable steps to secure both health and financial well-being.


