Overview
The article emphasizes the critical role of the 19 place of service codes in accurate Medicare billing, underscoring their significance in ensuring compliance and reducing claim denials. Notably, the precise application of these codes can markedly enhance reimbursement rates and streamline the claims process. Data reveals that incorrect coding accounts for approximately 30% of billing errors, highlighting the necessity for diligence in this area. By understanding and implementing these codes correctly, healthcare providers can significantly improve their financial outcomes.
Introduction
In the intricate world of healthcare billing, the accurate use of Place of Service (POS) codes is paramount for ensuring compliance and optimizing reimbursement. With the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) overseeing a comprehensive set of guidelines, healthcare providers must navigate a landscape where misclassification can lead to significant financial repercussions.
As telehealth services evolve and new coding practices emerge, the need for precise interpretation of Medicare claims data becomes increasingly critical. This article delves into the vital role of POS codes in billing accuracy, highlighting the insights provided by industry leaders like CareSet and FindACode.
By understanding these nuances, healthcare organizations can enhance their financial performance and ultimately improve patient care outcomes.
CareSet: Comprehensive Medicare Data Insights for Place of Service Codes
CareSet excels in extracting and interpreting complex Medicare claims data, providing comprehensive insights into the 19 place of service classifications. By examining over $1.1 trillion in yearly claims data, CareSet equips healthcare stakeholders with the essential information needed to navigate the complexities of charges and reimbursement related to various service locations. This expertise is crucial for ensuring accurate claims submissions, which directly impacts revenue cycles and patient care strategies.
The significance of the 19 place of service numbers in Medicare invoicing is extremely important and cannot be overstated. Precise programming is vital for adherence and can greatly reduce claim denials, as highlighted in a case study focusing on the correct allocation of facility and non-facility service identifiers. Misclassification can lead to complications in the claims processing workflow, underscoring the necessity for precise data interpretation. Ensuring compliance with the 19 place of service coding rules significantly decreases claim rejections, facilitating smoother claim processing.
Recent analyses of Medicare claims data demonstrate that the efficient application of the 19 place of service identifiers enhances invoicing precision and maximizes providers’ financial outcomes. With CareSet analyzing over $1.1 trillion in annual Medicare claims data, the credibility of this assertion is reinforced. As of 2025, the incorporation of revised programming practices, including the application of G2025 with modifier 95 for synchronous telemedicine services, reflects the evolving landscape of medical service delivery. These updates are essential to ensure compliance and improve reimbursement processes.
Expert opinions emphasize that accurate Medicare claims data is foundational for effective market access and patient engagement strategies. By leveraging CareSet’s extensive insights into the 19 place of service codes, organizations in the medical field can refine their invoicing processes, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and strategic growth in a competitive landscape. As articulated by the Office of Inspector General, “By tackling the root causes, improving education and training, and enforcing strong auditing procedures, we can strive for a more effective and transparent system,” underscoring the importance of addressing these issues concerning POS coding and financial accuracy.
To explore how CareSet can empower your organization with actionable insights from Medicare data, contact us today.
CMS: Official Place of Service Code Set for Accurate Billing
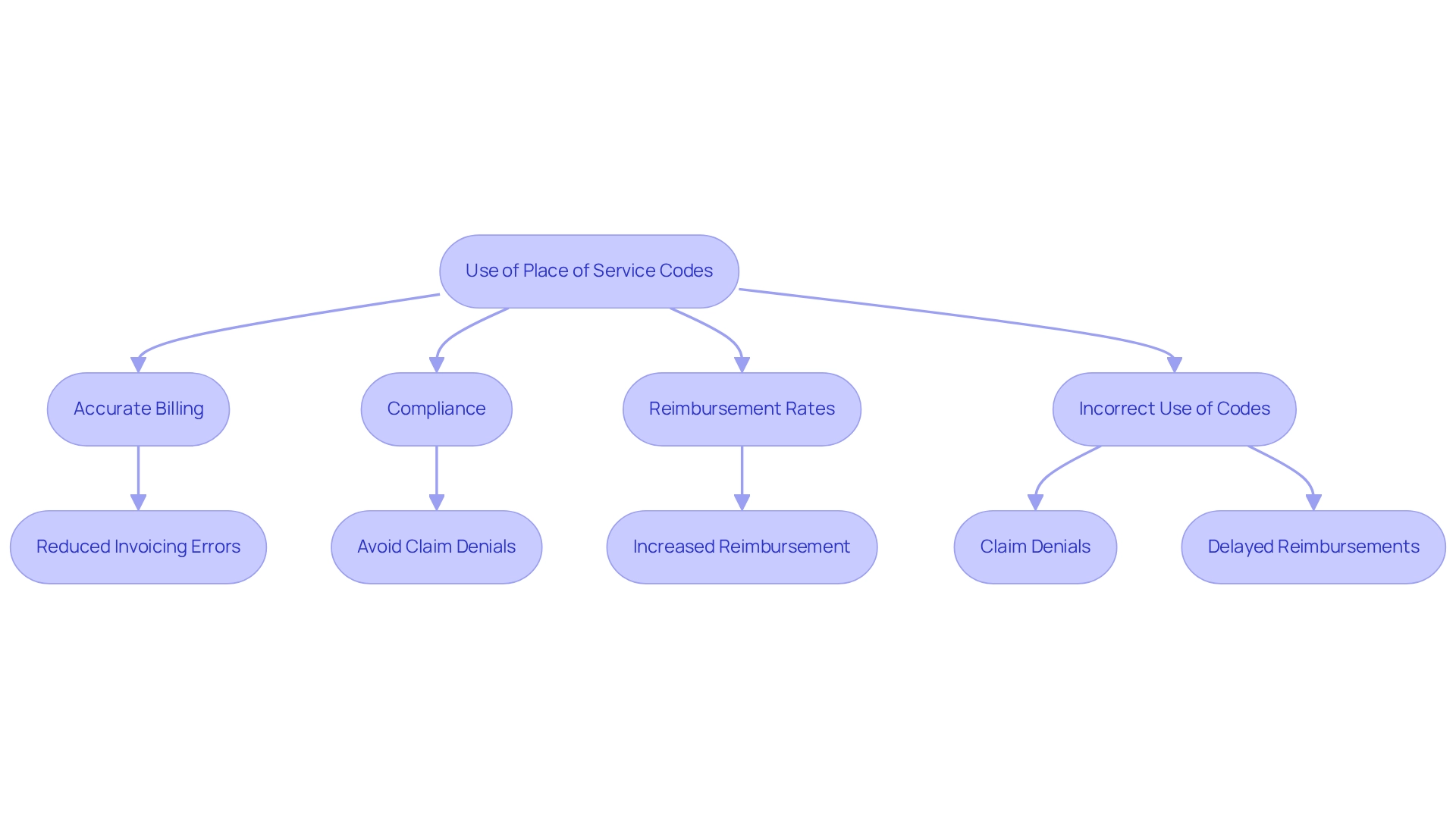
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) governs an official Code Set for the 19 place of service that healthcare providers must utilize on professional claims. These two-digit identifiers denote the specific area where services are rendered, playing a crucial role in accurate invoicing and reimbursement. Staying informed about the latest CMS guidelines is essential for providers to ensure compliance and mitigate the risk of costly invoicing errors. For example, reimbursement rates can vary significantly based on the POS designation applied; services performed in a physician’s office typically receive higher reimbursement than those conducted in outpatient hospitals or ambulatory surgical centers.
In 2025, CMS updated the 19 place of service code set to reflect changes in medical delivery and billing practices. Accurate reporting of these identifiers is vital, as statistics indicate that incorrect POS identifiers contribute to approximately 30% of invoicing errors, leading to claim denials and delayed reimbursements. Case studies demonstrate that medical providers who adhere to CMS guidelines effectively sidestep these challenges, ensuring smoother payment processes and enhanced financial outcomes. Specifically, the case study titled “Impact of Place of Service (POS) Codes on Reimbursement” illustrates that precise reporting can substantially increase reimbursement rates, highlighting the necessity of compliance.
As telehealth services continue to develop, particularly with numerous pandemic-era policies remaining in effect for 2024—such as the removal of in-person requirements for mental health services—understanding and applying the correct 19 place of service codes will be increasingly critical for compliance and reimbursement success. CareSet’s integration of over 100 external data sources equips medical stakeholders with comprehensive Medicare data insights, improving billing accuracy and effectively navigating the complexities of Medicare billing. This approach not only enhances patient care but also drives business success for medical providers.
FindACode: Essential List of Place of Service Codes for Healthcare Providers
FindACode serves as an essential reference for healthcare professionals, providing a comprehensive list of 19 place of service numbers, complete with detailed descriptions to aid in selecting the appropriate number based on the service location. For example, POS number 11 indicates services rendered in a physician’s office, whereas number 21 pertains to inpatient hospital services.
The precise application of these identifiers is critical, particularly the 19 place of service, as they directly affect claims processing durations and reimbursement rates. Improper reporting of the 19 place of service codes can lead to claims being returned or denied, emphasizing the importance of compliance with Medicare’s billing requirements.
By utilizing resources like FindACode, medical providers can enhance their claims submissions, ensuring timely reimbursements and minimizing the risk of errors. CareSet’s integration of over 100 external data sources further enriches the analysis available to medical providers, underscoring the importance of accurate POS coding. CareSet’s extensive healthcare data insights empower providers to understand and effectively utilize these classifications, ultimately improving their reimbursement strategies.
Additionally, independent laboratories conducting diagnostic tests outside of institutions or physician offices must adhere to appropriate reporting for the 19 place of service, as discrepancies can significantly impact their payment processes. Rural health facilities, which provide primary medical services in underserved areas, also rely on accurate POS identifiers to navigate the unique challenges of invoicing in these contexts.
Overall, comprehending and correctly applying the 19 place of service classifications is essential for healthcare providers aiming to optimize their reimbursement strategies.
CodingIntel: Guidance on CPT Split/Shared Services and Place of Service Codes
Precise billing in facility environments necessitates a comprehensive understanding of CPT designations for split/shared services and their corresponding 19 place of service identifiers. Adhering to Medicare guidelines mandates the accurate application of these classifications, particularly when both a physician and a non-physician practitioner (NPP) provide services to a patient. For instance, employing the appropriate 19 place of service identifier is crucial for accurately representing the shared service, which ensures that claims are submitted correctly and that providers receive the reimbursement they deserve.
As we approach 2025, guidelines for implementing the 19 place of service classifications in shared services will continue to evolve, highlighting the necessity for healthcare providers to stay informed. Statistics reveal that invoicing errors related to CPT split/shared services account for approximately 30% of all discrepancies, highlighting the critical importance of precise coding practices. Case studies demonstrate successful adherence to Medicare guidelines through the proper use of POS classifications in facility environments, illustrating how compliance with these standards can enhance operational efficiency and financial outcomes. A recent case study, for instance, showcased a facility that improved its invoicing accuracy by 25% after initiating a comprehensive training program on CPT and POS usage.
Experts in programming emphasize the intricate relationship between CPT numbers and the 19 place of service, asserting that precise classification not only facilitates appropriate reimbursement but also upholds the integrity of the payment process. As one programming expert stated, “Grasping the subtleties of CPT and POS classifications is crucial for optimizing reimbursement and ensuring compliance with Medicare regulations.” As the healthcare landscape evolves, understanding these codes will be essential for effectively navigating the complexities of Medicare billing.
Conclusion
The significance of Place of Service (POS) codes in healthcare billing is paramount. Accurate coding is essential not only for compliance but also for optimizing reimbursement and enhancing financial performance. Insights from industry leaders such as CareSet, CMS, FindACode, and CodingIntel highlight that the evolving landscape of telehealth and updated coding practices necessitates a thorough understanding of these codes.
Healthcare providers face substantial risks if they misclassify services; approximately 30% of billing errors stem from incorrect POS code usage, leading to claim denials and delayed reimbursements. By adhering to the latest CMS guidelines and leveraging comprehensive data insights, organizations can significantly improve their billing processes. This adherence not only facilitates smoother claim submissions but also ultimately leads to better patient care outcomes.
In conclusion, integrating accurate POS coding into billing practices is a critical step for healthcare organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of Medicare billing successfully. Emphasizing education, training, and robust auditing procedures will foster a more efficient and transparent healthcare system, reinforcing the importance of precise coding as a cornerstone of financial health and compliance in the industry.


